
Question Number 36185 by prof Abdo imad last updated on 30/May/18
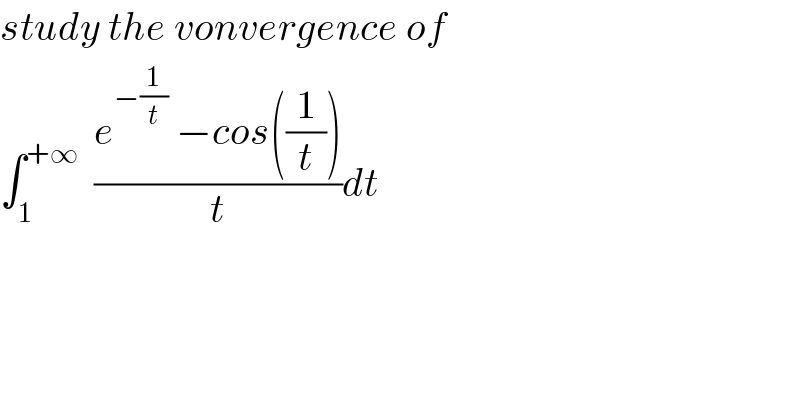
$${study}\:{the}\:{vonvergence}\:{of}\: \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}} \:−{cos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}\right)}{{t}}{dt} \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 19/Aug/18
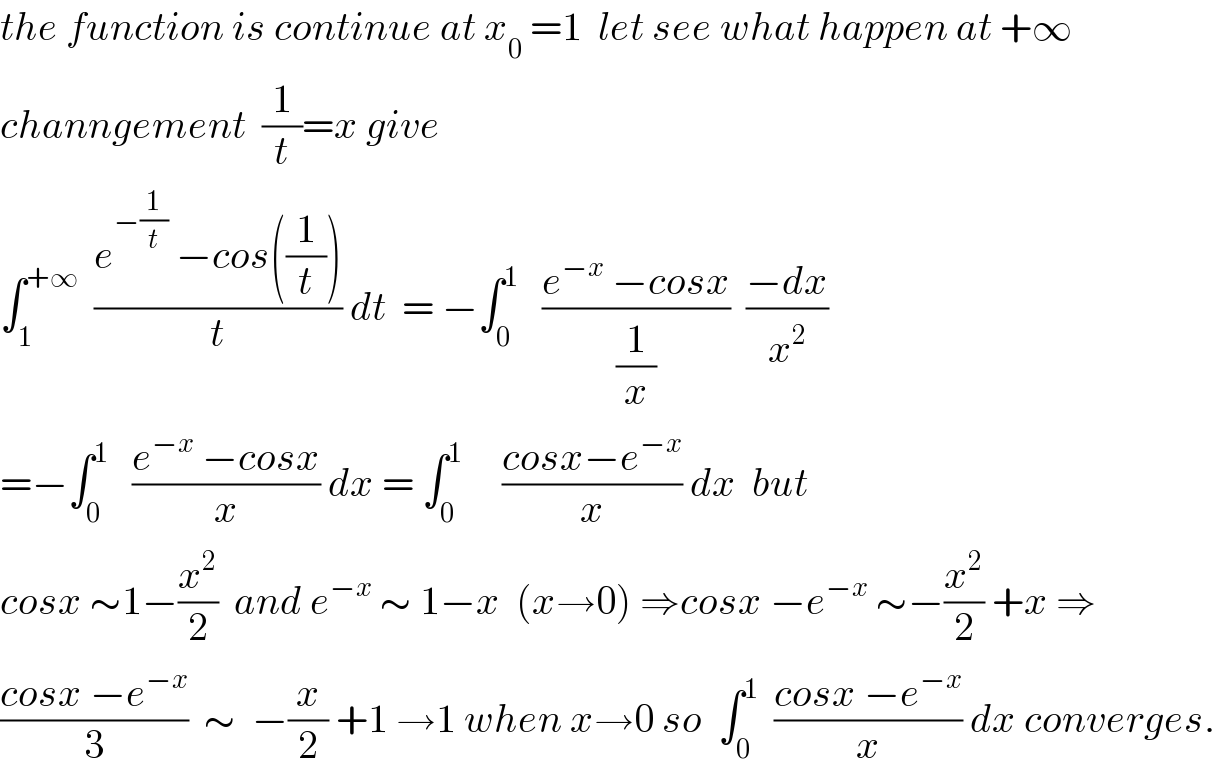
$${the}\:{function}\:{is}\:{continue}\:{at}\:{x}_{\mathrm{0}} \:=\mathrm{1}\:\:{let}\:{see}\:{what}\:{happen}\:{at}\:+\infty \\ $$$${channgement}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}={x}\:{give} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{1}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{e}^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}} \:−{cos}\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{t}}\right)}{{t}}\:{dt}\:\:=\:−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−{x}} \:−{cosx}}{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}}\:\:\frac{−{dx}}{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$$=−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\frac{{e}^{−{x}} \:−{cosx}}{{x}}\:{dx}\:=\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\:\:\:\frac{{cosx}−{e}^{−{x}} }{{x}}\:{dx}\:\:{but} \\ $$$${cosx}\:\sim\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\:{and}\:{e}^{−{x}} \:\sim\:\mathrm{1}−{x}\:\:\left({x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right)\:\Rightarrow{cosx}\:−{e}^{−{x}} \:\sim−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+{x}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{cosx}\:−{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:\:\sim\:\:−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\mathrm{1}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{1}\:{when}\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:{so}\:\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{cosx}\:−{e}^{−{x}} }{{x}}\:{dx}\:{converges}. \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 19/Aug/18
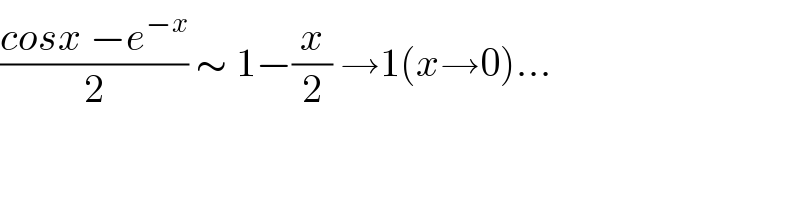
$$\frac{{cosx}\:−{e}^{−{x}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\sim\:\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\rightarrow\mathrm{1}\left({x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\right)... \\ $$
