
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 63703 by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 07/Jul/19
![sin^3 x+cos^3 x=1−(1/2)sin2x :x∈[0,2π]. find x](Q63703.png)
Commented by Prithwish sen last updated on 08/Jul/19
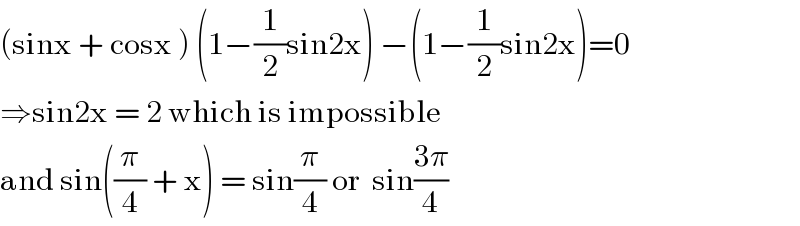
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 08/Jul/19
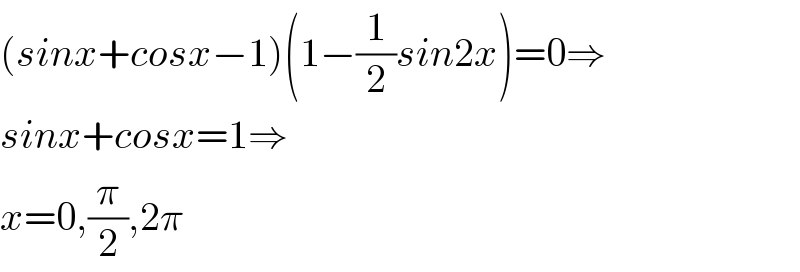
Answered by MJS last updated on 07/Jul/19
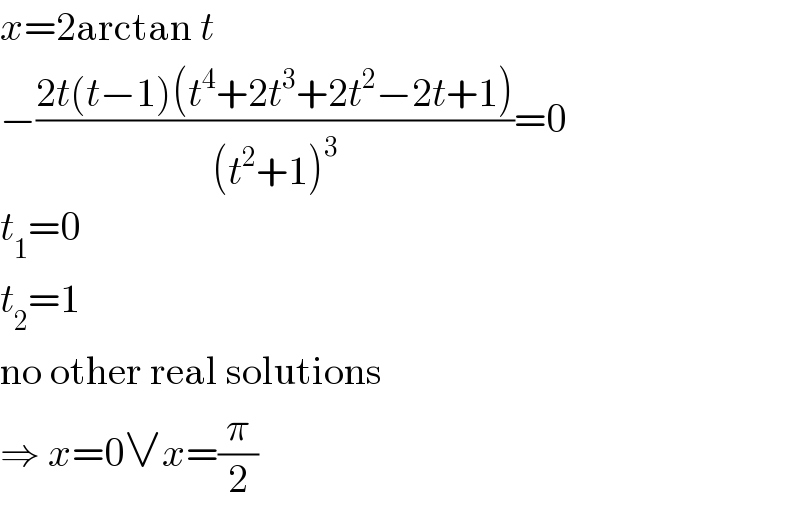
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 08/Jul/19
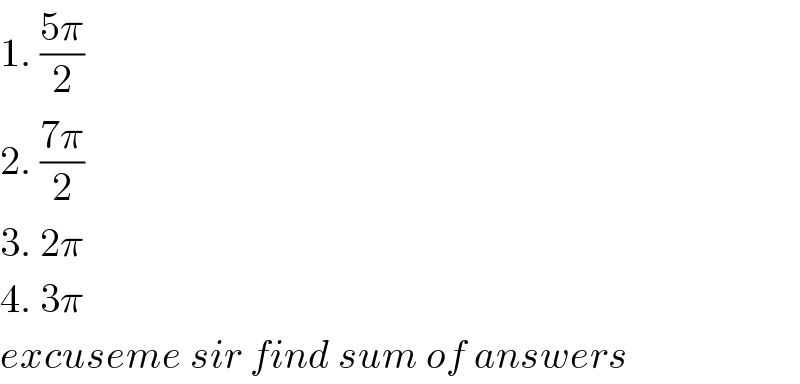
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 08/Jul/19
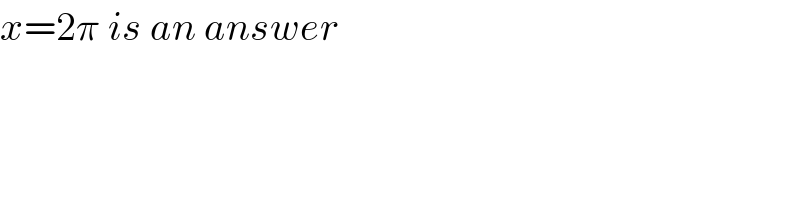
Commented by MJS last updated on 08/Jul/19
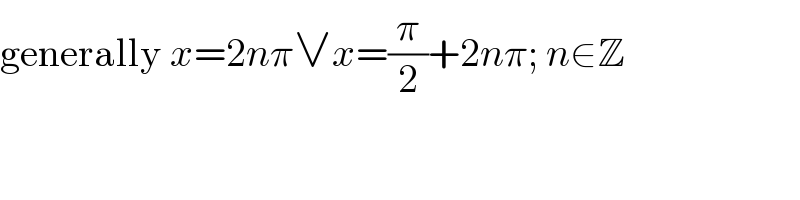
Commented by MJS last updated on 08/Jul/19
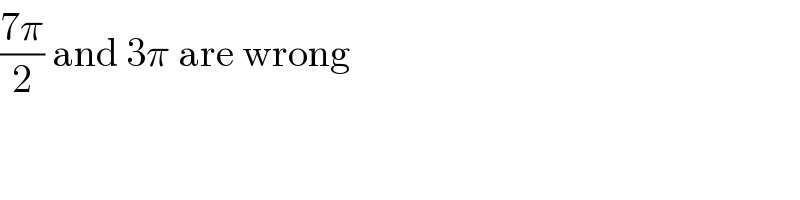
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 08/Jul/19
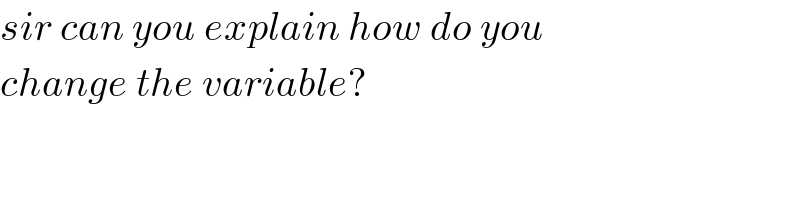
Commented by MJS last updated on 08/Jul/19

Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 08/Jul/19

