
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 4820 by love math last updated on 16/Mar/16
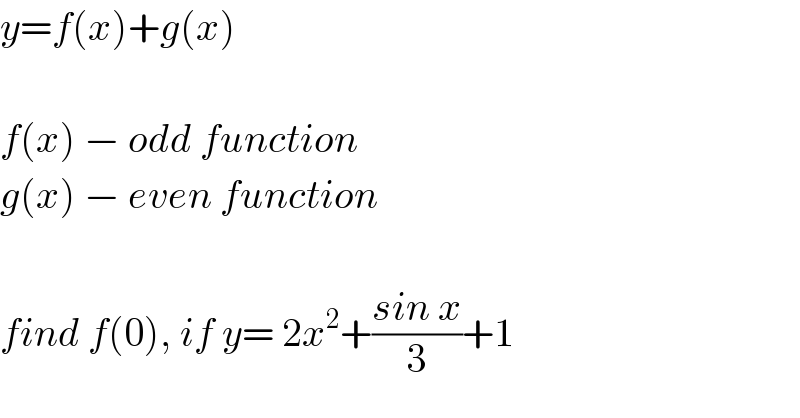
$${y}={f}\left({x}\right)+{g}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)\:−\:{odd}\:{function} \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)\:−\:{even}\:{function} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${find}\:{f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right),\:{if}\:{y}=\:\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 16/Mar/16
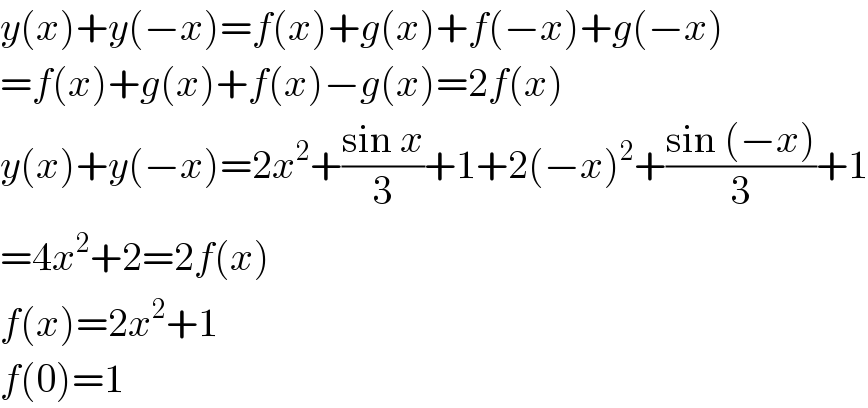
$${y}\left({x}\right)+{y}\left(−{x}\right)={f}\left({x}\right)+{g}\left({x}\right)+{f}\left(−{x}\right)+{g}\left(−{x}\right) \\ $$$$={f}\left({x}\right)+{g}\left({x}\right)+{f}\left({x}\right)−{g}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$${y}\left({x}\right)+{y}\left(−{x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}\left(−{x}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:\left(−{x}\right)}{\mathrm{3}}+\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$=\mathrm{4}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{2}{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{1} \\ $$
Commented by Yozzii last updated on 16/Mar/16
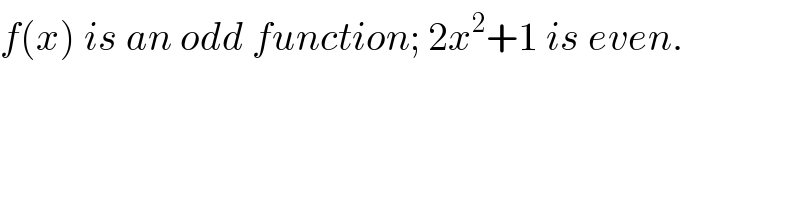
$${f}\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{an}\:{odd}\:{function};\:\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1}\:{is}\:{even}. \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 16/Mar/16

$${f}\left({x}\right)\:{is}\:{an}\:{odd}\:{function},\:{sof}\left(−{x}\right)\:=−{f}\left({x}\right) \\ $$$$\therefore\:{y}\left({x}\right)+{y}\left(−{x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{g}\left({x}\right) \\ $$
Commented by prakash jain last updated on 16/Mar/16
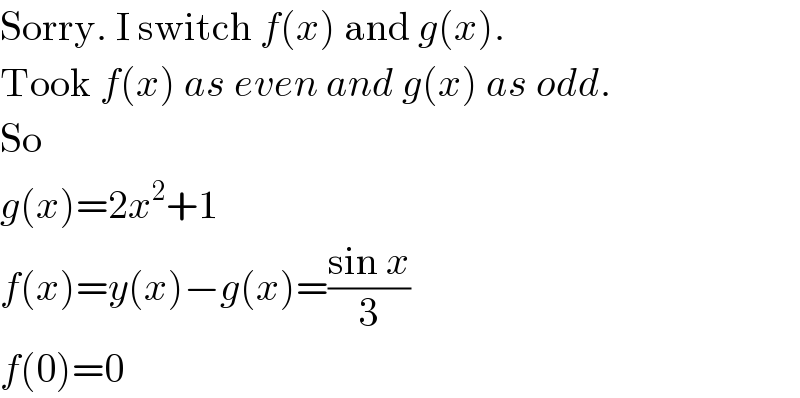
$$\mathrm{Sorry}.\:\mathrm{I}\:\mathrm{switch}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:\mathrm{and}\:{g}\left({x}\right). \\ $$$$\mathrm{Took}\:{f}\left({x}\right)\:{as}\:{even}\:{and}\:{g}\left({x}\right)\:{as}\:{odd}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{So}\: \\ $$$${g}\left({x}\right)=\mathrm{2}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${f}\left({x}\right)={y}\left({x}\right)−{g}\left({x}\right)=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\:{x}}{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$${f}\left(\mathrm{0}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
