
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 47295 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 07/Nov/18
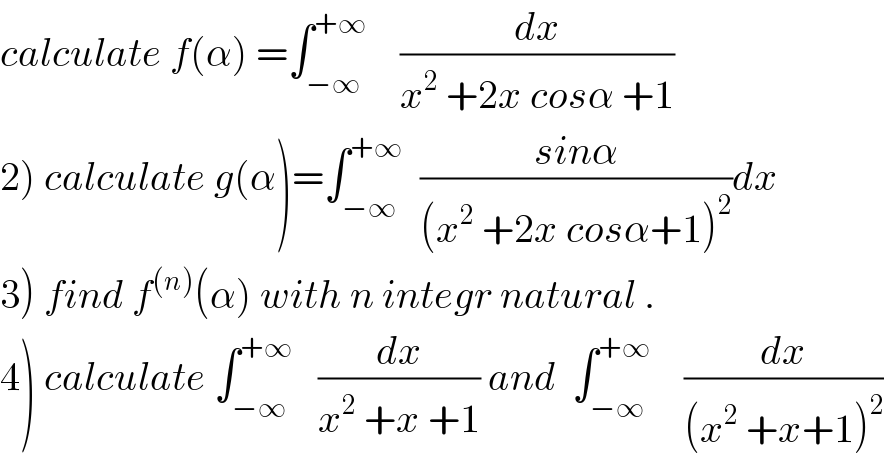
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Nov/18
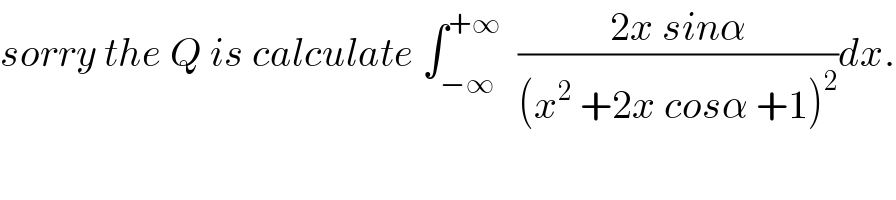
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Nov/18
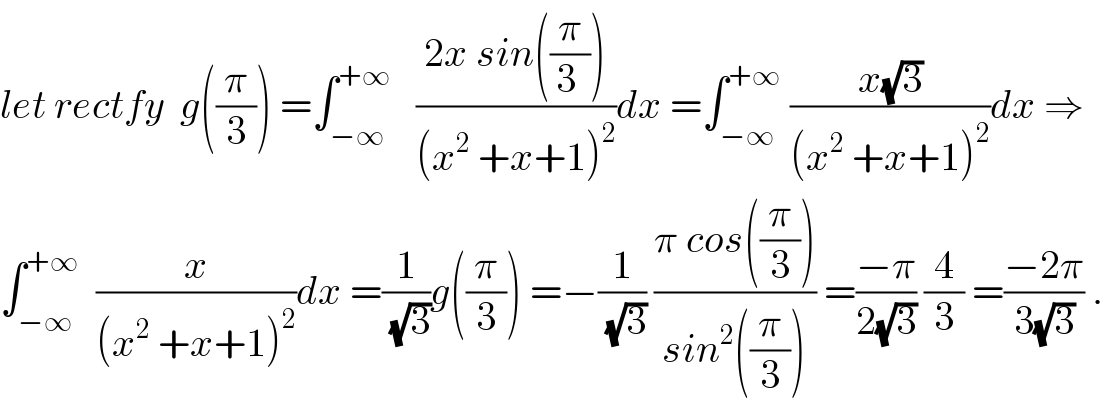
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Nov/18
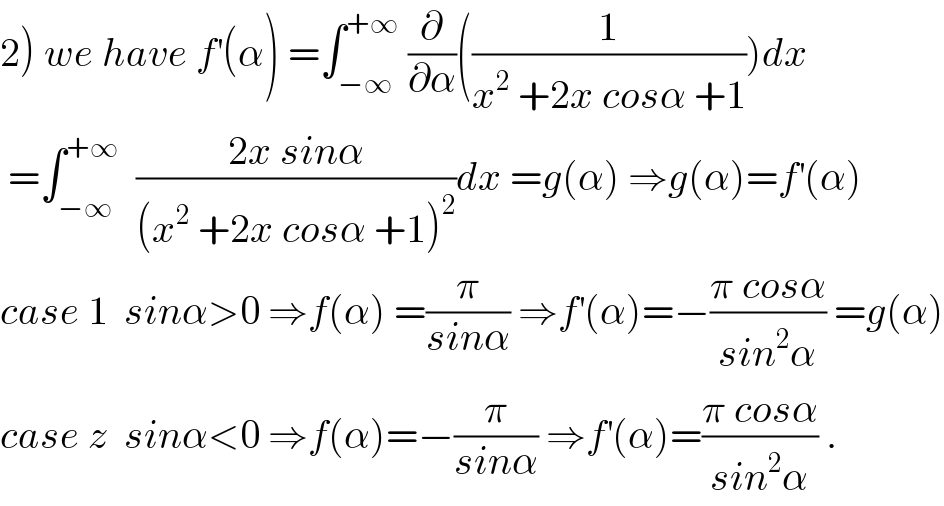
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Nov/18
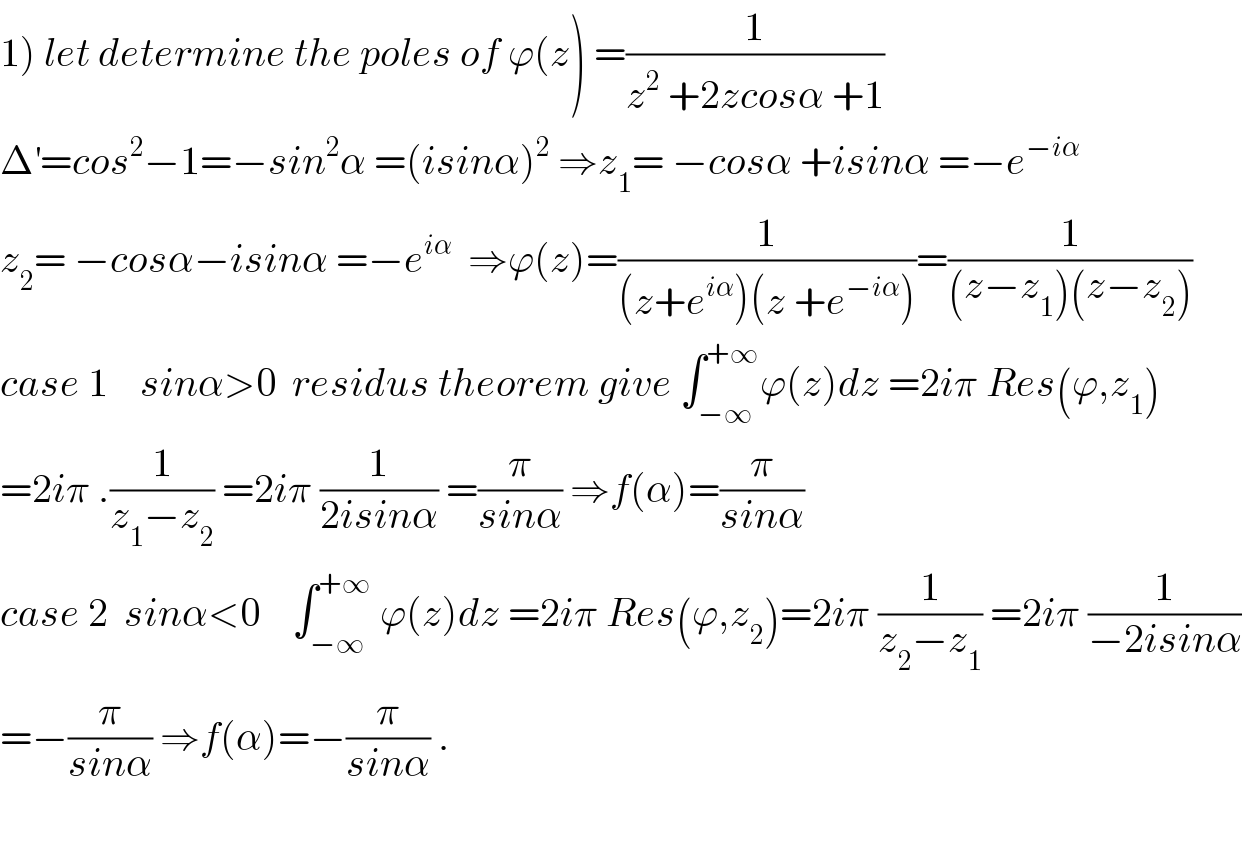
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Nov/18
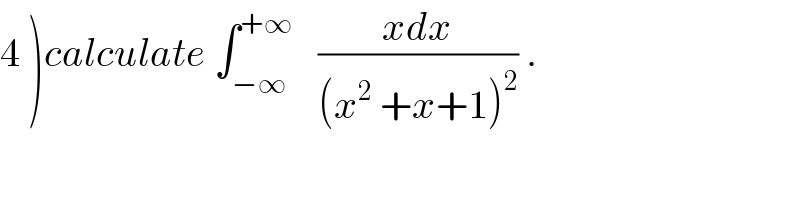
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 08/Nov/18
![4) ★we have x^2 +x +1 =x^2 +2(1/2)x +1 =x^2 +2x cos((π/3))+1 ⇒ ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/(x^2 +x+1)) =f((π/3)) =(π/(sin((π/3)))) =((2π)/(√3)) another way ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/(x^2 +x+1)) =∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/((x+(1/2))^2 +(3/4))) =_(x+(1/2)=((√3)/2)t) ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (1/((3/(4 ))(1+t^2 ))) ((√3)/2)dt =(4/3) ((√3)/2) ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dt/(1+t^2 )) =(2/(√3)) [arctan(t)]_(−∞) ^(+∞) =(2/(√3)){(π/2)+(π/2)} =((2π)/(√3)) . ★ we have g((π/3))=∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) ((sin((π/3)))/((x^2 +x+1)^2 )) dx ⇒ ∫_(−∞) ^(+∞) (dx/((x^2 +x+1)^2 )) =(1/(sin((π/3)))) g((π/3)) =(2/(√3)) ((π cos((π/3)))/(sin^2 ((π/3)))) =(π/(√3)) (1/(3/4)) =((4π)/(3(√3))) .](Q47358.png)
