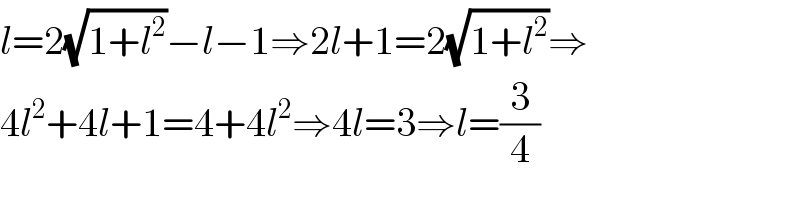Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 56828 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 24/Mar/19
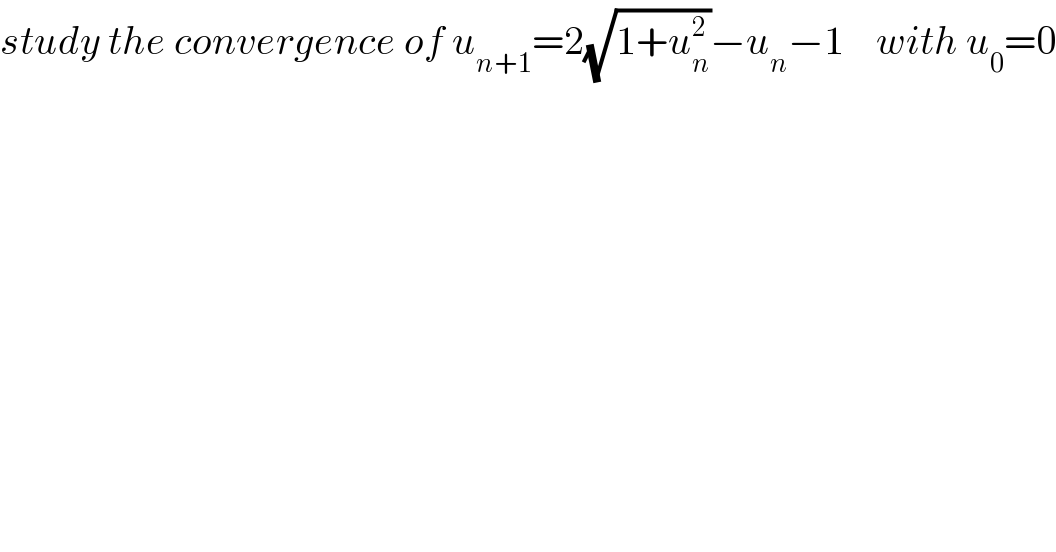
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 16/Apr/19

Answered by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 25/Mar/19