
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 38101 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 21/Jun/18
![let A_n = ∫_0 ^n e^(x−[x]) dx 1) calculate A_n 2) find lim_(n→+∞) A_n](Q38101.png)
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 22/Jun/18
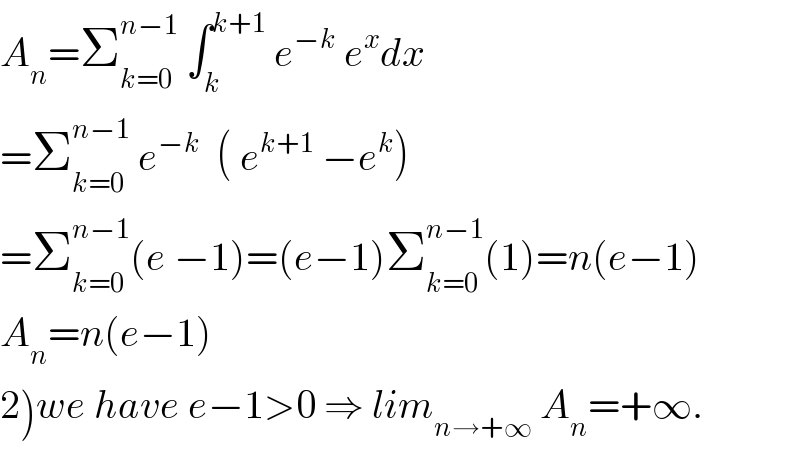
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 38101 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 21/Jun/18 | ||
![let A_n = ∫_0 ^n e^(x−[x]) dx 1) calculate A_n 2) find lim_(n→+∞) A_n](Q38101.png) | ||
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 22/Jun/18 | ||
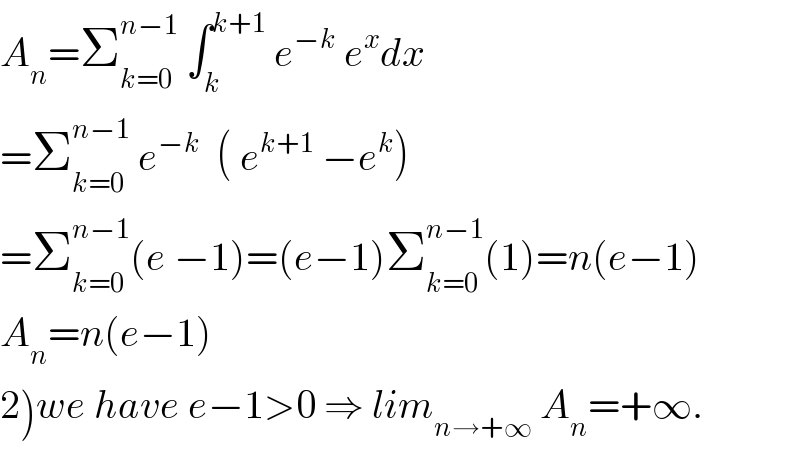 | ||