
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 38198 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 22/Jun/18
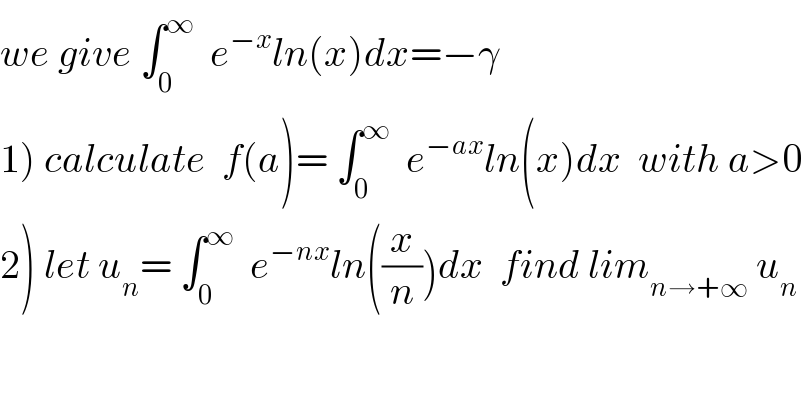
Commented byabdo.msup.com last updated on 24/Jun/18
![1) changement ax=t give f(a)= ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) ln((t/a))(dt/a) = (1/a){ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) ln(t)dt −ln(a) ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−t) dt} =(1/a){ γ −ln(a) [ −e^(−t) ]_0 ^(+∞) } = ((γ +ln(a))/a) f(a)=((γ +ln(a))/a) with a>0](Q38316.png)
Commented byabdo.msup.com last updated on 24/Jun/18
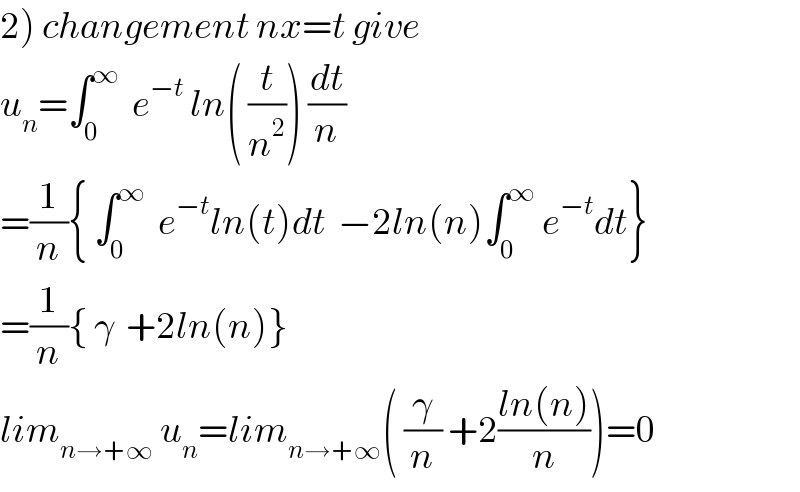
Commented bymath khazana by abdo last updated on 24/Jun/18

Commented bymath khazana by abdo last updated on 24/Jun/18

Commented bymath khazana by abdo last updated on 24/Jun/18

