
Question Number 5921 by FilupSmith last updated on 05/Jun/16
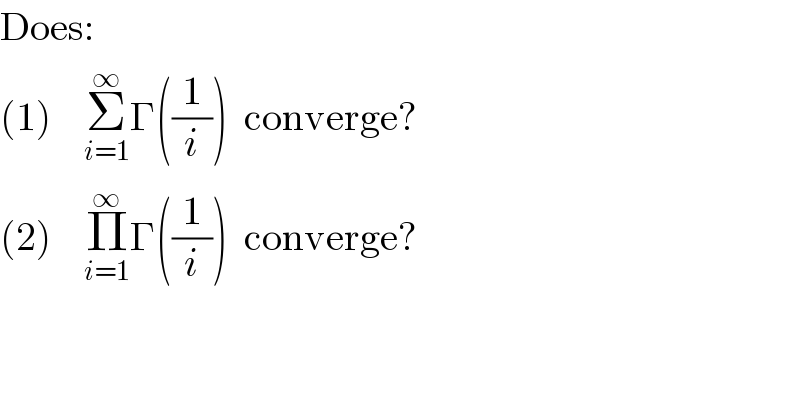
$$\mathrm{Does}:\: \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\:\:\:\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\Gamma\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{i}}\right)\:\:\mathrm{converge}? \\ $$$$\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:\:\:\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}\Gamma\left(\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{i}}\right)\:\:\mathrm{converge}? \\ $$
Commented by Yozzii last updated on 05/Jun/16
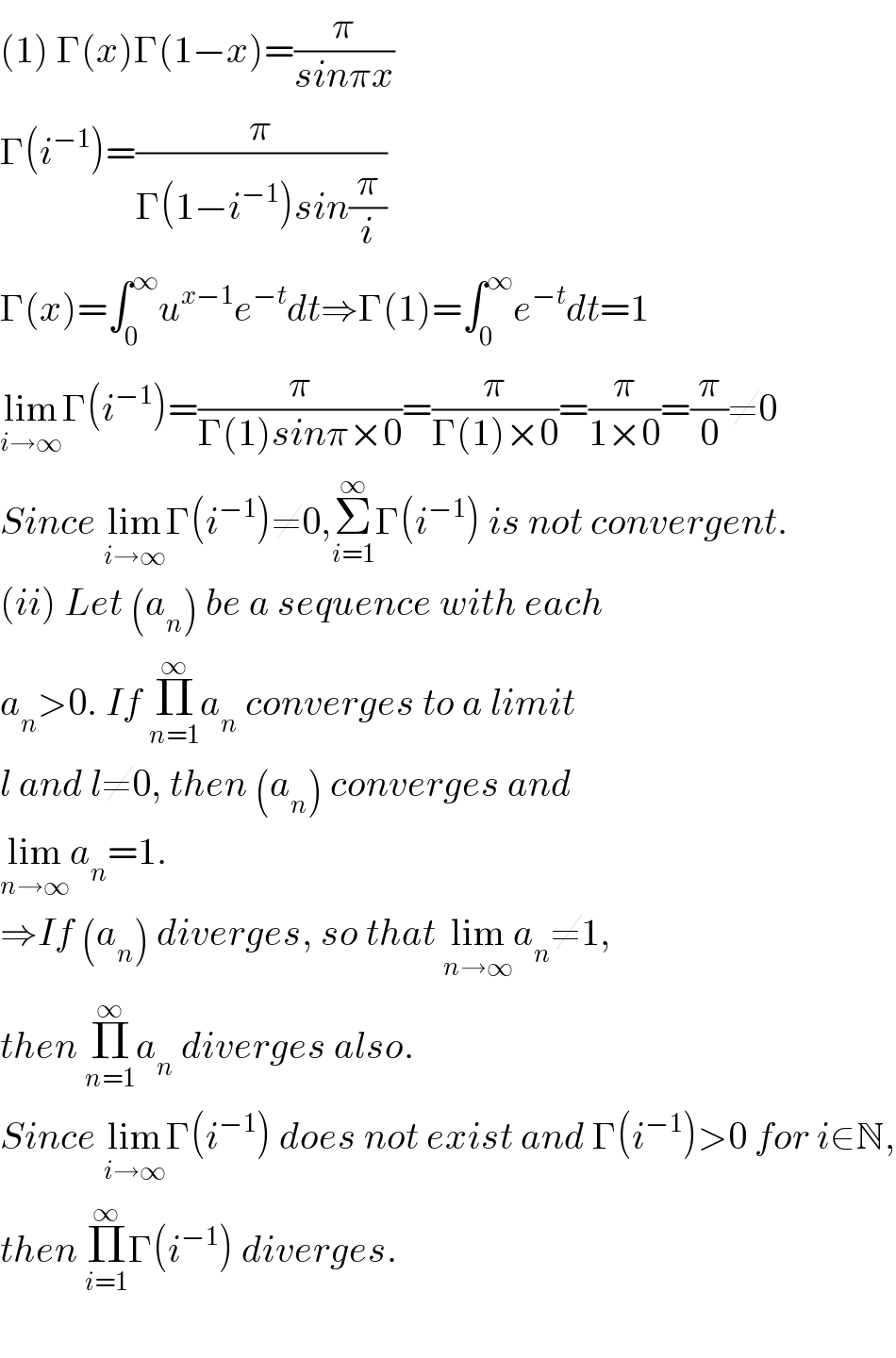
$$\left(\mathrm{1}\right)\:\Gamma\left({x}\right)\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}−{x}\right)=\frac{\pi}{{sin}\pi{x}} \\ $$$$\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)=\frac{\pi}{\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}−{i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right){sin}\frac{\pi}{{i}}} \\ $$$$\Gamma\left({x}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {u}^{{x}−\mathrm{1}} {e}^{−{t}} {dt}\Rightarrow\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}\right)=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} {e}^{−{t}} {dt}=\mathrm{1} \\ $$$$\underset{{i}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)=\frac{\pi}{\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}\right){sin}\pi×\mathrm{0}}=\frac{\pi}{\Gamma\left(\mathrm{1}\right)×\mathrm{0}}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{1}×\mathrm{0}}=\frac{\pi}{\mathrm{0}}\neq\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${Since}\:\underset{{i}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)\neq\mathrm{0},\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)\:{is}\:{not}\:{convergent}. \\ $$$$\left({ii}\right)\:{Let}\:\left({a}_{{n}} \right)\:{be}\:{a}\:{sequence}\:{with}\:{each} \\ $$$${a}_{{n}} >\mathrm{0}.\:{If}\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}{a}_{{n}} \:{converges}\:{to}\:{a}\:{limit} \\ $$$${l}\:{and}\:{l}\neq\mathrm{0},\:{then}\:\left({a}_{{n}} \right)\:{converges}\:{and}\: \\ $$$$\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{a}_{{n}} =\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{If}\:\left({a}_{{n}} \right)\:{diverges},\:{so}\:{that}\:\underset{{n}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{a}_{{n}} \neq\mathrm{1}, \\ $$$${then}\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}{a}_{{n}} \:{diverges}\:{also}. \\ $$$${Since}\:\underset{{i}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)\:{does}\:{not}\:{exist}\:{and}\:\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)>\mathrm{0}\:{for}\:{i}\in\mathbb{N}, \\ $$$${then}\:\underset{{i}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}\Gamma\left({i}^{−\mathrm{1}} \right)\:{diverges}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Commented by FilupSmith last updated on 05/Jun/16

$$\mathrm{Amazing}! \\ $$
