Question and Answers Forum
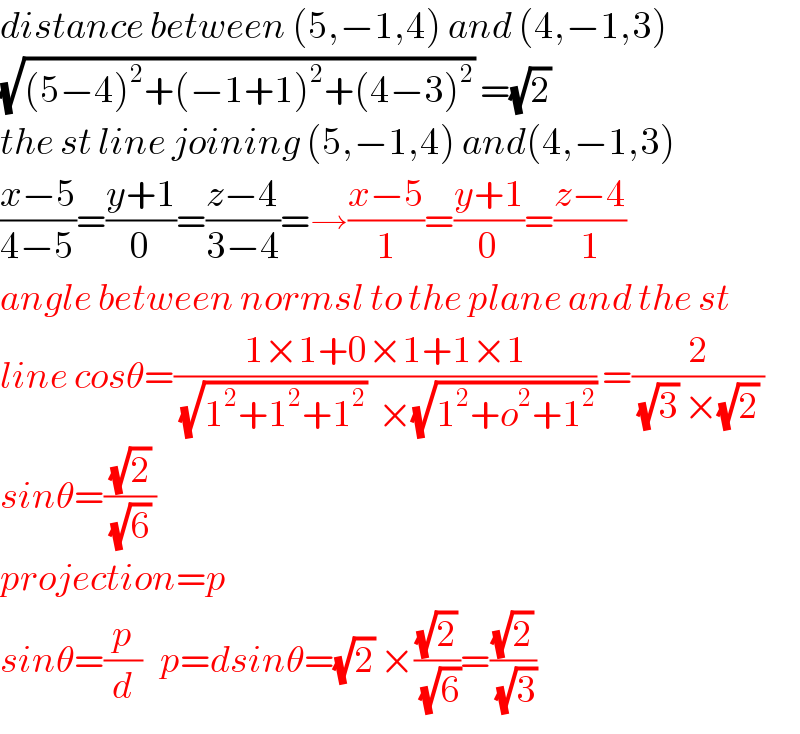
Question Number 45575 by rahul 19 last updated on 14/Oct/18

Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 14/Oct/18

Commented by MrW3 last updated on 14/Oct/18

Commented by MrW3 last updated on 14/Oct/18
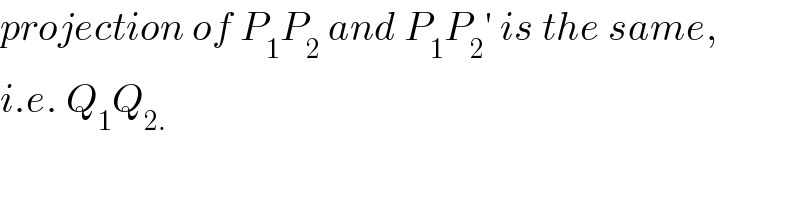
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 14/Oct/18

Answered by MrW3 last updated on 14/Oct/18

Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 14/Oct/18