Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 66620 by Mohamed Amine Bouguezzoul last updated on 18/Aug/19
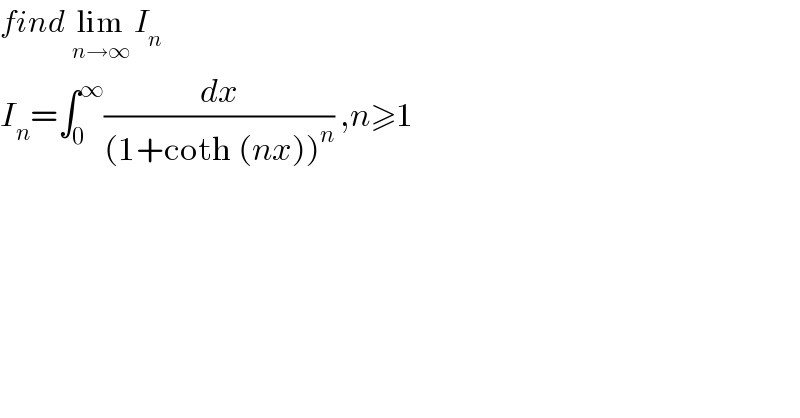
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 19/Aug/19

Commented by Mohamed Amine Bouguezzoul last updated on 20/Aug/19

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Aug/19