
Previous in Probability and Statistics Next in Probability and Statistics
Question Number 56045 by mr W last updated on 09/Mar/19
Commented by mr W last updated on 09/Mar/19

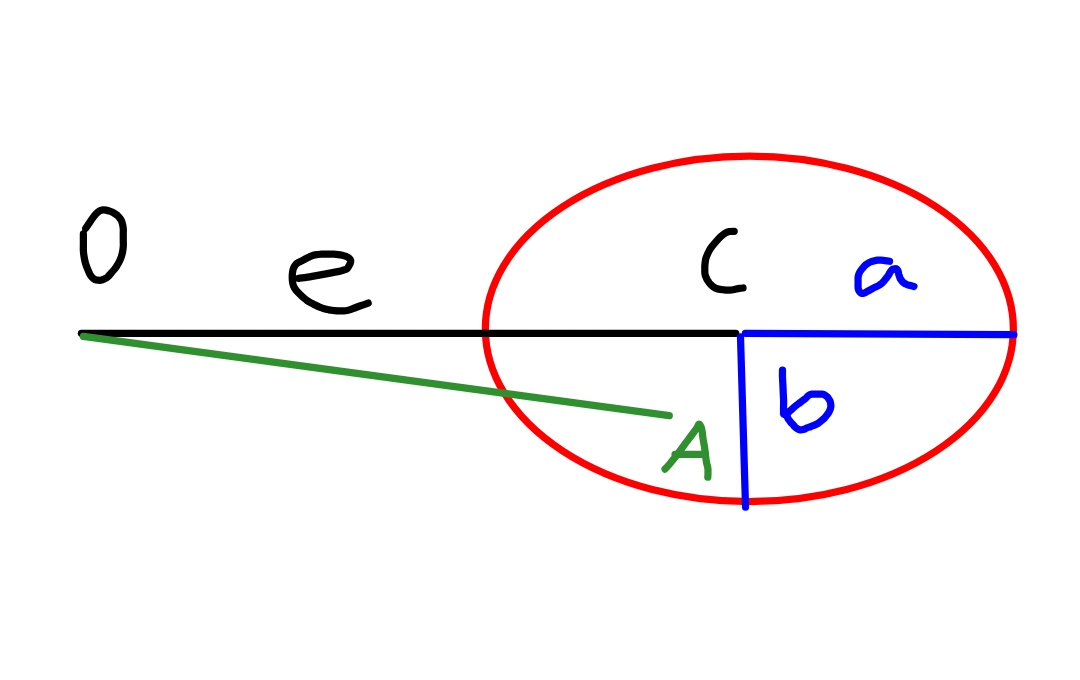
$${An}\:{ellipse}\:{with}\:{semi}\:{axes}\:{a}\:{and}\:{b}\:{has} \\ $$$${a}\:{distance}\:{e}\:\left({e}>{a}\right)\:{from}\:{its}\:{center}\:{C}\:{to} \\ $$$${point}\:{O}.\:{Point}\:{A}\:{is}\:{choosen}\:{randomly} \\ $$$${inside}\:{the}\:{ellipse}.\:{Let}\:{d}\:{be}\:{the}\:{distance} \\ $$$${from}\:{A}\:{to}\:{O}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}.\:{Find}\:{the}\:{probability}\:{that}\:{d}\leqslant{e}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{2}.\:{Find}\:{the}\:{average}\:{value}\:{of}\:{d}. \\ $$
Answered by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/19
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/19
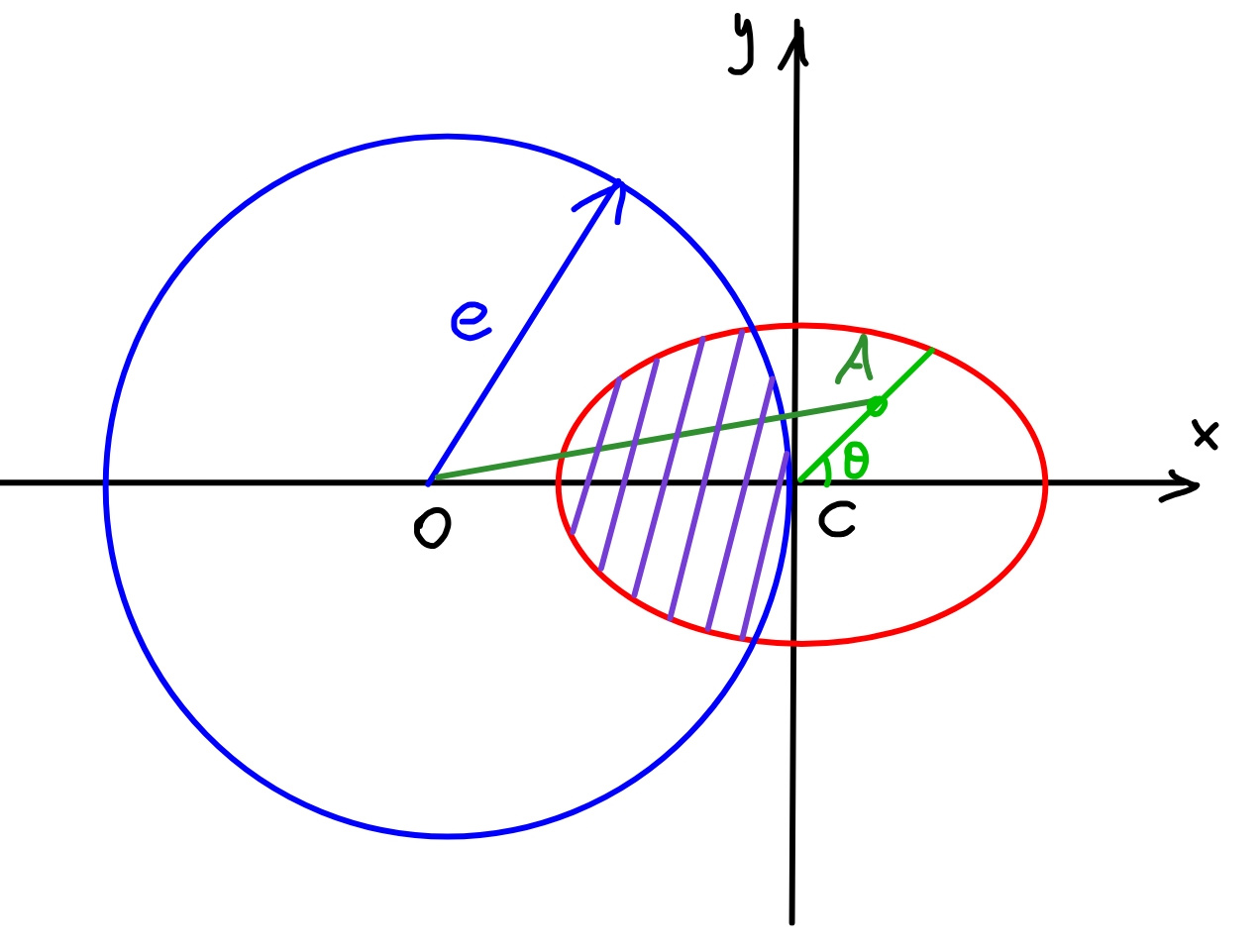
![Q1: Points in shaded area have distance to point O which is equal or less than e, therefore the probability is p=((Area shaded)/(Area ellipse)) eqn. of ellipse: (x^2 /a^2 )+(y^2 /b^2 )=1 or y=±b(√(1−(x^2 /a^2 ))) eqn. of circle: (x+e)^2 +y^2 =e^2 or y=±(√(−x(x+2e))) intersection: (x^2 /a^2 )+((e^2 −(x+e)^2 )/b^2 )=1 (a^2 −b^2 )x^2 +2ea^2 x+a^2 b^2 =0 if a=b: ⇒x=−(b^2 /(2e))=−(μ^2 /2)e=−αe if a≠b: ⇒x=((−ea^2 +(√(e^2 a^4 −a^2 b^2 (a^2 −b^2 ))))/(a^2 −b^2 )) with λ=(b/a),μ=(b/e) ⇒x=x_1 =−[((1−(√(1−μ^2 (1−λ^2 ))))/(1−λ^2 ))]e=−αe A_(shaded) =2∫_(−a) ^( x_1 ) b(√(1−(x^2 /a^2 )))dx+2∫_x_1 ^( 0) (√(−x(x+2e)))dx A_(shaded) =2[b∫_(αe) ^( a) (√(1−(x^2 /a^2 )))dx+∫_0 ^( αe) (√(x(2e−x)))dx] A_(shaded) =2(((ab)/2)[(x/a)(√(1−(x^2 /a^2 )))+sin^(−1) (x/a)]_(αe) ^a +(1/2)[e^2 sin^(−1) ((x−e)/e)+(x−e)(√(x(2e−x)))]_0 ^(αe) ) A_(shaded) =ab[(x/a)(√(1−(x^2 /a^2 )))+sin^(−1) (x/a)]_(αe) ^a +e^2 [sin^(−1) (1−(x/e))+(1−(x/e))(√((x/e)(2−(x/e))))]_(αe) ^0 A_(shaded) =ab((π/2)−((αe)/a)(√(1−((α^2 e^2 )/a^2 )))−sin^(−1) ((αe)/a))+e^2 ((π/2)−sin^(−1) (1−α)−(1−α)(√(α(2−α))) A_(ellipse) =πab ⇒p=(1/2)(1+(e^2 /(ab)))−(1/π)[(((αe)/a))(√(1−(((αe)/a))^2 ))+sin^(−1) (((αe)/a))]−(e^2 /(πab))[sin^(−1) (1−α)+(1−α)(√(α(2−α)))] special case with a=b=e: α=(1/2) ⇒p=(2/3)−((√3)/(2π))≈0.391](Q56085.png)
$${Q}\mathrm{1}: \\ $$$${Points}\:{in}\:{shaded}\:{area}\:{have}\:{distance} \\ $$$${to}\:{point}\:{O}\:{which}\:{is}\:{equal}\:{or}\:{less}\:{than}\:{e}, \\ $$$${therefore}\:{the}\:{probability}\:{is} \\ $$$${p}=\frac{{Area}\:{shaded}}{{Area}\:{ellipse}} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${eqn}.\:{of}\:{ellipse}: \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${or}\:{y}=\pm{b}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }} \\ $$$${eqn}.\:{of}\:{circle}: \\ $$$$\left({x}+{e}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +{y}^{\mathrm{2}} ={e}^{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$${or}\:{y}=\pm\sqrt{−{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}{e}\right)} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${intersection}: \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} −\left({x}+{e}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\left({a}^{\mathrm{2}} −{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{ea}^{\mathrm{2}} {x}+{a}^{\mathrm{2}} {b}^{\mathrm{2}} =\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${if}\:{a}={b}: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=−\frac{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}{e}}=−\frac{\mu^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{e}=−\alpha{e} \\ $$$${if}\:{a}\neq{b}: \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}=\frac{−{ea}^{\mathrm{2}} +\sqrt{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} {a}^{\mathrm{4}} −{a}^{\mathrm{2}} {b}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({a}^{\mathrm{2}} −{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}}{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} −{b}^{\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$$${with}\:\lambda=\frac{{b}}{{a}},\mu=\frac{{b}}{{e}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{x}={x}_{\mathrm{1}} =−\left[\frac{\mathrm{1}−\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\mu^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\mathrm{1}−\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} \right)}}{\mathrm{1}−\lambda^{\mathrm{2}} }\right]{e}=−\alpha{e} \\ $$$${A}_{{shaded}} =\mathrm{2}\int_{−{a}} ^{\:{x}_{\mathrm{1}} } {b}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx}+\mathrm{2}\int_{{x}_{\mathrm{1}} } ^{\:\mathrm{0}} \sqrt{−{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}{e}\right)}{dx} \\ $$$${A}_{{shaded}} =\mathrm{2}\left[{b}\int_{\alpha{e}} ^{\:{a}} \sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}{dx}+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\:\alpha{e}} \sqrt{{x}\left(\mathrm{2}{e}−{x}\right)}{dx}\right] \\ $$$${A}_{{shaded}} =\mathrm{2}\left(\frac{{ab}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[\frac{{x}}{{a}}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}+\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{{a}}\right]_{\alpha{e}} ^{{a}} +\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left[{e}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}−{e}}{{e}}+\left({x}−{e}\right)\sqrt{{x}\left(\mathrm{2}{e}−{x}\right)}\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\alpha{e}} \right) \\ $$$${A}_{{shaded}} ={ab}\left[\frac{{x}}{{a}}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}+\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{{x}}{{a}}\right]_{\alpha{e}} ^{{a}} +{e}^{\mathrm{2}} \left[\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{{e}}\right)+\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{{e}}\right)\sqrt{\frac{{x}}{{e}}\left(\mathrm{2}−\frac{{x}}{{e}}\right)}\right]_{\alpha{e}} ^{\mathrm{0}} \\ $$$${A}_{{shaded}} ={ab}\left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\alpha{e}}{{a}}\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\alpha^{\mathrm{2}} {e}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }}−\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \frac{\alpha{e}}{{a}}\right)+{e}^{\mathrm{2}} \left(\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{2}}−\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−\alpha\right)−\left(\mathrm{1}−\alpha\right)\sqrt{\alpha\left(\mathrm{2}−\alpha\right.}\right) \\ $$$${A}_{{ellipse}} =\pi{ab} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{1}+\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{ab}}\right)−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\pi}\left[\left(\frac{\alpha{e}}{{a}}\right)\sqrt{\mathrm{1}−\left(\frac{\alpha{e}}{{a}}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }+\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\frac{\alpha{e}}{{a}}\right)\right]−\frac{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\pi{ab}}\left[\mathrm{sin}^{−\mathrm{1}} \left(\mathrm{1}−\alpha\right)+\left(\mathrm{1}−\alpha\right)\sqrt{\alpha\left(\mathrm{2}−\alpha\right)}\right] \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${special}\:{case}\:{with}\:{a}={b}={e}:\:\alpha=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}} \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{p}=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\mathrm{3}}−\frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}\pi}\approx\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{391} \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/19
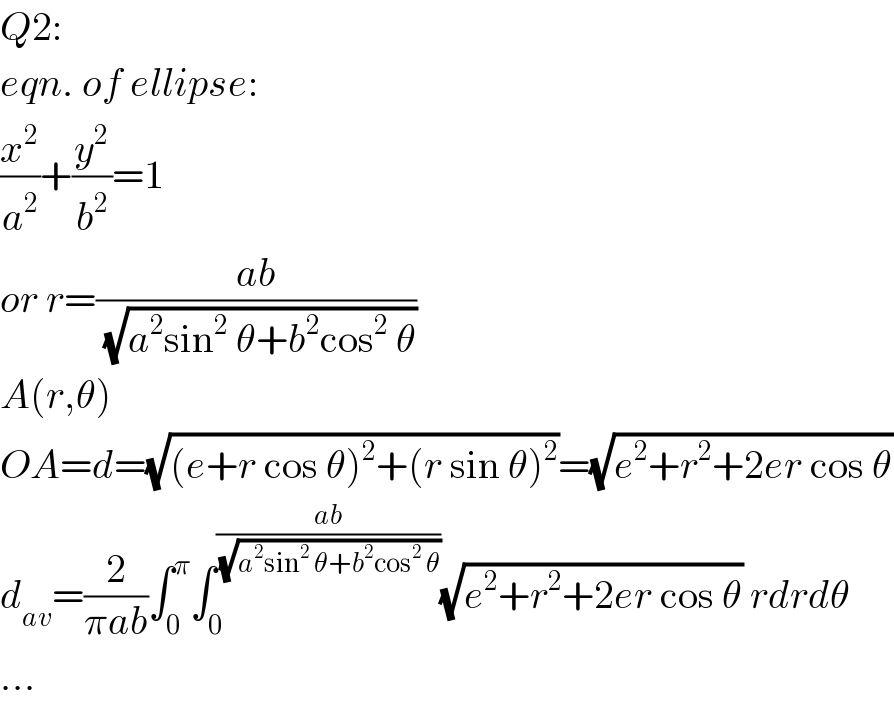
$${Q}\mathrm{2}: \\ $$$${eqn}.\:{of}\:{ellipse}: \\ $$$$\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} }+\frac{{y}^{\mathrm{2}} }{{b}^{\mathrm{2}} }=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${or}\:{r}=\frac{{ab}}{\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta}} \\ $$$${A}\left({r},\theta\right) \\ $$$${OA}={d}=\sqrt{\left({e}+{r}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\theta\right)^{\mathrm{2}} +\left({r}\:\mathrm{sin}\:\theta\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }=\sqrt{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{er}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\theta} \\ $$$${d}_{{av}} =\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\pi{ab}}\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\pi} \int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{{ab}}{\sqrt{{a}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta+{b}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{cos}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\theta}}} \sqrt{{e}^{\mathrm{2}} +{r}^{\mathrm{2}} +\mathrm{2}{er}\:\mathrm{cos}\:\theta}\:{rdrd}\theta \\ $$$$... \\ $$
Commented by behi83417@gmail.com last updated on 10/Mar/19

$${great}\:{job}\:{done}\:{dear}\:{master}.{thank}\:{you} \\ $$$${very}\:{much}\:{for}\:{good}\:{question}\:{and}\:{also} \\ $$$${so}\:{nice}\:{solution}. \\ $$
Commented by mr W last updated on 10/Mar/19

$${thanks}\:{alot}\:{sir}! \\ $$
