
Question Number 63139 by Tawa1 last updated on 29/Jun/19

$$\underset{\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\mathrm{m}} {\sum}}\:\frac{\mathrm{log}\:\mathrm{n}}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{3}/\mathrm{2}} } \\ $$
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 30/Jun/19
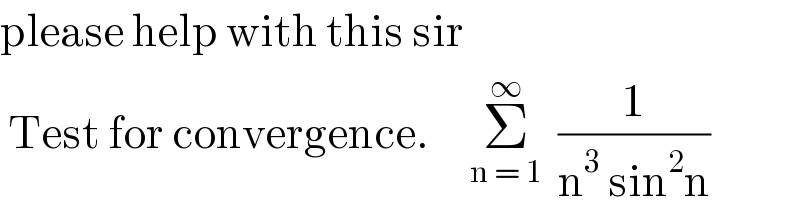
$$\mathrm{please}\:\mathrm{help}\:\mathrm{with}\:\mathrm{this}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{Test}\:\mathrm{for}\:\mathrm{convergence}.\:\:\:\:\:\underset{\mathrm{n}\:=\:\mathrm{1}} {\overset{\infty} {\sum}}\:\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{n}^{\mathrm{3}} \:\mathrm{sin}^{\mathrm{2}} \mathrm{n}} \\ $$
Commented by Tawa1 last updated on 30/Jun/19
$$\mathrm{God}\:\mathrm{bless}\:\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{sir} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 30/Jun/19
![if you need convergence let S_m =Σ_(n=1) ^m ((ln(n))/n^(3/2) ) we have lim_(n→+∞) S_m =Σ_(n=2) ^∞ ((ln(n))/n^(3/2) ) let ϕ(x) =((ln(x))/x^(3/2) ) with x>1 we have ϕ^′ (x) =(((x^(3/2) /x)−ln(x)(3/2)x^(1/2) )/x^3 ) =(((√x)−(3/2)(√x)ln(x))/x^3 ) =((√x)/x^3 ){1−(3/2)ln(x)} ⇒∃n_0 >0/ for x>n_0 ϕ is decreazing on]x_0 ,+∞[ so the serie and ∫_2 ^(+∞) ((ln(x))/x^(3/2) ) dx have the same nature but ∫_2 ^(+∞) ((ln(x))/x^(3/2) )dx =_(ln(x)=t) ∫_(ln(2)) ^(+∞) (t/e^((3/2)t) ) e^(t ) dt = ∫_(ln(2)) ^(+∞) t e^((1−(3/2))t) dt =∫_(ln(2)) ^(+∞) te^(−(t/2)) dt this integral converges because lim_(t→+∞) t^2 (t e^(−(t/2)) )=0 so Σ_(n=1) ^∞ ((ln(n))/n^(3/2) ) converges .](Q63209.png)
$${if}\:{you}\:{need}\:{convergence}\:\:{let}\:{S}_{{m}} =\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{{m}} \:\frac{{ln}\left({n}\right)}{{n}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} } \\ $$$${we}\:{have}\:{lim}_{{n}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{S}_{{m}} =\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{2}} ^{\infty} \:\:\frac{{ln}\left({n}\right)}{{n}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\:\:\:{let}\:\varphi\left({x}\right)\:=\frac{{ln}\left({x}\right)}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\:\:{with}\:{x}>\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${we}\:{have}\:\varphi^{'} \left({x}\right)\:=\frac{\frac{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}}−{ln}\left({x}\right)\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}} }{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:=\frac{\sqrt{{x}}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\sqrt{{x}}{ln}\left({x}\right)}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\:=\frac{\sqrt{{x}}}{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }\left\{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({x}\right)\right\} \\ $$$$\left.\Rightarrow\exists{n}_{\mathrm{0}} \:\:>\mathrm{0}/\:{for}\:{x}>{n}_{\mathrm{0}} \:\:\:\varphi\:{is}\:{decreazing}\:{on}\right]{x}_{\mathrm{0}} \:,+\infty\left[\:{so}\:\:{the}\:{serie}\:{and}\:\right. \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{+\infty} \:\frac{{ln}\left({x}\right)}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\:{dx}\:{have}\:{the}\:{same}\:{nature}\:{but} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{2}} ^{+\infty} \:\:\frac{{ln}\left({x}\right)}{{x}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }{dx}\:=_{{ln}\left({x}\right)={t}} \:\:\:\:\:\int_{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:\:\frac{{t}}{{e}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}{t}} }\:{e}^{{t}\:} {dt}\:=\:\int_{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} ^{+\infty} \:\:\:{t}\:\:{e}^{\left(\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){t}} {dt} \\ $$$$=\int_{{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)} ^{+\infty} \:\:{te}^{−\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}} \:{dt}\:\:\:\:\:{this}\:{integral}\:{converges}\:{because}\:{lim}_{{t}\rightarrow+\infty} \:{t}^{\mathrm{2}} \left({t}\:{e}^{−\frac{{t}}{\mathrm{2}}} \right)=\mathrm{0}\:{so} \\ $$$$\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{1}} ^{\infty} \:\frac{{ln}\left({n}\right)}{{n}^{\frac{\mathrm{3}}{\mathrm{2}}} }\:\:{converges}\:. \\ $$
