
Question Number 56708 by gunawan last updated on 22/Mar/19
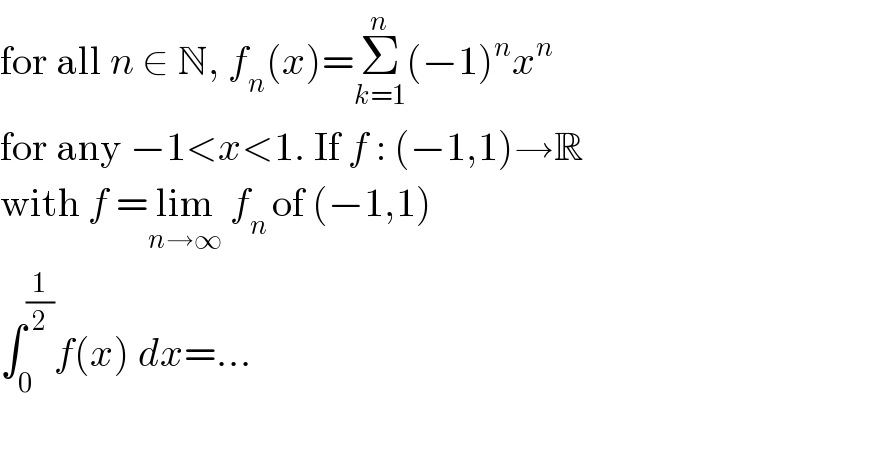
$$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{all}\:{n}\:\in\:\mathbb{N},\:{f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)=\underset{{k}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{n}} {\sum}}\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {x}^{{n}} \\ $$ $$\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{any}\:−\mathrm{1}<{x}<\mathrm{1}.\:\mathrm{If}\:{f}\::\:\left(−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right)\rightarrow\mathbb{R} \\ $$ $$\mathrm{with}\:{f}\:=\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\:{f}_{{n}\:} \mathrm{of}\:\left(−\mathrm{1},\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$ $$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} {f}\left({x}\right)\:{dx}=... \\ $$ $$ \\ $$
Commented byAbdo msup. last updated on 22/Mar/19
![we have f_n (x)=Σ_(k=1) ^n (−x)^k =Σ_(k=0) ^n (−x)^k −1 =((1−(−x)^(n+1) )/(1+x)) −1 =((1−(−x)^(n+1) −1−x)/(1+x)) but ∣x∣<1 ⇒lim_(n→+∞) f_n (x)=((−x)/(1+x)) ⇒ f(x)=((−x)/(1+x)) ⇒∫_0 ^(1/2) f(x)dx =−∫_0 ^(1/2) ((1+x−1)/(1+x))dx =−(1/2) +∫_0 ^(1/2) (dx/(1+x)) =−(1/2) +[ln∣1+x∣]_0 ^(1/2) =−(1/2) +ln((3/2)) . here i have used that lim f_n =f .](Q56712.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:{f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)=\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{n}} \left(−{x}\right)^{{k}} \:=\sum_{{k}=\mathrm{0}} ^{{n}} \left(−{x}\right)^{{k}} −\mathrm{1} \\ $$ $$=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:−\mathrm{1}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}−\left(−{x}\right)^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} −\mathrm{1}−{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}} \\ $$ $${but}\:\mid{x}\mid<\mathrm{1}\:\Rightarrow{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:\:\:{f}_{{n}} \left({x}\right)=\frac{−{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$ $${f}\left({x}\right)=\frac{−{x}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:\Rightarrow\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} {f}\left({x}\right){dx}\:=−\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+{x}−\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}{dx} \\ $$ $$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+\left[{ln}\mid\mathrm{1}+{x}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} \\ $$ $$=−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\:+{ln}\left(\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right)\:. \\ $$ $${here}\:{i}\:{have}\:{used}\:{that}\:{lim}\:{f}_{{n}} ={f}\:. \\ $$
