
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 57578 by rahul 19 last updated on 07/Apr/19
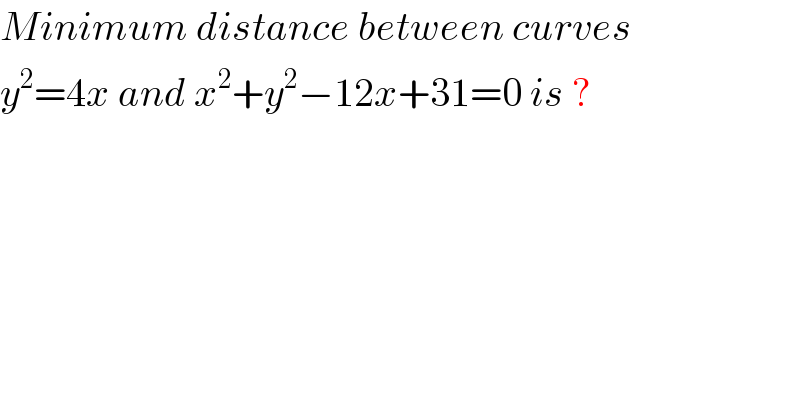
Answered by mr W last updated on 07/Apr/19

Commented by mr W last updated on 07/Apr/19

Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 08/Apr/19
thank you sir.
Answered by MJS last updated on 07/Apr/19
![the center of the circle is ((6),(0) ); r=(√5) ⇒ the point of the parabola with minimum distance from this center is the same as the point with the minimum distance of the circle. ∣ [(x),((2(√x))) ]− [(6),(0) ]∣^2 =x^2 −8x+36 (d/dx)[x^2 −8x+36]=2x−8=0 ⇒ x=4 distance=(√(x^2 −8x+36))−(√5)=(√(20))−(√5)=(√5)](Q57582.png)
Commented by rahul 19 last updated on 08/Apr/19
thank you sir.
