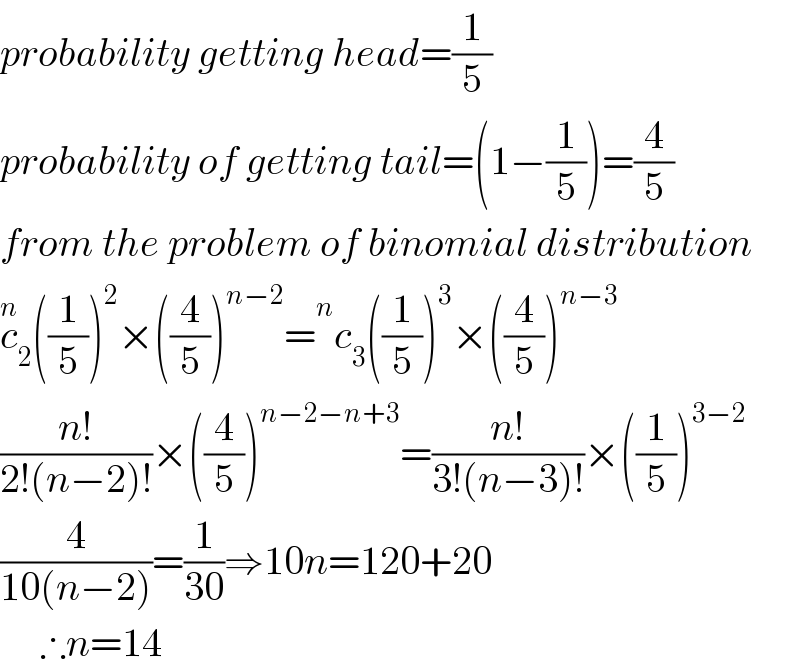Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Permutation and Combination Next in Permutation and Combination
Question Number 43659 by Joel578 last updated on 13/Sep/18
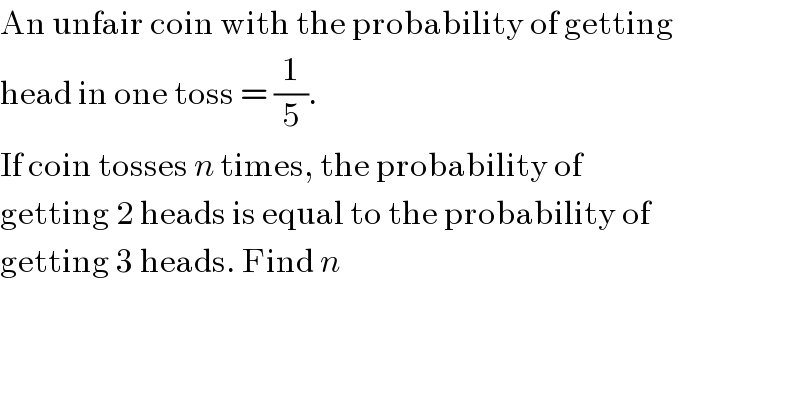
Commented by math1967 last updated on 14/Sep/18

Commented by Joel578 last updated on 17/Sep/18

Answered by math1967 last updated on 17/Sep/18