
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 50834 by Tinkutara last updated on 21/Dec/18

Commented by ajfour last updated on 21/Dec/18
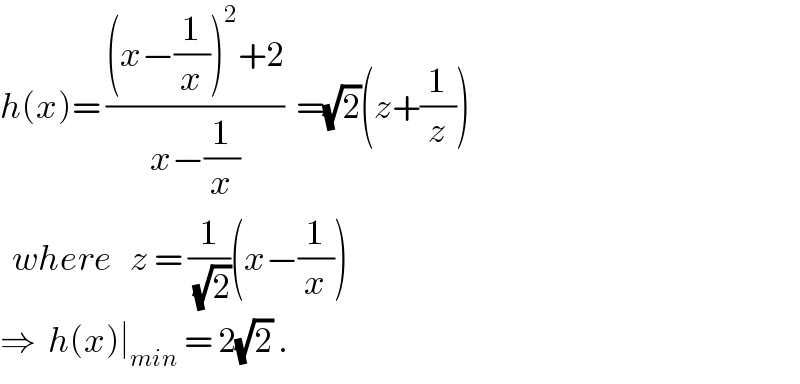
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 21/Dec/18

Commented by ajfour last updated on 21/Dec/18

Commented by Tinkutara last updated on 22/Dec/18
Thanks Sir!
