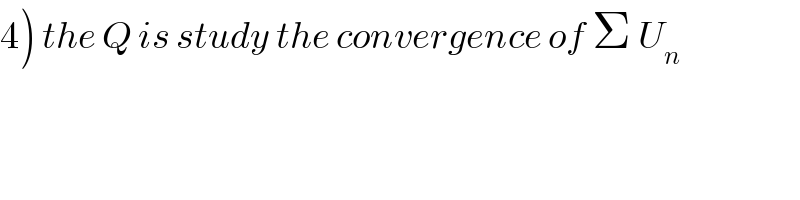Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 62128 by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 15/Jun/19
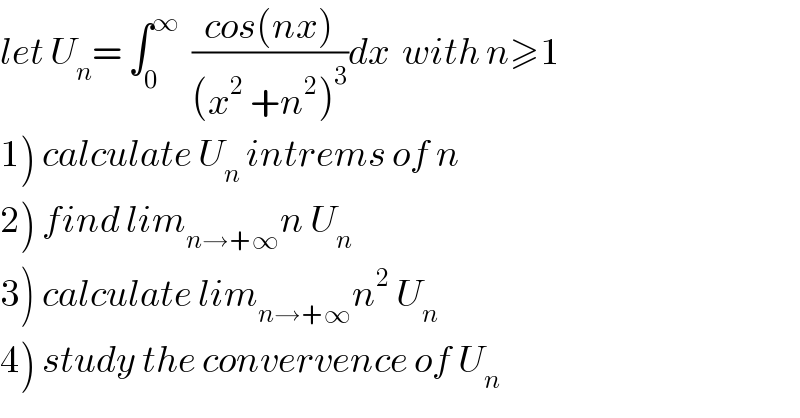
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 16/Jun/19

Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 16/Jun/19
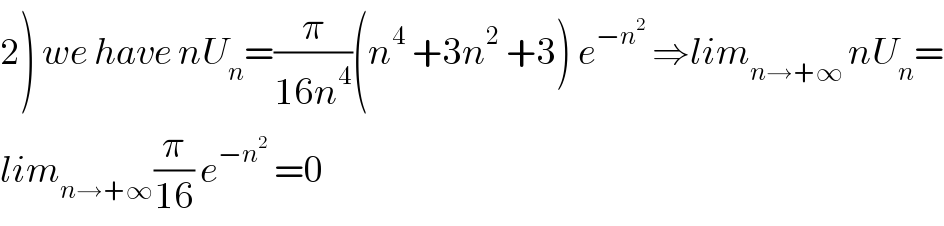
Commented by maxmathsup by imad last updated on 16/Jun/19