
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 42785 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 02/Sep/18
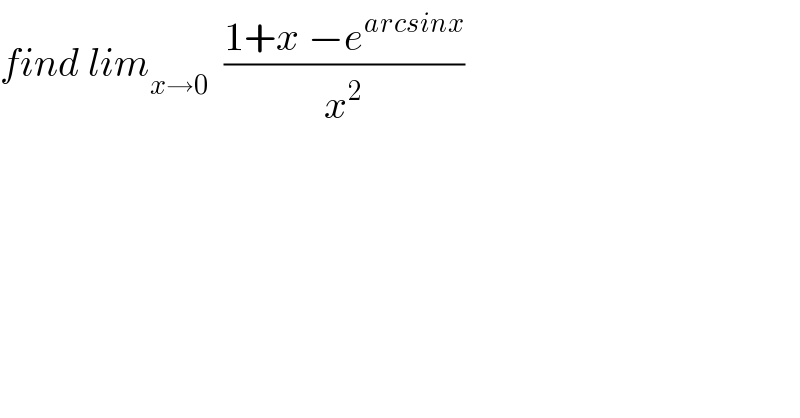
$${find}\:{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+{x}\:−{e}^{{arcsinx}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 30/Sep/18
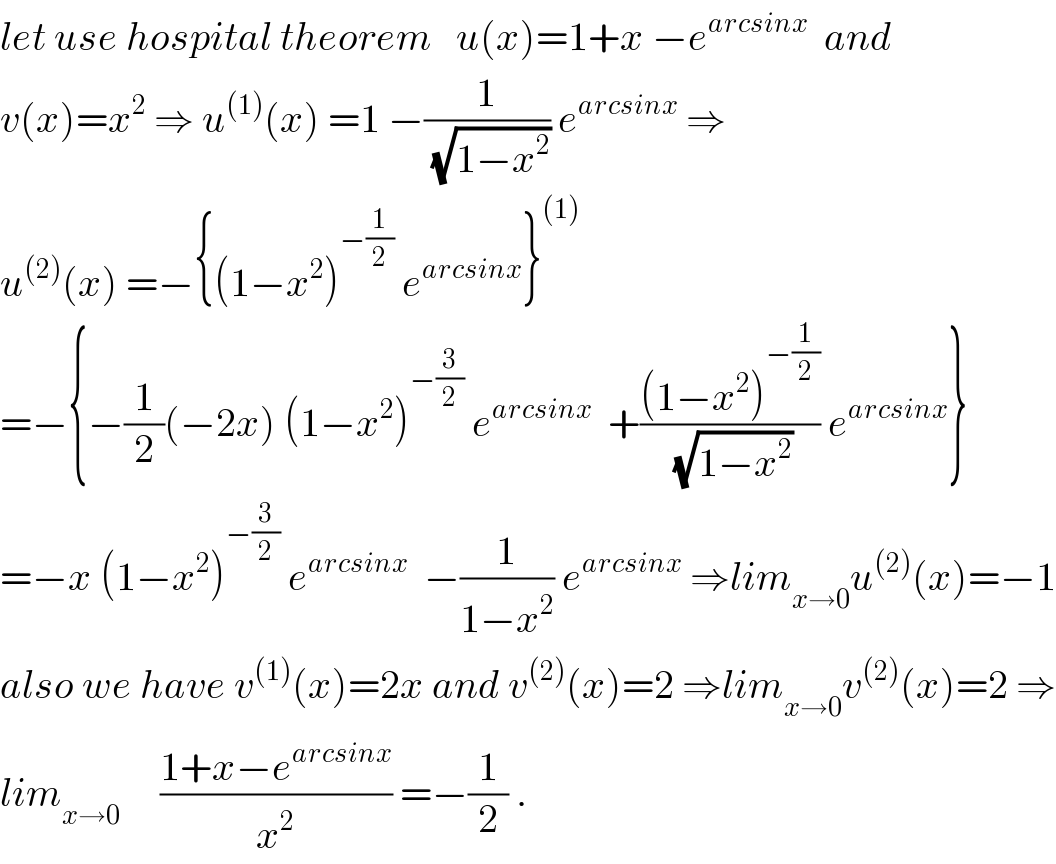
$${let}\:{use}\:{hospital}\:{theorem}\:\:\:{u}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{1}+{x}\:−{e}^{{arcsinx}} \:\:{and} \\ $$$${v}\left({x}\right)={x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\Rightarrow\:{u}^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} \left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{1}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:{e}^{{arcsinx}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${u}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \left({x}\right)\:=−\left\{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{e}^{{arcsinx}} \right\}^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} \\ $$$$=−\left\{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(−\mathrm{2}{x}\right)\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{e}^{{arcsinx}} \:\:+\frac{\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} }{\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:{e}^{{arcsinx}} \right\} \\ $$$$=−{x}\:\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)^{−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{e}^{{arcsinx}} \:\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:{e}^{{arcsinx}} \:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {u}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \left({x}\right)=−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${also}\:{we}\:{have}\:{v}^{\left(\mathrm{1}\right)} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}\:{and}\:{v}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {v}^{\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} \left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${lim}_{{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+{x}−{e}^{{arcsinx}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:. \\ $$
Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 04/Sep/18
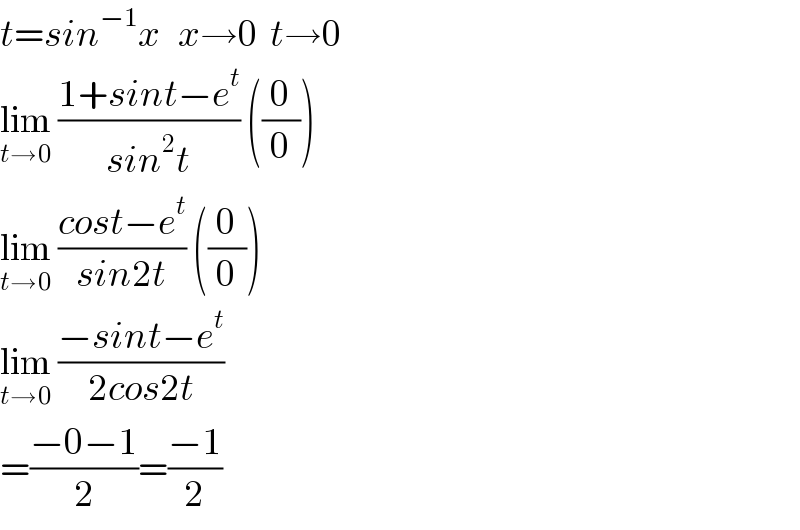
$${t}={sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} {x}\:\:\:{x}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}\:\:{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+{sint}−{e}^{{t}} }{{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} {t}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{{cost}−{e}^{{t}} }{{sin}\mathrm{2}{t}}\:\left(\frac{\mathrm{0}}{\mathrm{0}}\right) \\ $$$$\underset{{t}\rightarrow\mathrm{0}} {\mathrm{lim}}\:\frac{−{sint}−{e}^{{t}} }{\mathrm{2}{cos}\mathrm{2}{t}} \\ $$$$=\frac{−\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}=\frac{−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$
