
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 54699 by rahul 19 last updated on 09/Feb/19
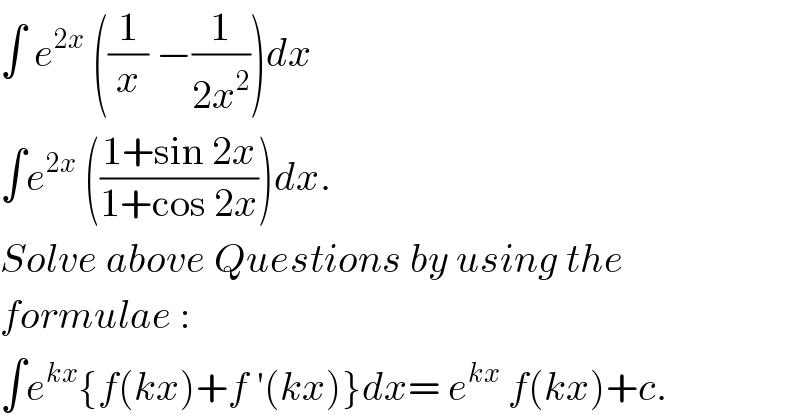
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 10/Feb/19
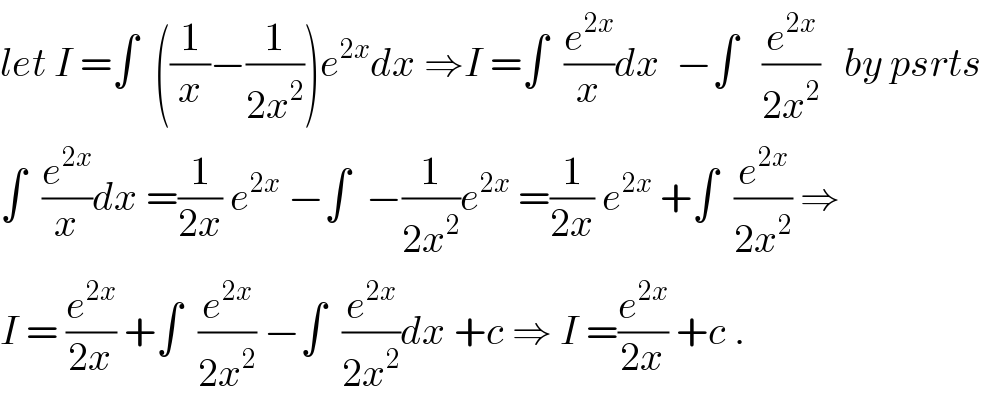
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 10/Feb/19
thank you profAbdo .
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 11/Feb/19
Answered by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 09/Feb/19
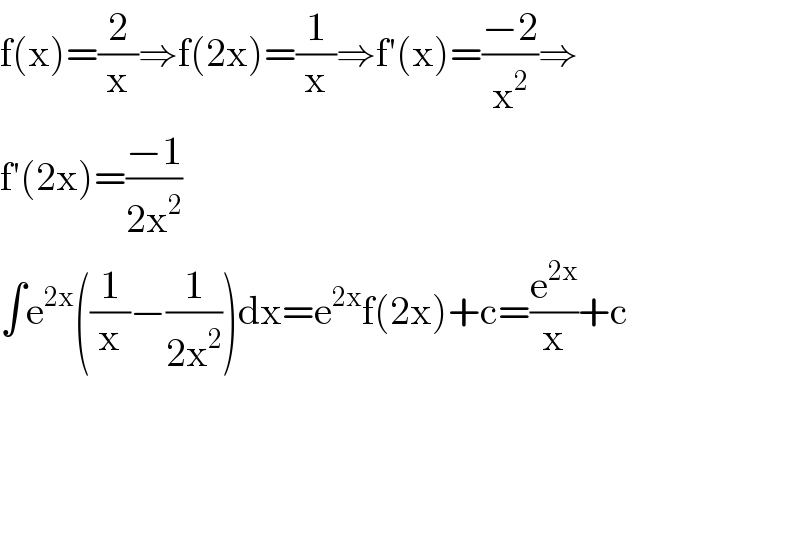
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 09/Feb/19
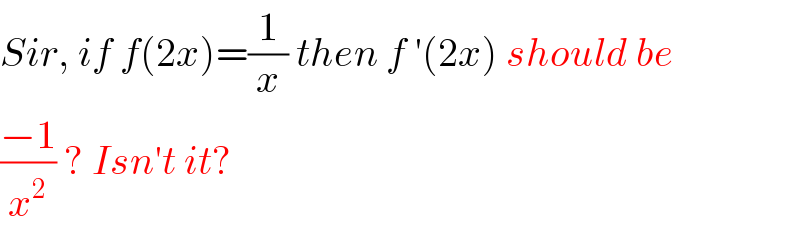
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 09/Feb/19

Answered by tanmay.chaudhury50@gmail.com last updated on 09/Feb/19
![1)(1/2)∫[(1/x)×(d/dx)(e^(2x) )+e^(2x) (d/dx)((1/x))]dx (1/2)∫(d/dx)((1/x)e^(2x) )dx (1/2)((e^(2x) /x))+c 2)∫e^(2x) (((1+2sinxcosx)/(2cos^2 x))) ∫e^(2x) ((1/2)sec^2 x+tanx)dx (1/2)∫[e^(2x) ×(d/dx)(tanx)+tanx×(d/dx)(e^(2x) )]dx =(1/2)∫(d/(dx ))(e^(2x) tanx)dx ((e^(2x) tanx)/2)+c](Q54706.png)
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 10/Feb/19
thank you sir �� but how to do by using given formulae ?
