
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 43602 by peter frank last updated on 12/Sep/18

Answered by $@ty@m last updated on 12/Sep/18
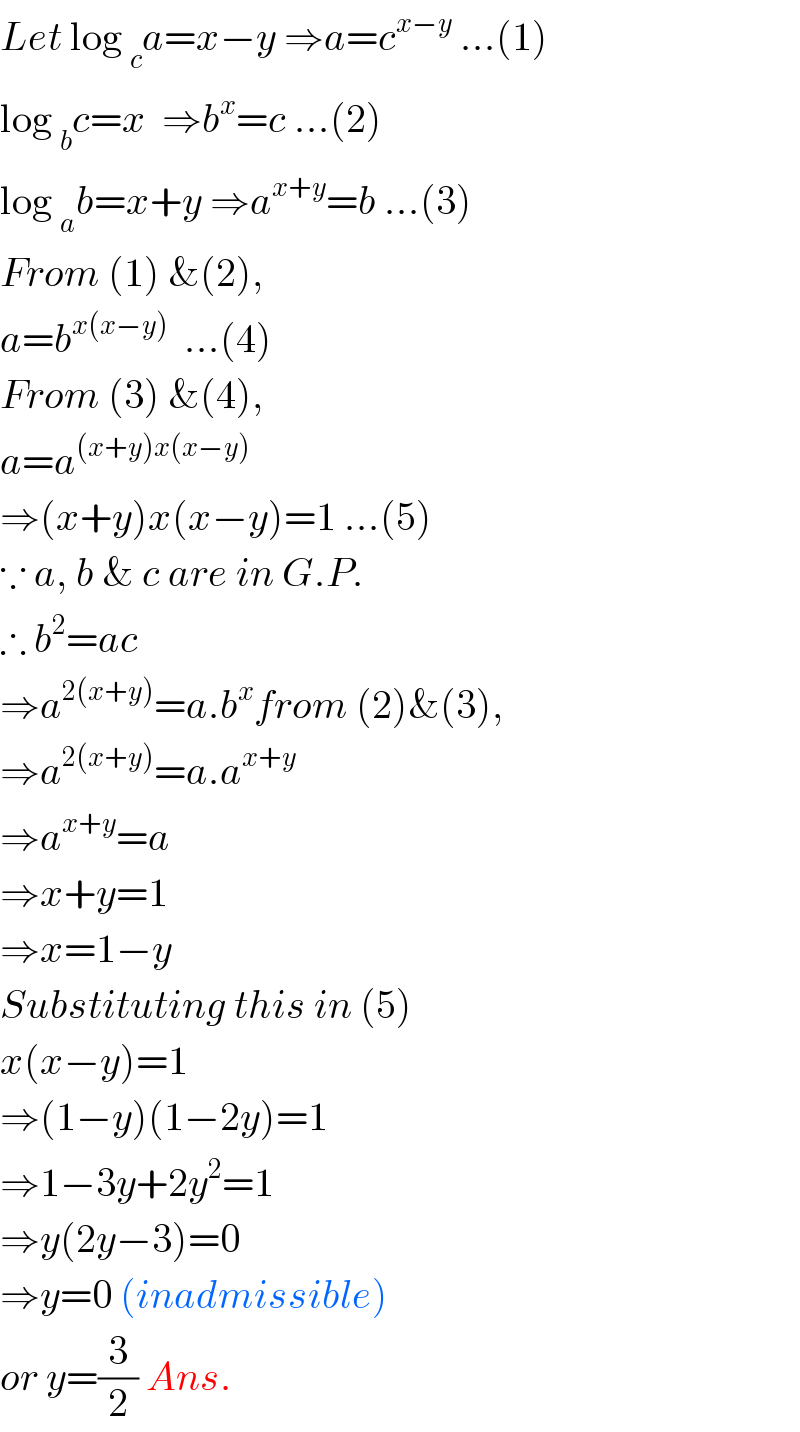
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 43602 by peter frank last updated on 12/Sep/18 | ||
 | ||
Answered by $@ty@m last updated on 12/Sep/18 | ||
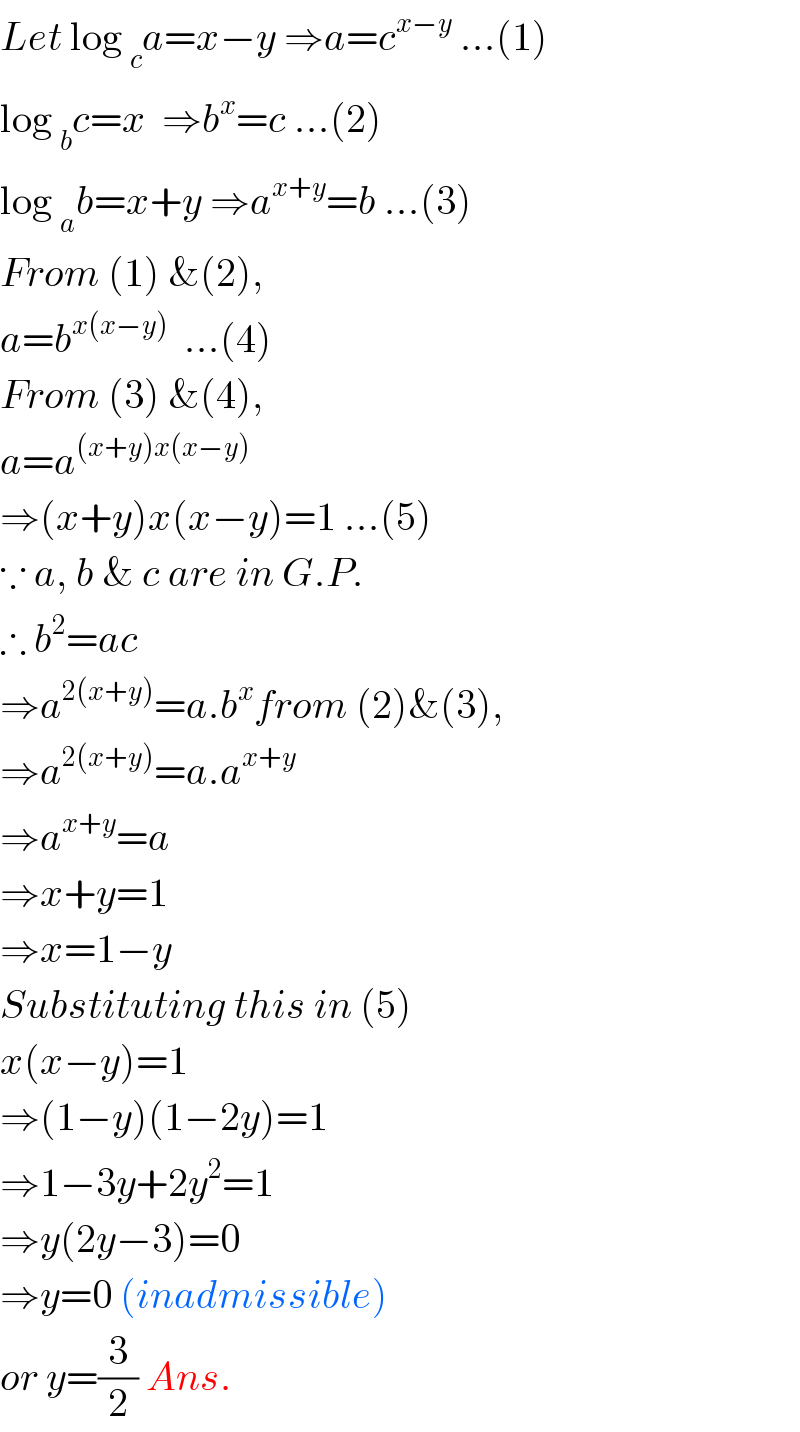 | ||
| ||