
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 45043 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 07/Oct/18
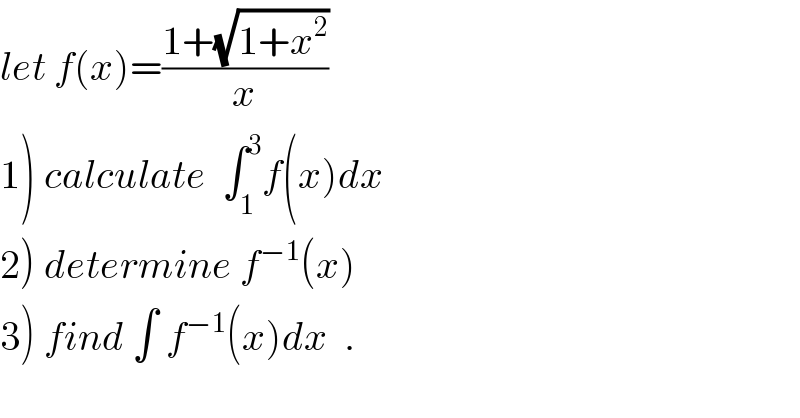
Answered by MJS last updated on 08/Oct/18
![∫((1+(√(x^2 +1)))/x)dx= [t=(√(x^2 +1)) → dx=((√(x^2 +1))/x)dt] =∫(t/(t−1))dt= [u=t−1 → dt=du] =∫((u+1)/u)du=u+ln u=t−1+ln(t−1)= =(√(x^2 +1))−1+ln∣(√(x^2 +1))−1∣= =ln∣1−(√(x^2 +1))∣+(√(x^2 +1))+C (1) ∫_1 ^3 f(x)dx=ln((√(10))+2(√5)−(√2)−1) +((√5)−1)(√2)≈3.40060](Q45098.png)
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Oct/18
Answered by MJS last updated on 08/Oct/18
![(2) f(x) is defined for x≠0 range is R\[−1; 1] solving x=((1+(√(y^2 +1)))/y) gives y=((2x)/(x^2 −1)) but this is defined for x∈R\{−1; 1} especially for x∈]−1; 1[ ⇒ f^(−1) (x)=((2x)/(x^2 −1)) with x∈R\[−1; 1]](Q45101.png)
Answered by MJS last updated on 08/Oct/18
![(3) ∫((2x)/(x^2 −1))dx= [t=x^2 −1 → dx=(dt/(2x))] =∫(dt/t)=ln t =ln ∣x^2 −1∣+C](Q45102.png)
