
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 106285 by bemath last updated on 04/Aug/20

Answered by bobhans last updated on 04/Aug/20
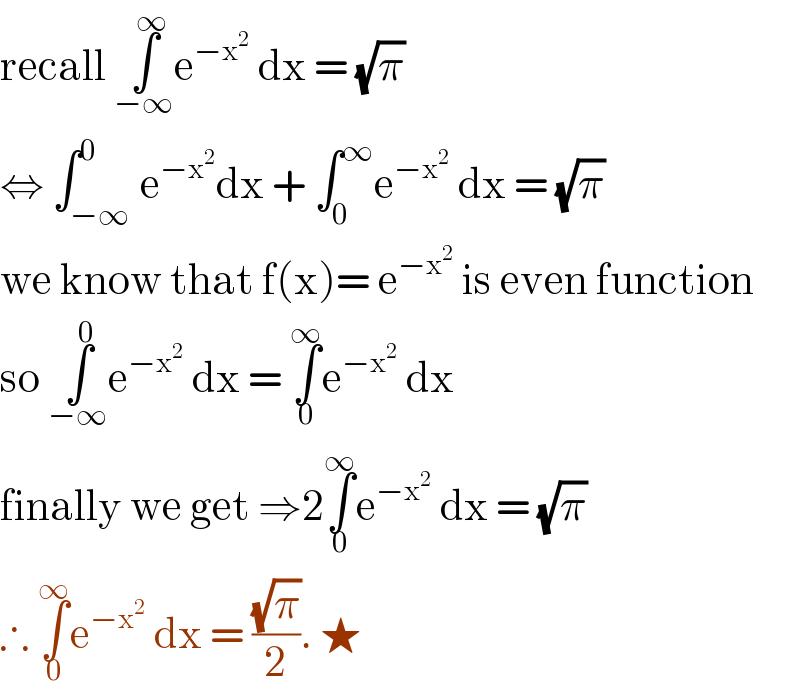
Answered by MAB last updated on 04/Aug/20
![I=∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x^2 ) dx I^2 =(∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x^2 ) dx)(∫_0 ^∞ e^(−y^2 ) dy) I^2 =∫_0 ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(x^2 +y^2 )) dxdy let x=rcos(θ) and y=rsin(θ) where r≥0 and 0≤θ≤π/2 dxdy=rdrdθ I^2 =∫_0 ^(π/2) ∫_0 ^∞ re^(−r^2 ) drdθ I^2 =∫_0 ^(π/2) (1/2)[e^(−r^2 ) ]_0 ^∞ dθ I^2 =(π/4) hence I=((√π)/2)](Q106296.png)
| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 106285 by bemath last updated on 04/Aug/20 | ||
 | ||
Answered by bobhans last updated on 04/Aug/20 | ||
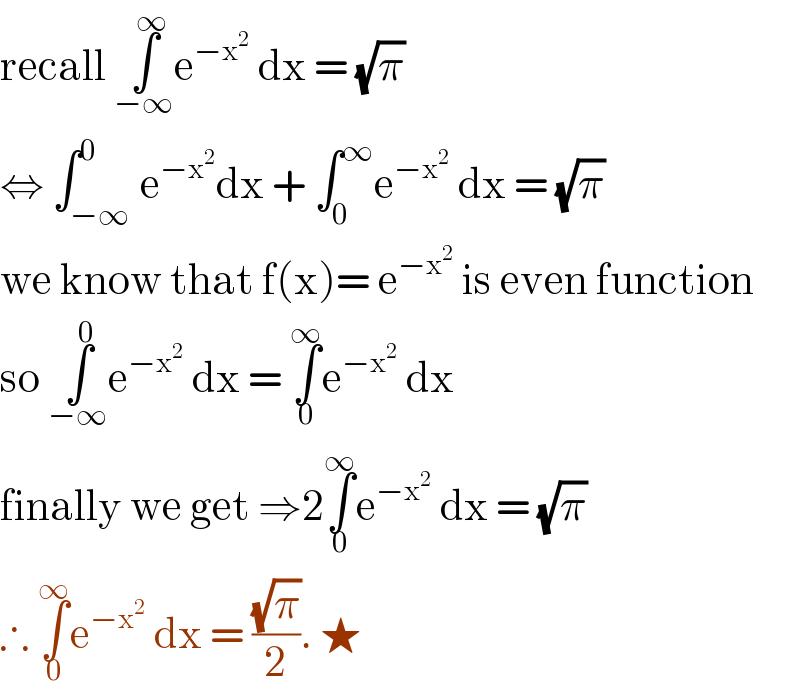 | ||
| ||
Answered by MAB last updated on 04/Aug/20 | ||
![I=∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x^2 ) dx I^2 =(∫_0 ^∞ e^(−x^2 ) dx)(∫_0 ^∞ e^(−y^2 ) dy) I^2 =∫_0 ^∞ ∫_0 ^∞ e^(−(x^2 +y^2 )) dxdy let x=rcos(θ) and y=rsin(θ) where r≥0 and 0≤θ≤π/2 dxdy=rdrdθ I^2 =∫_0 ^(π/2) ∫_0 ^∞ re^(−r^2 ) drdθ I^2 =∫_0 ^(π/2) (1/2)[e^(−r^2 ) ]_0 ^∞ dθ I^2 =(π/4) hence I=((√π)/2)](Q106296.png) | ||
| ||