
Question Number 5948 by 123456 last updated on 06/Jun/16
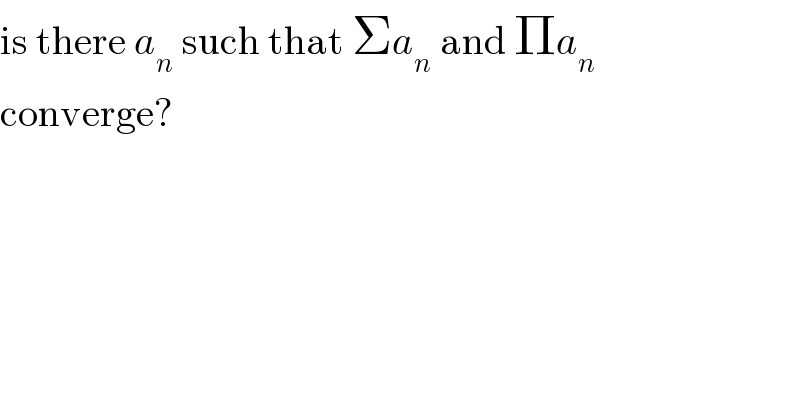
$$\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{there}\:{a}_{{n}} \:\mathrm{such}\:\mathrm{that}\:\Sigma{a}_{{n}} \:\mathrm{and}\:\Pi{a}_{{n}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{converge}? \\ $$
Answered by Yozzii last updated on 06/Jun/16
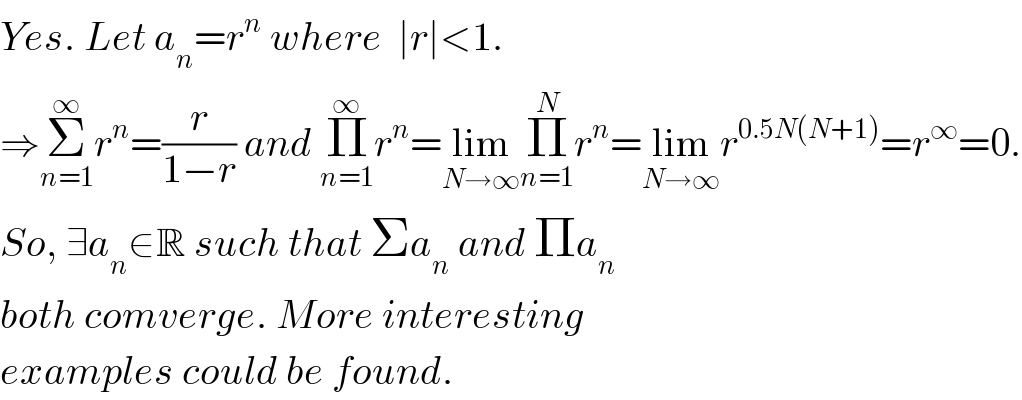
$${Yes}.\:{Let}\:{a}_{{n}} ={r}^{{n}} \:{where}\:\:\mid{r}\mid<\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}{r}^{{n}} =\frac{{r}}{\mathrm{1}−{r}}\:{and}\:\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\prod}}{r}^{{n}} =\underset{{N}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}\underset{{n}=\mathrm{1}} {\overset{{N}} {\prod}}{r}^{{n}} =\underset{{N}\rightarrow\infty} {\mathrm{lim}}{r}^{\mathrm{0}.\mathrm{5}{N}\left({N}+\mathrm{1}\right)} ={r}^{\infty} =\mathrm{0}. \\ $$$${So},\:\exists{a}_{{n}} \in\mathbb{R}\:{such}\:{that}\:\Sigma{a}_{{n}} \:{and}\:\Pi{a}_{{n}} \\ $$$${both}\:{comverge}.\:{More}\:{interesting} \\ $$$${examples}\:{could}\:{be}\:{found}. \\ $$
