
Question Number 425 by 123456 last updated on 25/Jan/15

$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{3}} ={z}^{\mathrm{4}} \:\mathrm{have}\:\mathrm{integer}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{solutions}}? \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 02/Jan/15
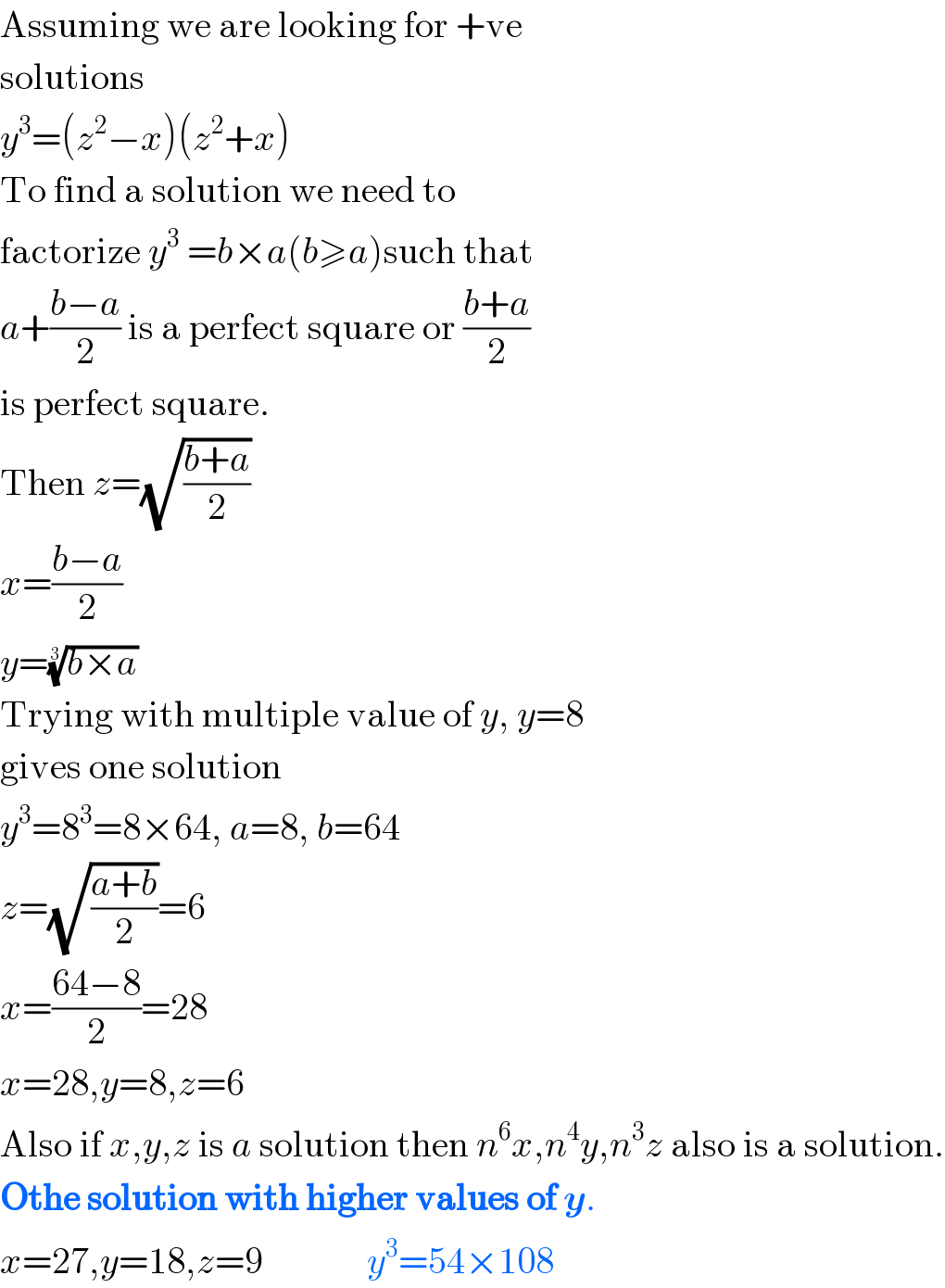
$$\mathrm{Assuming}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{looking}\:\mathrm{for}\:+\mathrm{ve} \\ $$$$\mathrm{solutions} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{3}} =\left({z}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}\right)\left({z}^{\mathrm{2}} +{x}\right) \\ $$$$\mathrm{To}\:\mathrm{find}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{we}\:\mathrm{need}\:\mathrm{to} \\ $$$$\mathrm{factorize}\:{y}^{\mathrm{3}} \:={b}×{a}\left({b}\geqslant{a}\right)\mathrm{such}\:\mathrm{that} \\ $$$${a}+\frac{{b}−{a}}{\mathrm{2}}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{perfect}\:\mathrm{square}\:\mathrm{or}\:\frac{{b}+{a}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{perfect}\:\mathrm{square}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{Then}\:{z}=\sqrt{\frac{{b}+{a}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{{b}−{a}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${y}=\sqrt[{\mathrm{3}}]{{b}×{a}}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{Trying}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{multiple}\:\mathrm{value}\:\mathrm{of}\:{y},\:{y}=\mathrm{8} \\ $$$$\mathrm{gives}\:\mathrm{one}\:\mathrm{solution} \\ $$$${y}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{8}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{8}×\mathrm{64},\:{a}=\mathrm{8},\:{b}=\mathrm{64} \\ $$$${z}=\sqrt{\frac{{a}+{b}}{\mathrm{2}}}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$${x}=\frac{\mathrm{64}−\mathrm{8}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{28} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{28},{y}=\mathrm{8},{z}=\mathrm{6} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Also}\:\mathrm{if}\:{x},{y},{z}\:\mathrm{is}\:{a}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{then}\:{n}^{\mathrm{6}} {x},{n}^{\mathrm{4}} {y},{n}^{\mathrm{3}} {z}\:\mathrm{also}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{solution}. \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Othe}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{solution}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{with}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{higher}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{values}}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{of}}\:\boldsymbol{{y}}. \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{27},{y}=\mathrm{18},{z}=\mathrm{9}\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{y}^{\mathrm{3}} =\mathrm{54}×\mathrm{108} \\ $$
