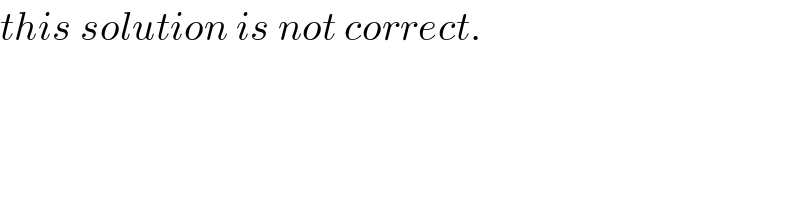Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 66589 by Tanmay chaudhury last updated on 17/Aug/19
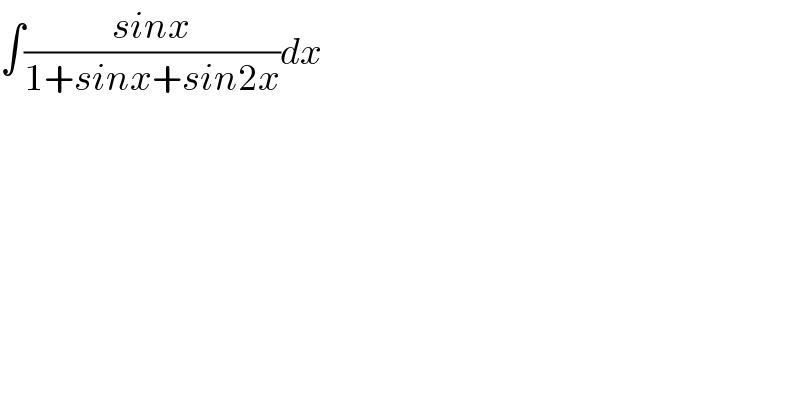
Commented by MJS last updated on 17/Aug/19
![Weierstrass [t=tan (x/2) → dx=((2dt)/(t^2 +1))] leads to 4∫(t/((t+1)(t^3 −3t^2 +5t+1)))dt t^3 −3t^2 +5t+1= =(t−α−β−1)(t^2 +(α+β−2)t+(α^2 +β^2 −αβ−α−β+1)) α=((−2−(2/9)(√(87))))^(1/3) β=((−2+(2/9)(√(87))))^(1/3) α+β+1=A α+β−2=B α^2 +β^2 −αβ−α−β+1=C 4∫(t/((t+1)(t−A)(t^2 +Bt+C)))dt= =−(4/((A+1)(B−C−1)))∫(dt/(t+1))+ +((4A)/((A+1)(A^2 +AB+C)))∫(dt/(t−A))+ +(4/((A^2 +AB+C)(B−C−1)))∫(((A+C)t+(A+B−1)C)/(t^2 +Bt+C))dt now solve these... I found no easier path](Q66603.png)
Commented by MJS last updated on 17/Aug/19

Commented by Tanmay chaudhury last updated on 17/Aug/19

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 18/Aug/19
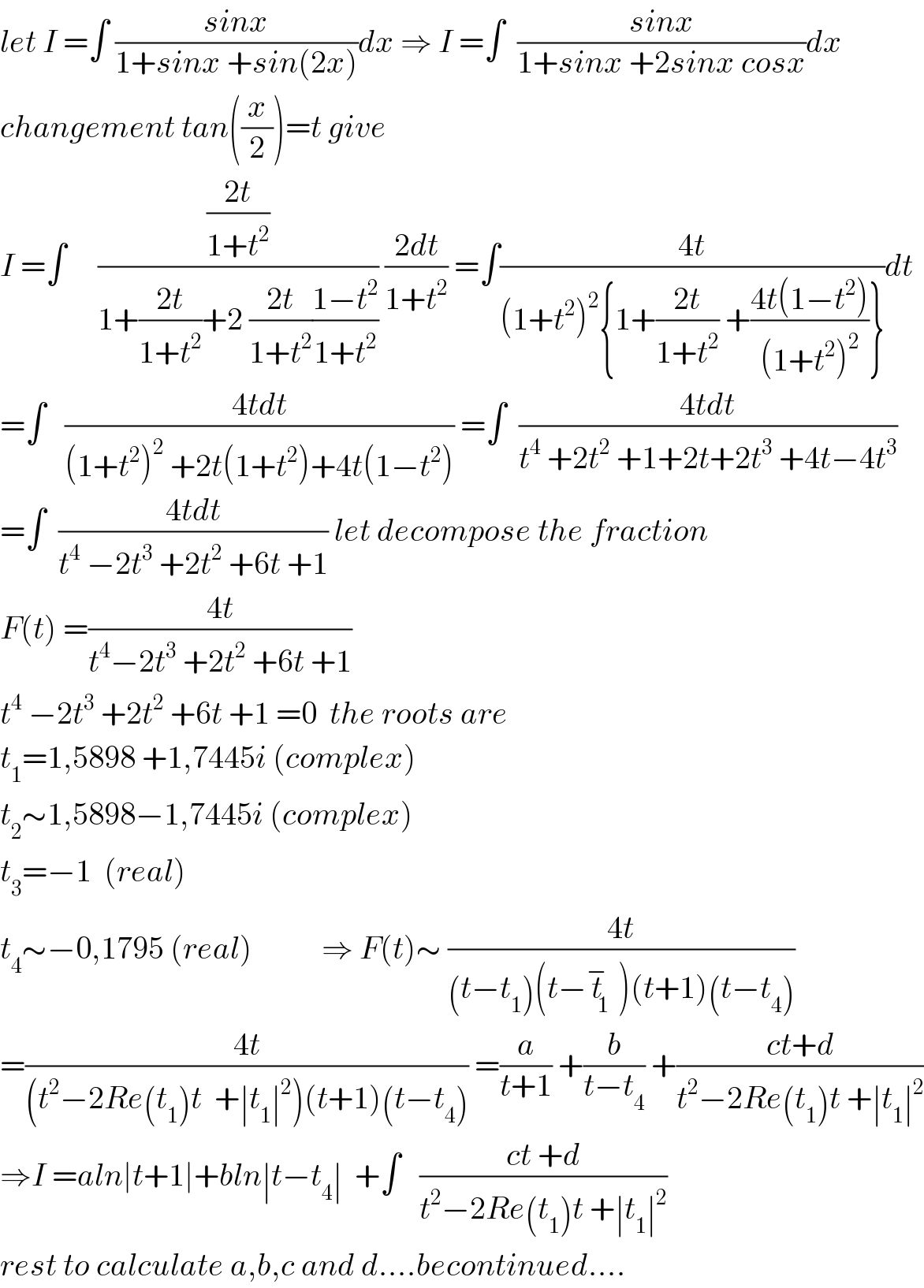
Commented by ~ À ® @ 237 ~ last updated on 18/Aug/19

Answered by Rio Michael last updated on 17/Aug/19
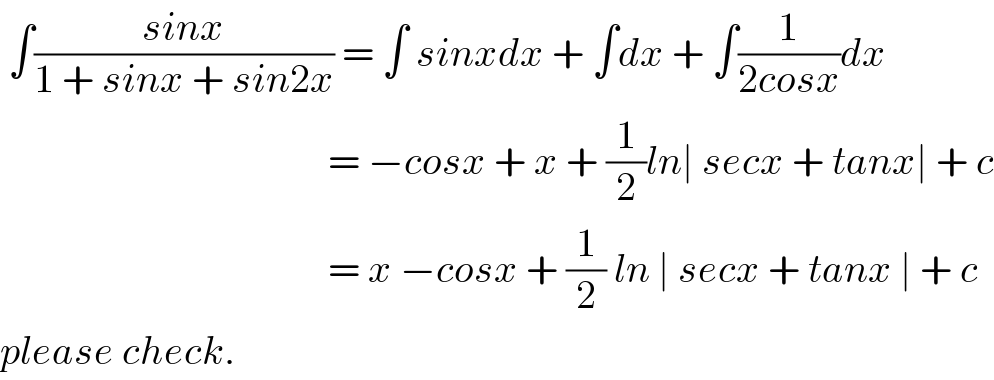
Commented by mr W last updated on 17/Aug/19

Commented by MJS last updated on 17/Aug/19

Commented by Cmr 237 last updated on 17/Aug/19

Answered by Cmr 237 last updated on 17/Aug/19

Commented by MJS last updated on 17/Aug/19

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 18/Aug/19