
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 40158 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 16/Jul/18
![let A_n = ∫_0 ^1 ((x^(2n+1) ln(x))/(x^2 −1))dx 1) justify the existence of A_n 2)calculate A_(n+1) −A_n 3) prove that x∈]0,1[ ⇒0<((xln(x))/(x^2 −1))<(1/2) 4) find lim_(n→+∞) A_n](Q40158.png)
Commented bymath khazana by abdo last updated on 19/Jul/18
![1) lim_(x→0^+ ) ((x^(2n+1) ln(x))/(x^2 −1)) =−lim_(x→0^+ ) x^(2n+1) ln(x)=0 also lim_(x→1) =lim_(x→1) (x^(2n+1) /(x+1)) ((lnx)/(x−1)) =(1/2) because lim_(x→1) ((ln(x))/(x−1)) =1 ⇒ A_n exist 2) A_(n+1) −A_n = ∫_0 ^1 ((x^(2n+3) ln(x))/(x^2 −1))dx−∫_0 ^1 ((x^(2n+1) ln(x))/(x^2 −1))dx = ∫_0 ^1 ((x^(2n+1) (x^2 −1)ln(x))/(x^2 −1))dx = ∫_0 ^1 x^(2n+1) ln(x)dx =[ (1/(2n+2)) x^(2n+2) lnx]_0 ^1 −∫_0 ^1 (1/(2n+2))x^(2n+2) (dx/x) =− (1/(2n+2))∫_0 ^1 x^(2n) dx =−(1/((2n+1)(2n+2)))](Q40328.png)
Commented bymath khazana by abdo last updated on 19/Jul/18
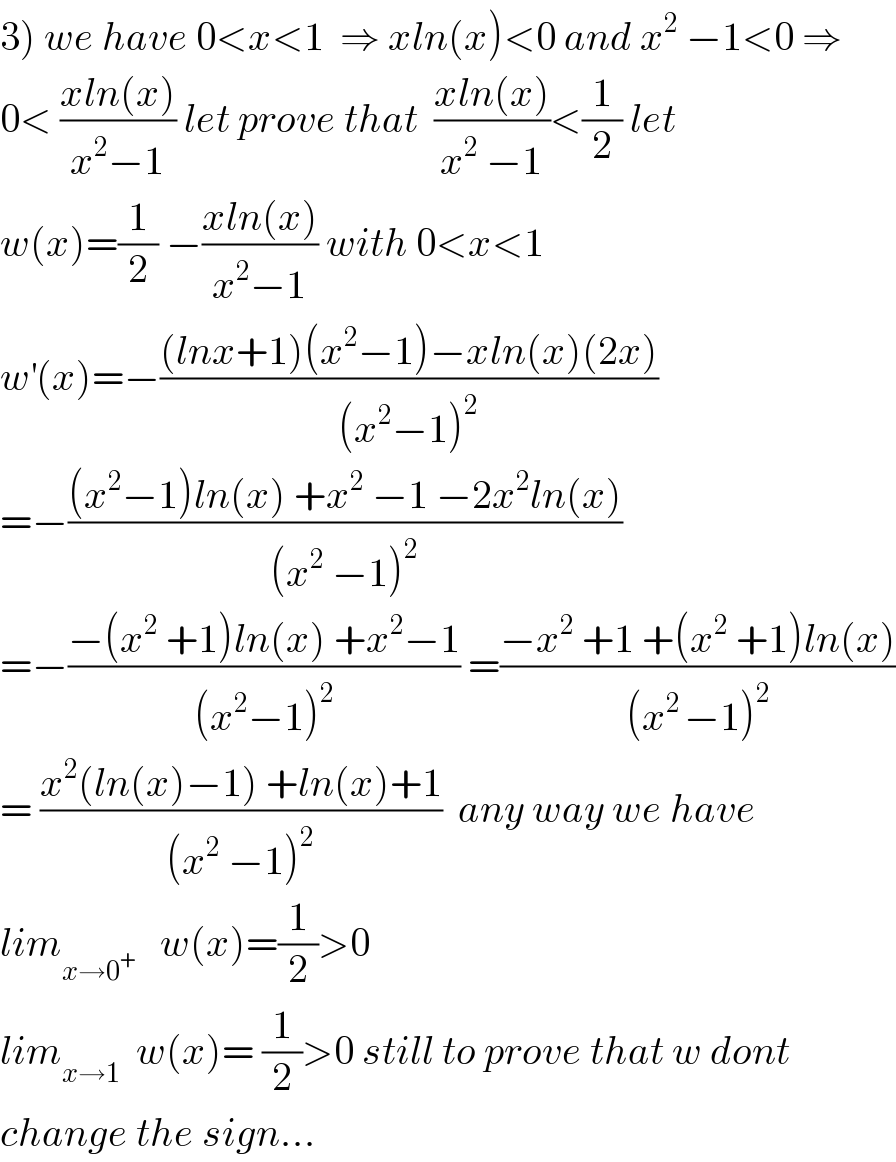
Commented bymath khazana by abdo last updated on 19/Jul/18

