
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 40276 by Raj Singh last updated on 18/Jul/18
Answered by MJS last updated on 18/Jul/18
![(d/dx)[((sin x)/(1+tan x))]=((cos^3 x −sin^3 x)/(1+2sin x cos x)) zeros at x=(π/4)(4k+1) ∧ k∈Z max at x=(π/4)(4k+1) ∧ k=2n ∧ n∈Z ⇒ ⇒ max ay x=(π/4)(8n+1) ∧ n∈Z ∧ y=((√2)/4) min at x=(π/4)(1+4k) ∧ k=2n+1 ∧ n∈Z ⇒ ⇒ min at x=(π/4)(8n+5) ∧ n∈Z ∧ y=−((√2)/4)](Q40279.png)
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 18/Jul/18
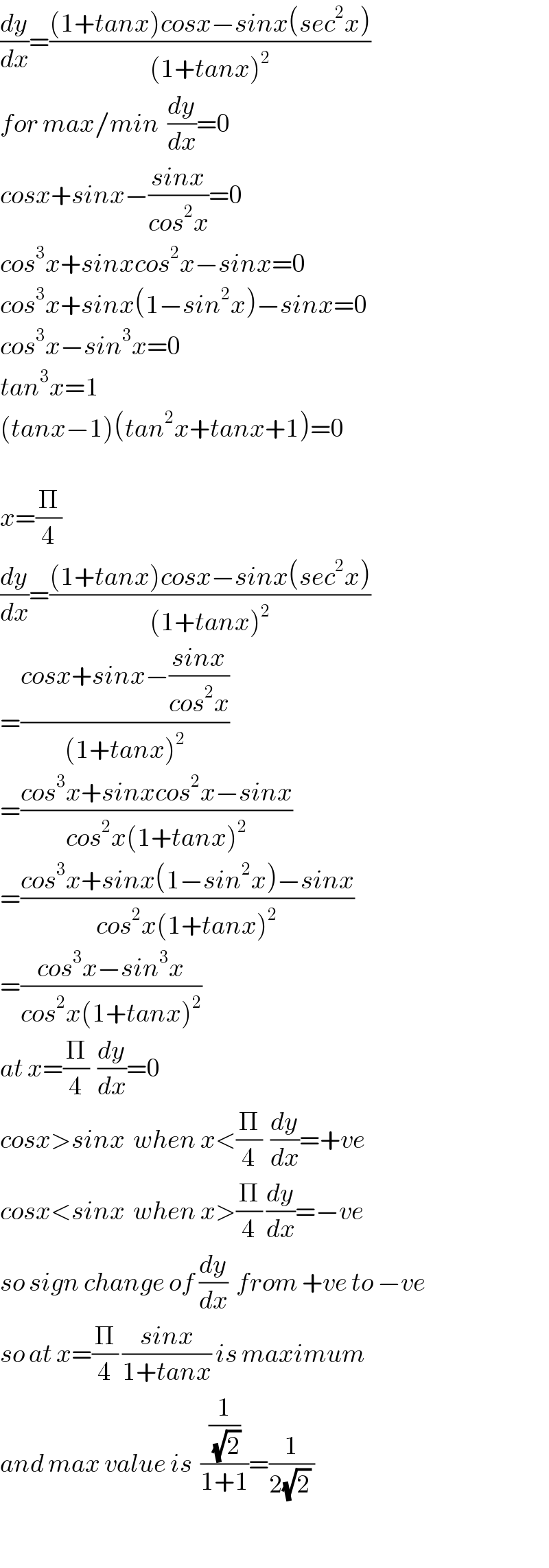
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 40276 by Raj Singh last updated on 18/Jul/18 | ||
 | ||
Answered by MJS last updated on 18/Jul/18 | ||
![(d/dx)[((sin x)/(1+tan x))]=((cos^3 x −sin^3 x)/(1+2sin x cos x)) zeros at x=(π/4)(4k+1) ∧ k∈Z max at x=(π/4)(4k+1) ∧ k=2n ∧ n∈Z ⇒ ⇒ max ay x=(π/4)(8n+1) ∧ n∈Z ∧ y=((√2)/4) min at x=(π/4)(1+4k) ∧ k=2n+1 ∧ n∈Z ⇒ ⇒ min at x=(π/4)(8n+5) ∧ n∈Z ∧ y=−((√2)/4)](Q40279.png) | ||
| ||
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 18/Jul/18 | ||
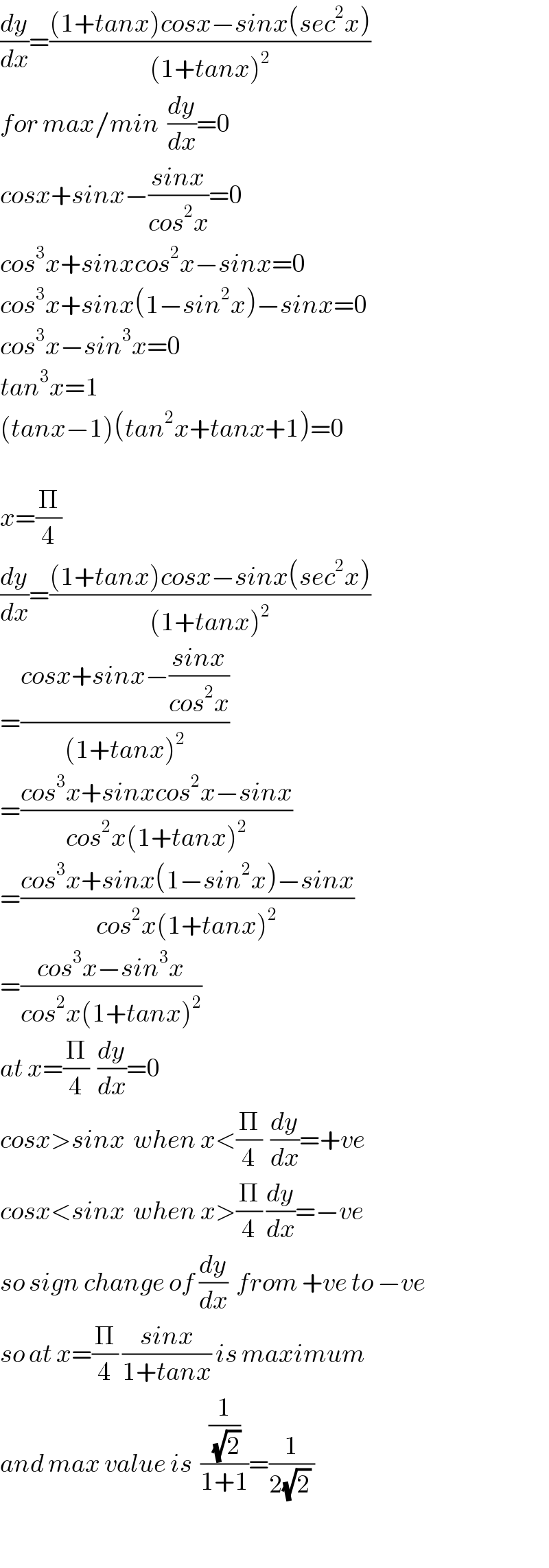 | ||
| ||