
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 38876 by tawa tawa last updated on 30/Jun/18
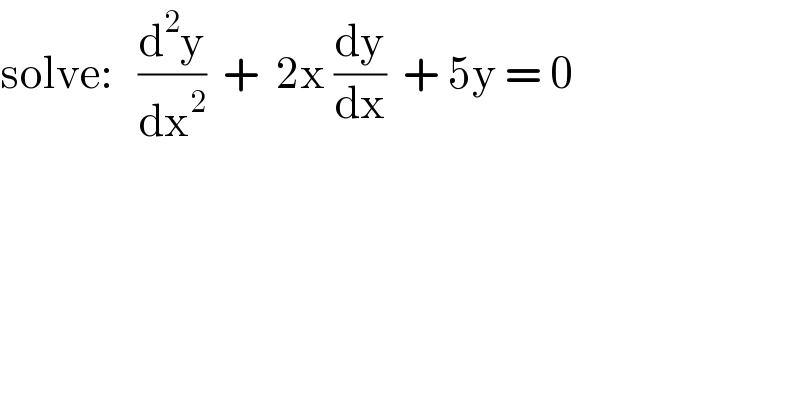
$$\mathrm{solve}:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{d}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\:+\:\:\mathrm{2x}\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}\:\:+\:\mathrm{5y}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 01/Jul/18

$${it}\:{is}\:{realy}\:{very}\:{good}\:{problem}...{in}\:{search}..{and} \\ $$$${finding}\:{way}\:{to}\:{solve}\:{it}... \\ $$
Commented by tawa tawa last updated on 01/Jul/18
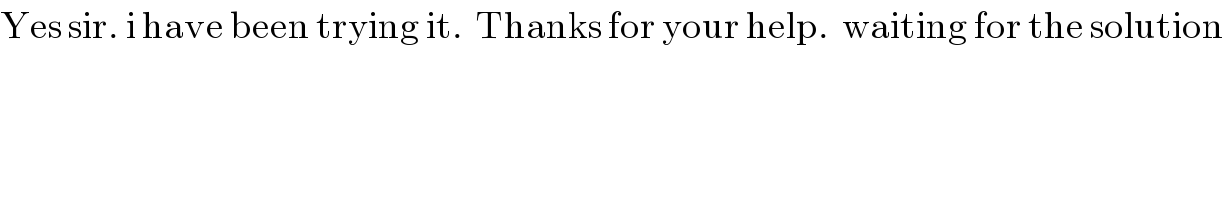
$$\mathrm{Yes}\:\mathrm{sir}.\:\mathrm{i}\:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{been}\:\mathrm{trying}\:\mathrm{it}.\:\:\mathrm{Thanks}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{help}.\:\:\mathrm{waiting}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{the}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$
Answered by $@ty@m last updated on 01/Jul/18
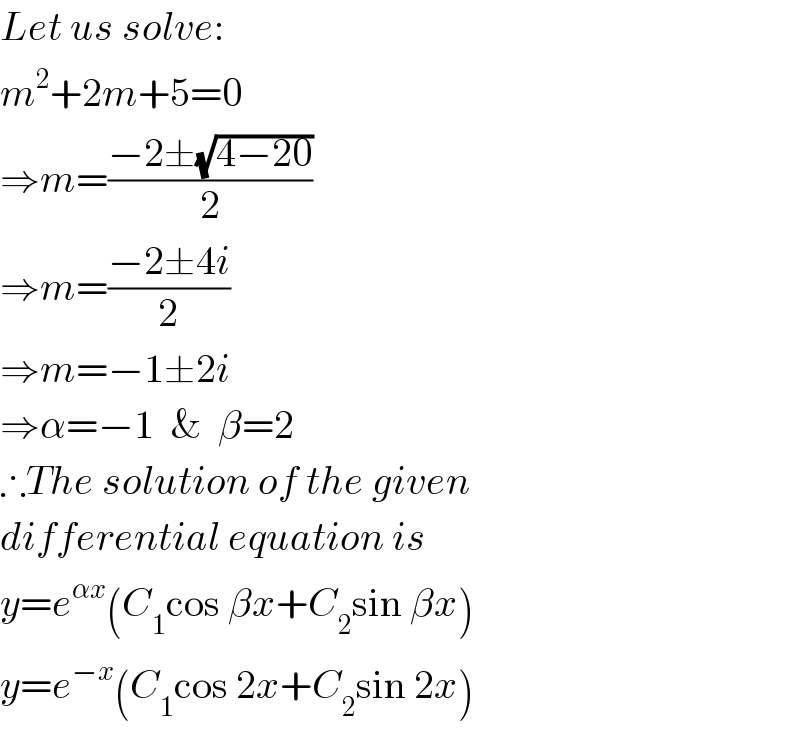
$${Let}\:{us}\:{solve}: \\ $$$${m}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{m}=\frac{−\mathrm{2}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{4}−\mathrm{20}}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{m}=\frac{−\mathrm{2}\pm\mathrm{4}{i}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{m}=−\mathrm{1}\pm\mathrm{2}{i} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\alpha=−\mathrm{1}\:\:\&\:\:\beta=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\therefore{The}\:{solution}\:{of}\:{the}\:{given} \\ $$$${differential}\:{equation}\:{is}\: \\ $$$${y}={e}^{\alpha{x}} \left({C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\beta{x}+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\beta{x}\right) \\ $$$${y}={e}^{−{x}} \left({C}_{\mathrm{1}} \mathrm{cos}\:\mathrm{2}{x}+{C}_{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}\:\mathrm{2}{x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by math khazana by abdo last updated on 01/Jul/18
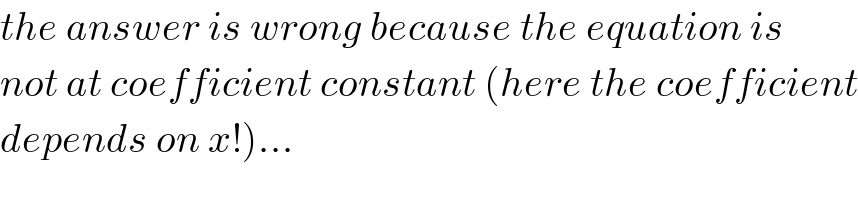
$${the}\:{answer}\:{is}\:{wrong}\:{because}\:{the}\:{equation}\:{is}\: \\ $$$${not}\:{at}\:{coefficient}\:{constant}\:\left({here}\:{the}\:{coefficient}\right. \\ $$$$\left.{depends}\:{on}\:{x}!\right)... \\ $$
Commented by tawa tawa last updated on 01/Jul/18

$$\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{think}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{wrong}\:\mathrm{sir}.\:\:\mathrm{what}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{the}\:\:\:\:\mathrm{x}\:\:\mathrm{in}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{based}\:\mathrm{on}\:\mathrm{your}\:\mathrm{auxilliary}\:\mathrm{equation},\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{should}\:\mathrm{have}:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\:\mathrm{2xm}\:+\:\mathrm{5}\:=\:\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{help}\:\mathrm{me}\:\mathrm{check}\:\mathrm{again} \\ $$
