
Question Number 67398 by mhmd last updated on 26/Aug/19
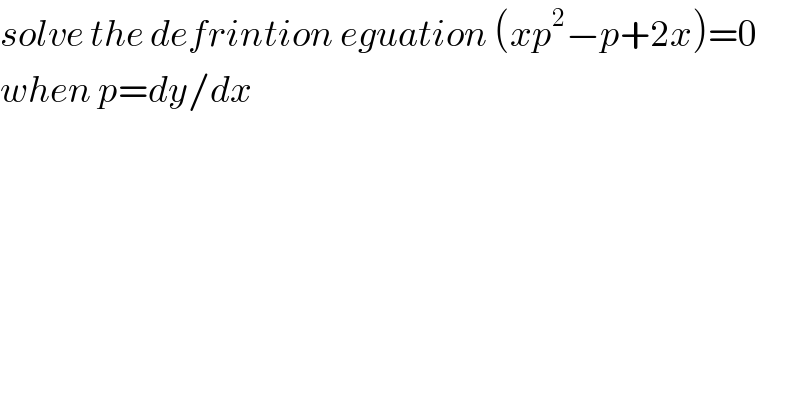
$${solve}\:{the}\:{defrintion}\:{eguation}\:\left({xp}^{\mathrm{2}} −{p}+\mathrm{2}{x}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${when}\:{p}={dy}/{dx} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 26/Aug/19
![xy^(′′) −y^′ =2x we use the changement y^′ =z (e) ⇒xz^′ −z =2x (he) →xz^′ −z =0 ⇒xz^′ =z ⇒(z^′ /z) =(1/x) ⇒ ln∣z∣ =ln∣x∣ +c ⇒z =K∣x∣ let determine the solution on ]0,+∞[ ⇒z =Kx let use mvc method z^′ =K^′ x +K (e) ⇒K^′ x^2 +Kx −Kx =2x ⇒K^′ =(2/x) ⇒K(x) =2lnx +c ⇒ z(x) =(2lnx +c)x =2xlnx +cx y^′ =z ⇒y^′ =2xln(x)+cx ⇒ y =∫ (2xlnx +cx)dx +λ =2 ∫ xlnxdx +((cx^2 )/2) +λ but ∫ xln(x)dx =_(by parts) (x^2 /2)ln(x)−∫ (x^2 /2)(dx/x) =(x^2 /2)lnx −(1/2)∫ xdx =(x^2 /2)lnx−(x^2 /4) ⇒y(x) =x^2 ln(x)−(x^2 /2) +((cx^2 )/2) +λ y(x) =x^2 ln(x)+((c/2)−(1/2))x^2 +λ .](Q67402.png)
$${xy}^{''} −{y}^{'} \:=\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:{we}\:{use}\:{the}\:{changement}\:{y}^{'} \:={z} \\ $$$$\left({e}\right)\:\Rightarrow{xz}^{'} −{z}\:=\mathrm{2}{x}\:\:\:\:\left({he}\right)\:\rightarrow{xz}^{'} −{z}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{xz}^{'} \:={z}\:\Rightarrow\frac{{z}^{'} }{{z}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left.{ln}\mid{z}\mid\:={ln}\mid{x}\mid\:+{c}\:\Rightarrow{z}\:={K}\mid{x}\mid\:\:{let}\:{determine}\:{the}\:{solution}\:{on}\:\right]\mathrm{0},+\infty\left[\right. \\ $$$$\Rightarrow{z}\:={Kx}\:\:\:\:{let}\:{use}\:{mvc}\:{method}\:\:\:{z}^{'} \:={K}^{'} {x}\:+{K} \\ $$$$\left({e}\right)\:\Rightarrow{K}^{'} {x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{Kx}\:−{Kx}\:=\mathrm{2}{x}\:\Rightarrow{K}^{'} \:=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}}\:\Rightarrow{K}\left({x}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}{lnx}\:+{c}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${z}\left({x}\right)\:=\left(\mathrm{2}{lnx}\:+{c}\right){x}\:=\mathrm{2}{xlnx}\:+{cx} \\ $$$${y}^{'} \:={z}\:\Rightarrow{y}^{'} \:=\mathrm{2}{xln}\left({x}\right)+{cx}\:\Rightarrow\:{y}\:=\int\:\:\left(\mathrm{2}{xlnx}\:+{cx}\right){dx}\:+\lambda \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}\:\int\:{xlnxdx}\:+\frac{{cx}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\lambda\:\:{but}\:\: \\ $$$$\int\:{xln}\left({x}\right){dx}\:=_{{by}\:{parts}} \:\:\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{ln}\left({x}\right)−\int\:\:\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\frac{{dx}}{{x}}\:=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{lnx}\:−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\int\:{xdx} \\ $$$$=\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}{lnx}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{4}}\:\Rightarrow{y}\left({x}\right)\:={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {ln}\left({x}\right)−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{{cx}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\lambda \\ $$$${y}\left({x}\right)\:={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {ln}\left({x}\right)+\left(\frac{{c}}{\mathrm{2}}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{2}}\right){x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+\lambda\:. \\ $$
Commented by prof Abdo imad last updated on 27/Aug/19

$${if}\:\:{p}^{\mathrm{2}} \:{means}\:\left({y}^{'} \right)^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:\:{i}\:{have}\:{solved}\:{another} \\ $$$${equation}... \\ $$
