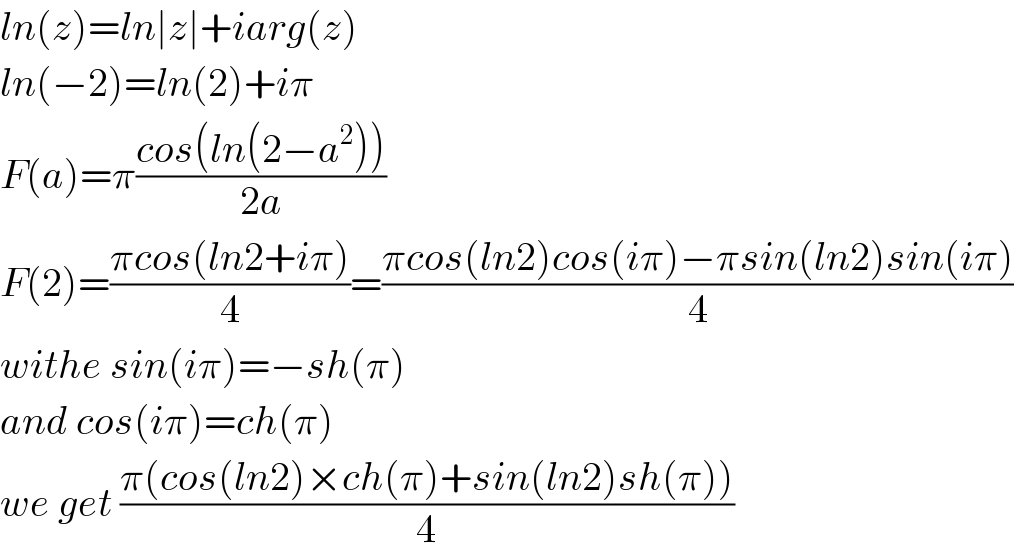Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 57490 by Abdo msup. last updated on 05/Apr/19
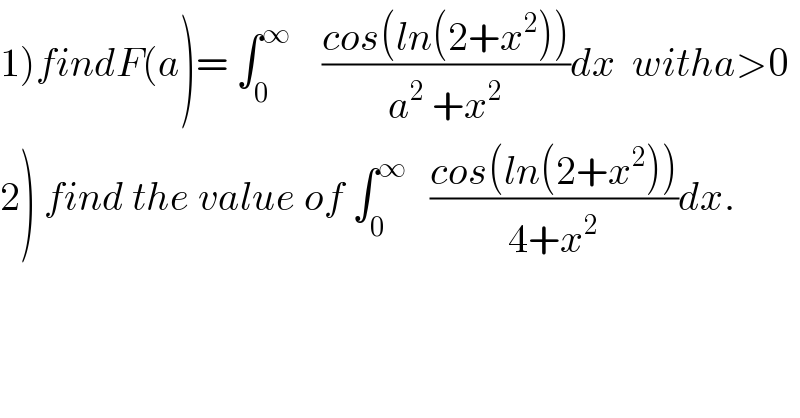
Commented bymaxmathsup by imad last updated on 06/Apr/19
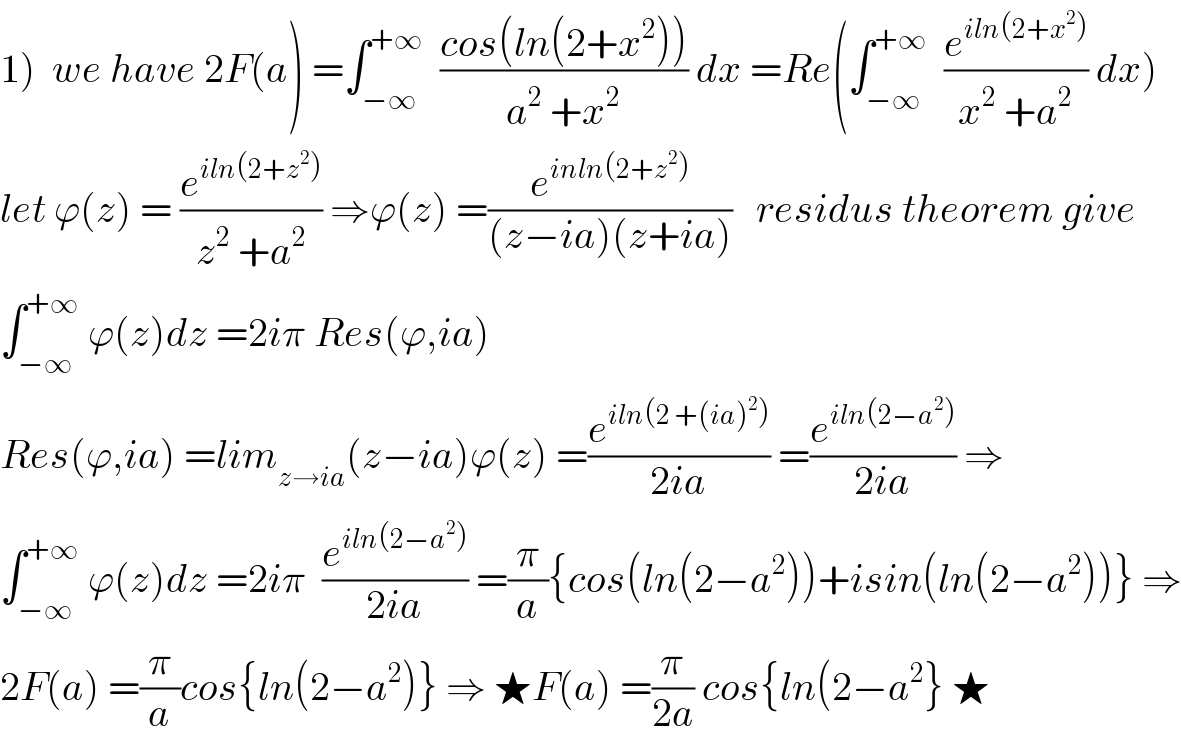
Commented bymaxmathsup by imad last updated on 06/Apr/19
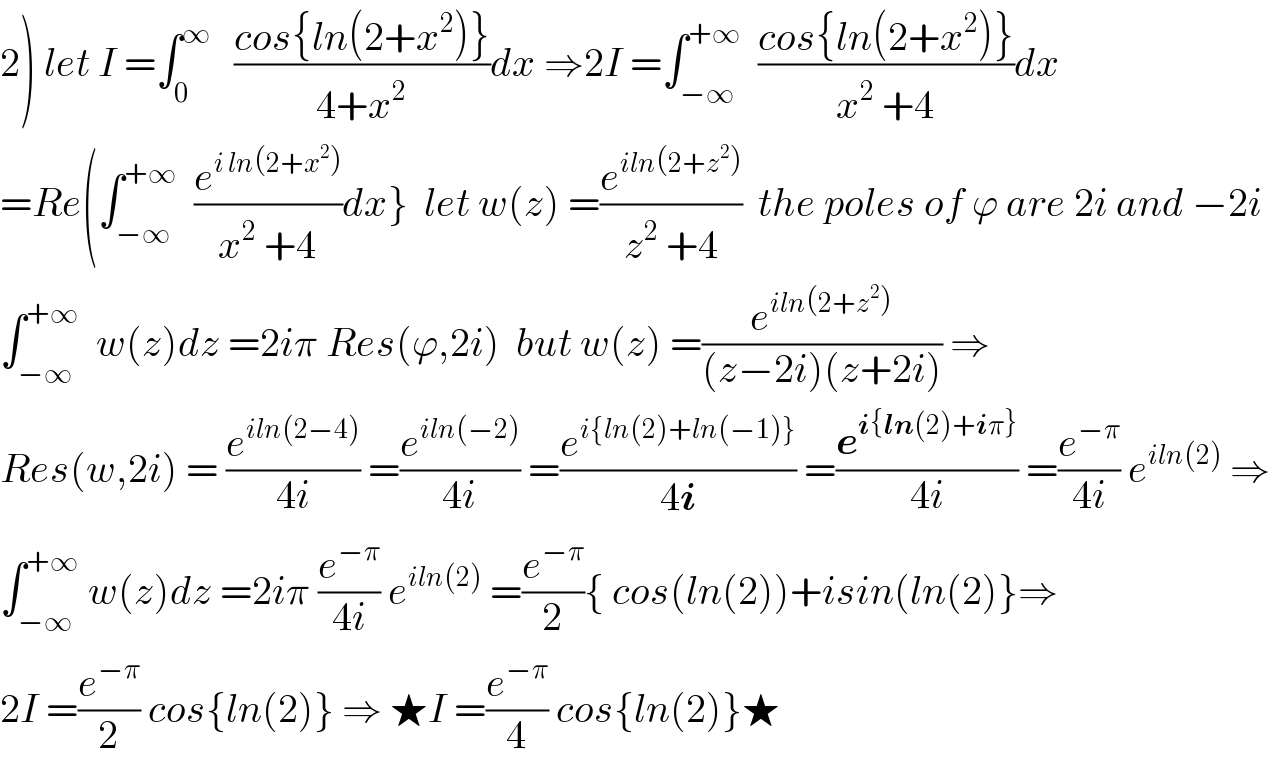
Answered by einsteindrmaths@hotmail.fr last updated on 05/Apr/19
![a)f(a)=(1/2)∫_(−∞) ^∞ ((cosln (2+x^2 ))/(a^2 +x^2 ))dx letf(z)=((cos(ln(2+z^2 )))/(a^2 +z^2 )) withe z≠{−i(√2) .i(√2) } res(f(z).ia)=lim_(z→ia) ((cos(ln(z^2 +2)))/((z+ia)))=((cos(ln(2−a^2 )))/(2ia)) we get f(a)=(1/2)2iπ×((cos(ln(2−a^2 )))/(2ia))=((πcos(ln(2−a^2 )))/(2a)) for a≠i(√2) 2)f(2)=π((cos(ln(−2)))/4)=(π/4)[cos( ln2).cosh(π)+sin (ln2) sh(π) ]](Q57497.png)
Commented bymaxmathsup by imad last updated on 05/Apr/19
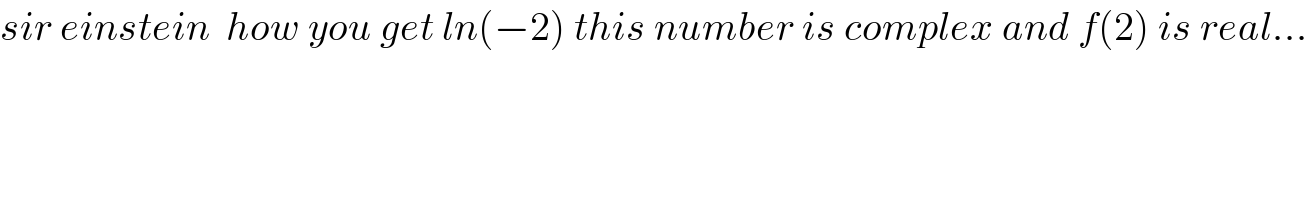
Commented byeinsteindrmaths@hotmail.fr last updated on 06/Apr/19