
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 55668 by mr W last updated on 01/Mar/19
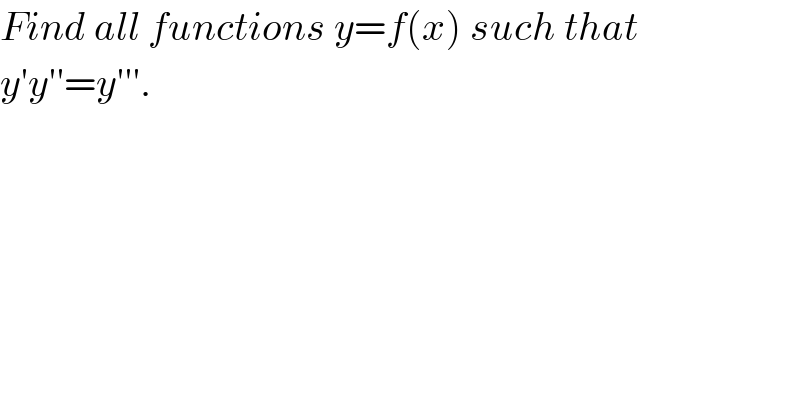
Commented by malwaan last updated on 02/Mar/19

Commented by mr W last updated on 02/Mar/19
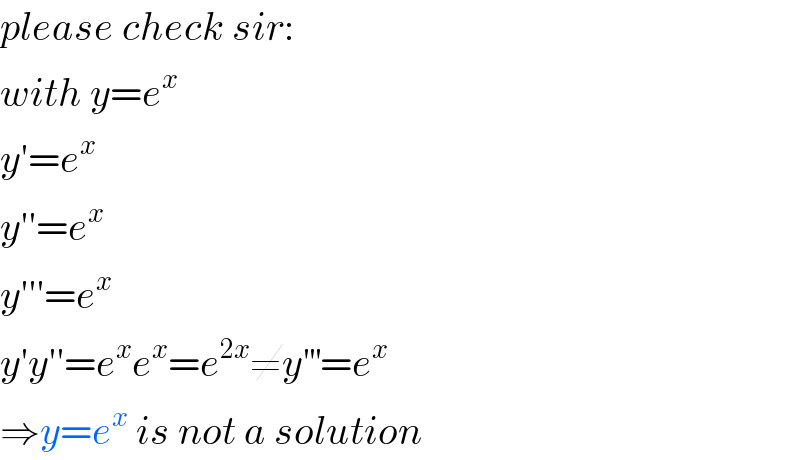
Commented by mr W last updated on 02/Mar/19
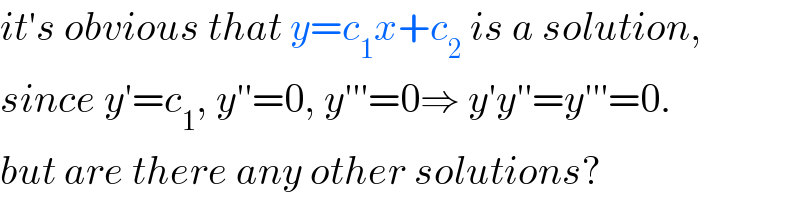
Answered by mr W last updated on 03/Mar/19
![let g(x)=y′=f′(x) ⇒gg′=g′′ let h(x)=g′(x) g′′=((dh(x))/dx)=((dh(x))/dg)×(dg/dx)=h(dh/dg) ⇒gh=h(dh/dg) if h≠0: (h=0⇒g(x)=c_1 ⇒y=c_1 x+c_2 ) ⇒gdg=dh ⇒∫gdg=∫dh ⇒((g^2 +c_1 )/2)=h=(dg/dx) ⇒(g^2 +c_1 )dx=2dg if g^2 +c_1 ≠0: ⇒(dg/(g^2 +c_1 ))=(dx/2) ⇒∫(dg/(g^2 +c_1 ))=∫(dx/2) if c_1 =0: ⇒∫(dg/g^2 )=∫(dx/2) ⇒−(1/g)=((x+c_2 )/2) ⇒g=y′=(dy/dx)=−(2/(x+c_2 )) ⇒dy=−((2dx)/(x+c_2 )) ⇒y=−2ln ∣x+c_2 ∣+c_3 if c_1 >0, say c_1 =c_4 ^2 ⇒∫(dg/(g^2 +c_4 ^2 ))=∫(dx/2) ⇒(1/c_4 )tan^(−1) (g/c_4 )=((x+c_5 )/2) ⇒g=y′=(dy/dx)=c_4 tan ((c_4 (x+c_5 ))/2) ⇒y=∫c_4 tan ((c_4 (x+c_5 ))/2)dx ⇒y=2∫tan ((c_4 (x+c_5 ))/2)d(((c_4 (x+c_5 ))/2)) ⇒y=−2ln ∣cos ((c_4 (x+c_5 ))/2)∣+c_6 if c_1 <0, say c_1 =−c_4 ^2 ⇒∫(dg/(g^2 −c_4 ^2 ))=∫(dx/2) ⇒(1/(2c_4 ))ln ∣((g−c_4 )/(g+c_4 ))∣=((x+c_5 )/2) ⇒ln ∣1−((2c_4 )/(g+c_4 ))∣=c_4 (x+c_5 ) ⇒1−((2c_4 )/(g+c_4 ))=e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ⇒((2c_4 )/(g+c_4 ))=1−e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ⇒g=y′=(dy/dx)=c_4 [(2/(1−e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ))−1] ⇒y=∫c_4 [(2/(1−e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ))−1]dx ⇒y=c_4 [∫((2dx)/(1−e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ))−x] ⇒y=c_4 [2(x+c_5 )−((2ln ∣1−e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ∣)/c_4 )−x] ⇒y=c_4 x−2ln ∣1−e^(c_4 (x+c_5 )) ∣+c_6 if g^2 +c_1 =0: if c_1 =0: ⇒g=y′=(dy/dx)=0 ⇒y=c_2 if c_1 >0: g^2 +c_1 ≠0 if c_1 <0: g^2 +c_1 =0 ⇒g^2 =−c_1 =c_2 ^2 say ⇒g=±c_2 ⇒g=(dy/dx)=±c_2 ⇒y=±c_2 x+c_3 summary: following functions are possible solutions: y=f(x)=c_1 x+c_2 y=f(x)=−2ln ∣x+c_1 ∣+c_2 y=f(x)=−2ln ∣cos (c_1 x+c_2 )∣+c_3 y=f(x)=−2ln ∣1−e^(c_1 x+c_2 ) ∣+c_1 x+c_3](Q55693.png)
Commented by MJS last updated on 02/Mar/19

Commented by otchereabdullai@gmail.com last updated on 02/Mar/19

Commented by malwaan last updated on 03/Mar/19

Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 03/Mar/19

