
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 61137 by Tawa1 last updated on 29/May/19

Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/May/19
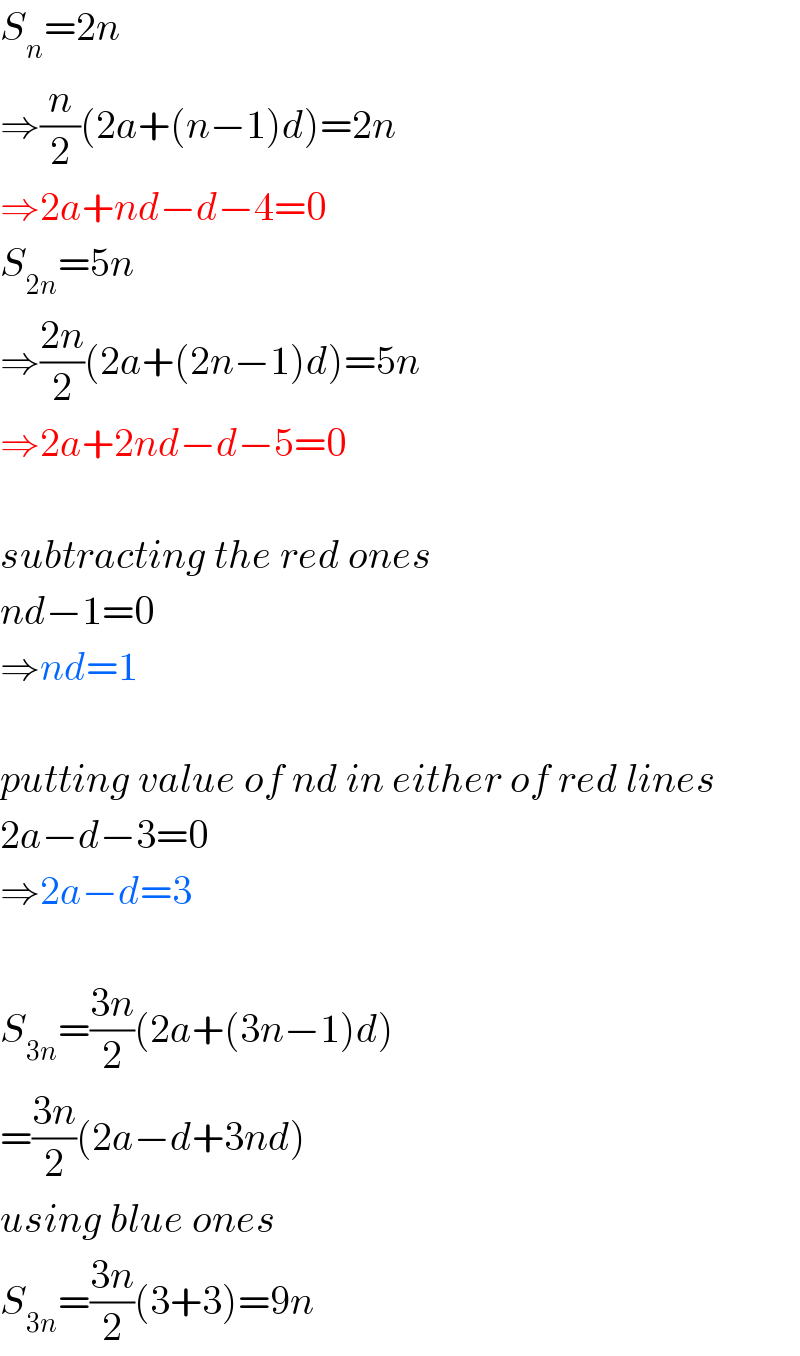
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/May/19
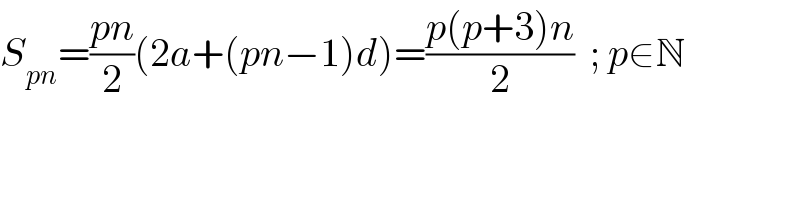
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 29/May/19

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 61137 by Tawa1 last updated on 29/May/19 | ||
 | ||
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/May/19 | ||
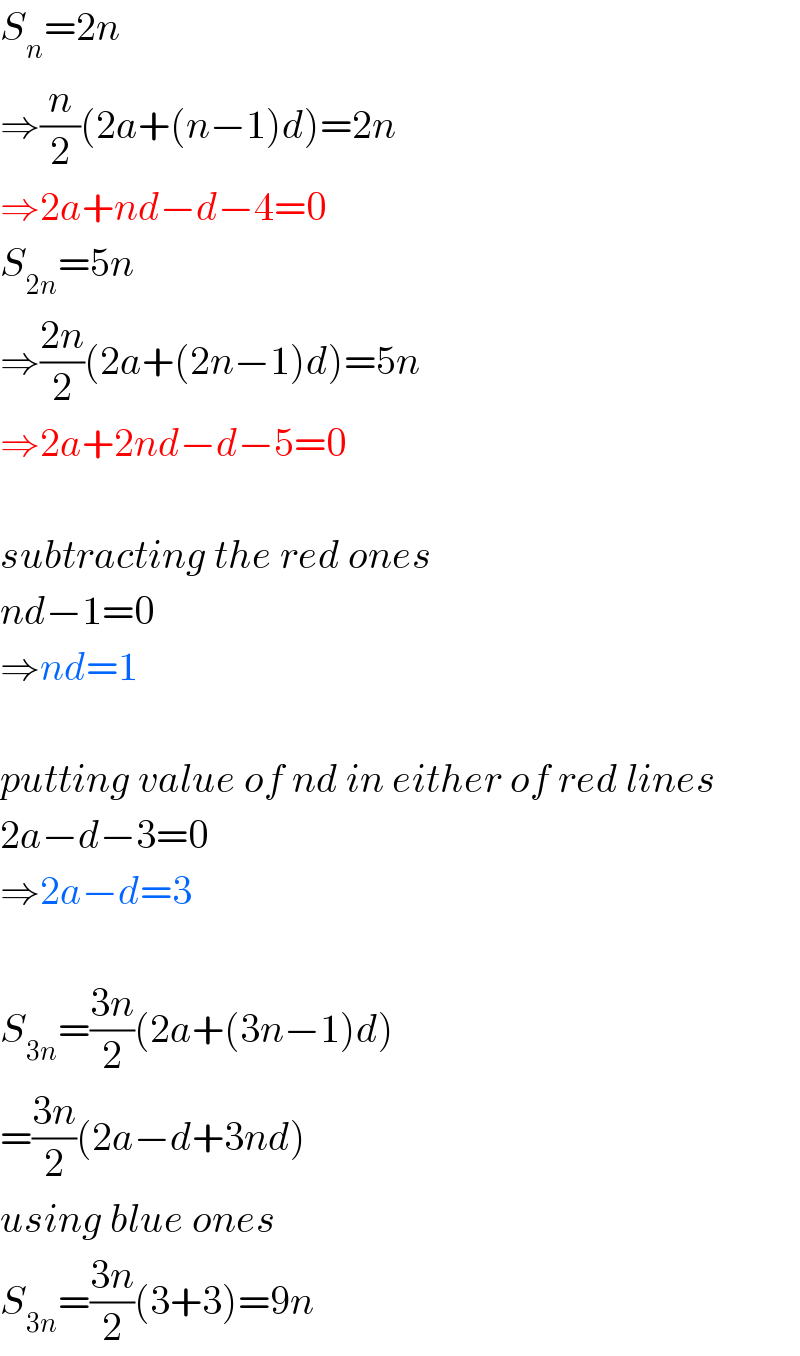 | ||
| ||
Commented by Kunal12588 last updated on 29/May/19 | ||
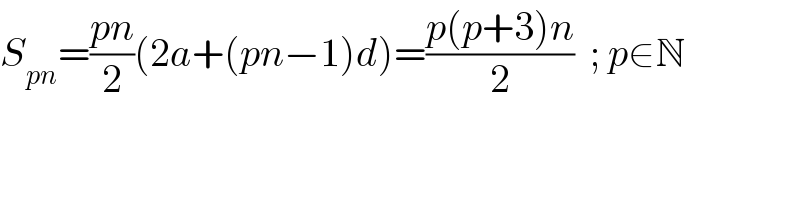 | ||
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 29/May/19 | ||
 | ||