
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 67759 by ugwu Kingsley last updated on 31/Aug/19
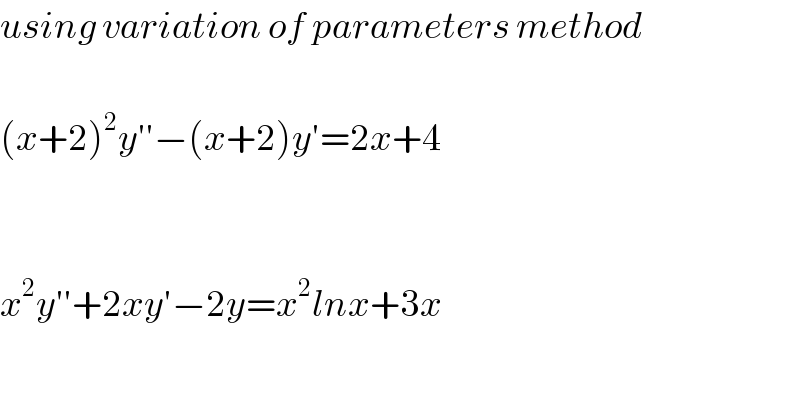
$${using}\:{variation}\:{of}\:{parameters}\:{method} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {y}''−\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right){y}'=\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} {y}''+\mathrm{2}{xy}'−\mathrm{2}{y}={x}^{\mathrm{2}} {lnx}+\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 31/Aug/19
![1) changement y^′ =z give (x+2)^2 z′−(x+2)z =2x+4 (he)→(x+2)^2 z^′ −(x+2)z =0 ⇒(x+2)^2 z^′ =(x+2)z ⇒ (z^′ /z) =((x+2)/((x+2)^2 )) ⇒(z^′ /z) =(1/(x+2)) ⇒ln∣z∣=ln∣x+2∣+c ⇒z =K∣x+2∣let find the solution on]−2,+∞[let use mvc method ⇒z^′ =K^′ (x+2)+K (e) ⇒(x+2)^2 K^′ (x+2) +K(x+2)^2 −(x+2)K(x+2) =2x+4 ⇒ (x+2)^3 K^′ =2(x+2) ⇒K^′ =(2/((x+2)^2 )) ⇒K(x)=−(2/(x+2)) +c ⇒ z(x) =(−(2/(x+2))+c)(x+2) =−2 +c y^′ =z ⇒y(x) =∫z(x) dx +λ =∫(−2+c)dx +λ =(−2+c)x +λ](Q67824.png)
$$\left.\mathrm{1}\right)\:{changement}\:{y}^{'} ={z}\:{give}\:\:\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {z}'−\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right){z}\:=\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4} \\ $$$$\left({he}\right)\rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {z}^{'} −\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right){z}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {z}^{'} =\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right){z}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{{z}^{'} }{{z}}\:=\frac{{x}+\mathrm{2}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow\frac{{z}^{'} }{{z}}\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:\Rightarrow{ln}\mid{z}\mid={ln}\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid+{c}\:\Rightarrow{z}\:={K}\mid{x}+\mathrm{2}\mid{let}\:{find} \\ $$$$\left.{the}\:{solution}\:{on}\right]−\mathrm{2},+\infty\left[{let}\:{use}\:\:\:{mvc}\:{method}\:\Rightarrow{z}^{'} ={K}^{'} \left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)+{K}\right. \\ $$$$\left({e}\right)\:\Rightarrow\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} {K}^{'} \left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:+{K}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} −\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right){K}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:=\mathrm{2}{x}+\mathrm{4}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{3}} \:{K}^{'} \:=\mathrm{2}\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow{K}^{'} \:=\frac{\mathrm{2}}{\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }\:\Rightarrow{K}\left({x}\right)=−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}\:+{c}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${z}\left({x}\right)\:=\left(−\frac{\mathrm{2}}{{x}+\mathrm{2}}+{c}\right)\left({x}+\mathrm{2}\right)\:=−\mathrm{2}\:+{c}\:\: \\ $$$${y}^{'} ={z}\:\Rightarrow{y}\left({x}\right)\:=\int{z}\left({x}\right)\:{dx}\:+\lambda\:\:=\int\left(−\mathrm{2}+{c}\right){dx}\:+\lambda \\ $$$$=\left(−\mathrm{2}+{c}\right){x}\:+\lambda\:\: \\ $$
