
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 58776 by George Mark Samuel last updated on 29/Apr/19
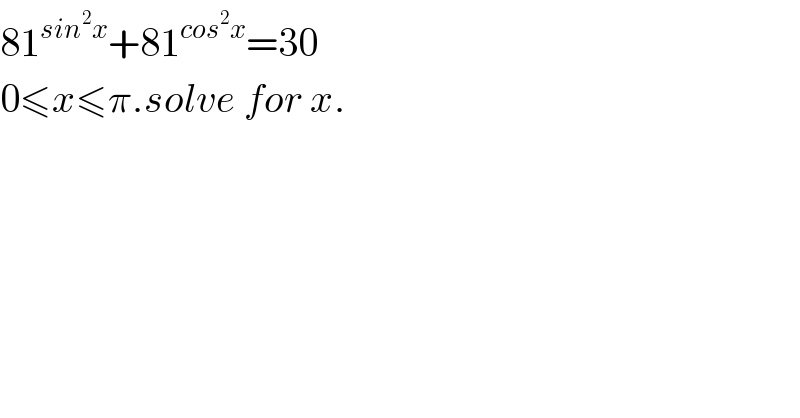
Answered by behi83417@gmail.com last updated on 29/Apr/19
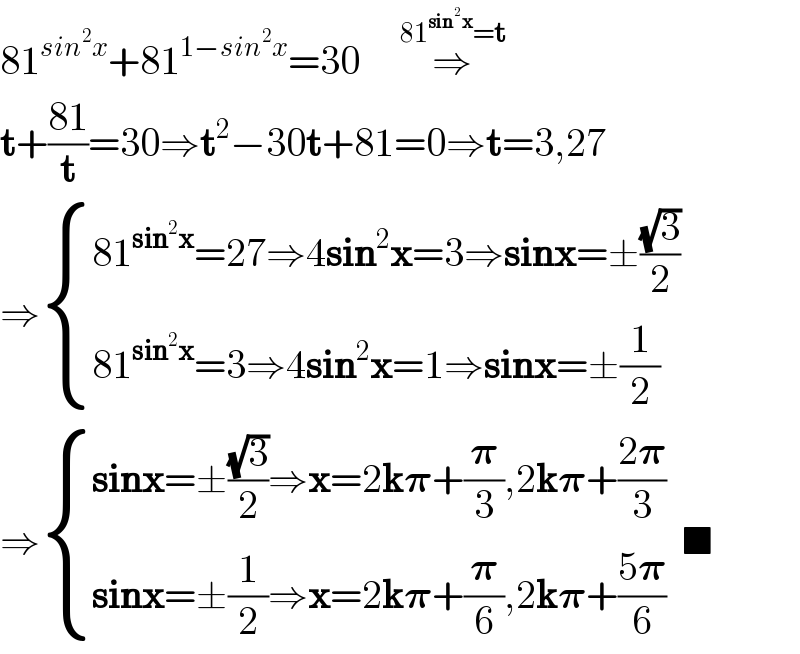
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 58776 by George Mark Samuel last updated on 29/Apr/19 | ||
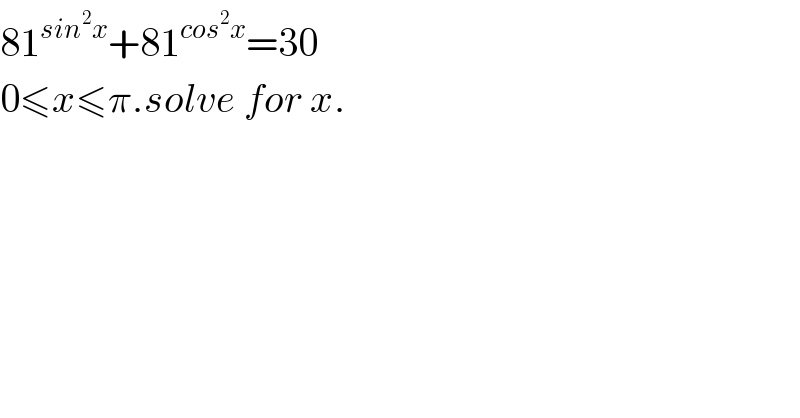 | ||
Answered by behi83417@gmail.com last updated on 29/Apr/19 | ||
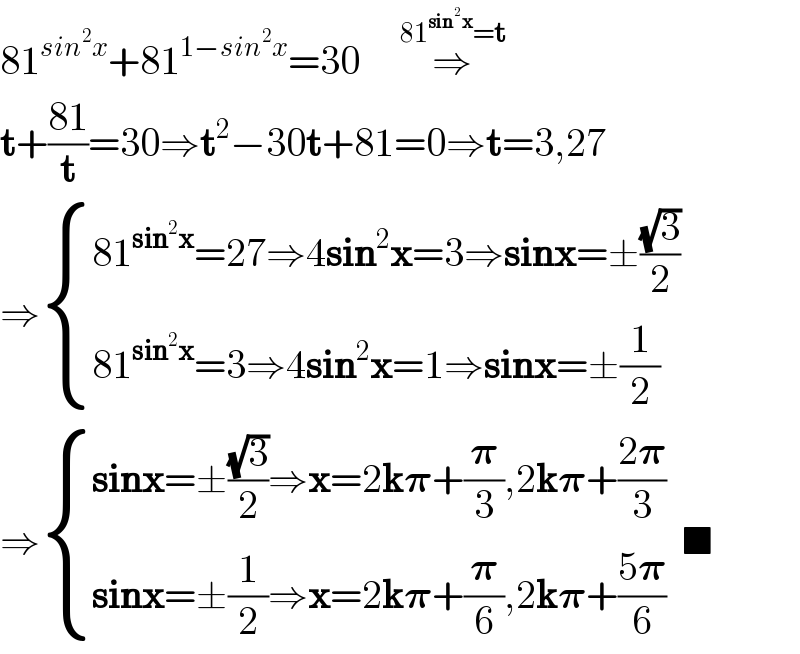 | ||
| ||