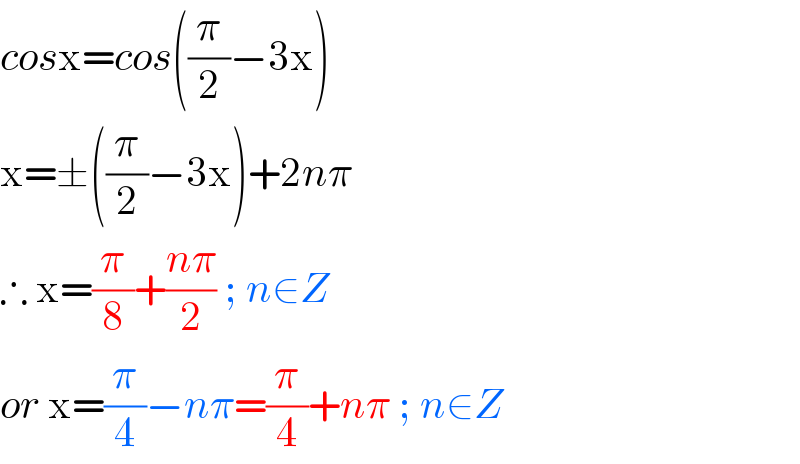Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 60536 by hovea cw last updated on 21/May/19

Answered by mr W last updated on 21/May/19
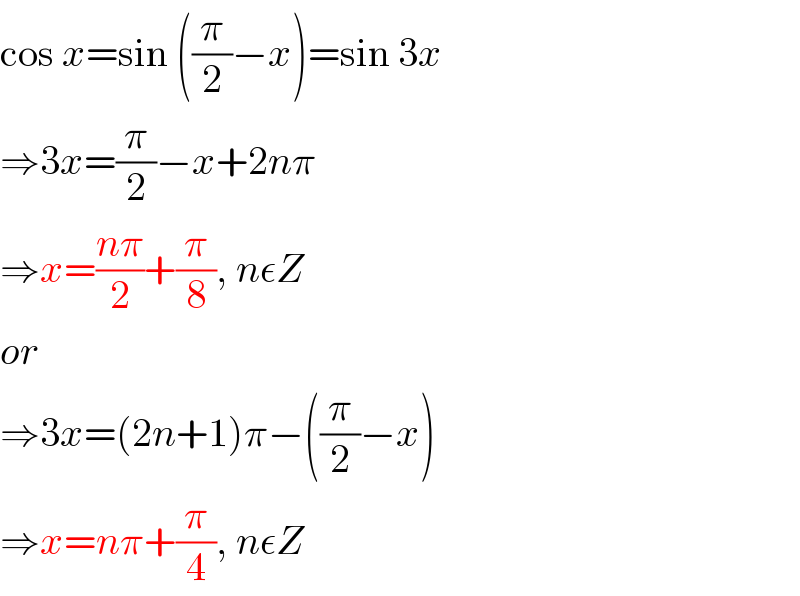
Commented by hovea cw last updated on 21/May/19

Answered by MJS last updated on 21/May/19
![cos x =sin 3x x=arctan t (1/(√(t^2 +1)))=((t(3−t^2 ))/(√((t^2 +1)^3 ))) t^2 +1=t(3−t^2 ) t^3 +t^2 −3t+1=0 (t−1)(t^2 +2t−1)=0 t_1 =−1−(√2); t_2 =−1+(√2); t_3 =1 x_1 =arctan (−1−(√2))=−((3π)/8)±πn x_2 =arctan (−1+(√2))=(π/8)±πn x_3 =arctan 1 =(π/4)±πn [n∈N]](Q60540.png)
Commented by hovea cw last updated on 21/May/19
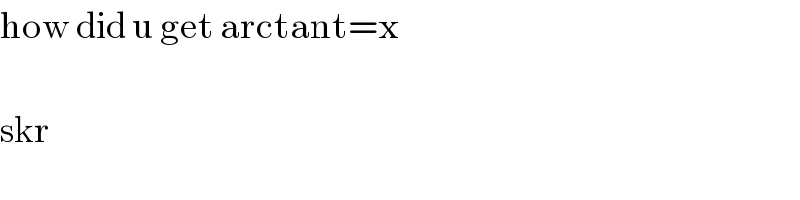
Commented by MJS last updated on 21/May/19
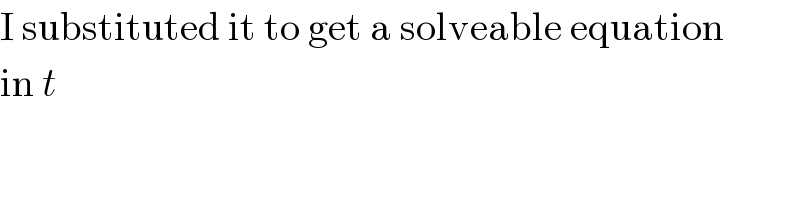
Commented by MJS last updated on 22/May/19
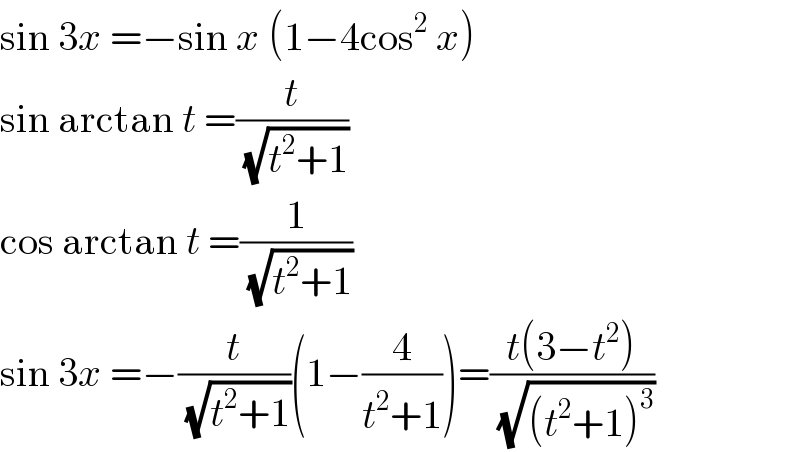
Answered by malwaan last updated on 22/May/19