
Question Number 68879 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 16/Sep/19
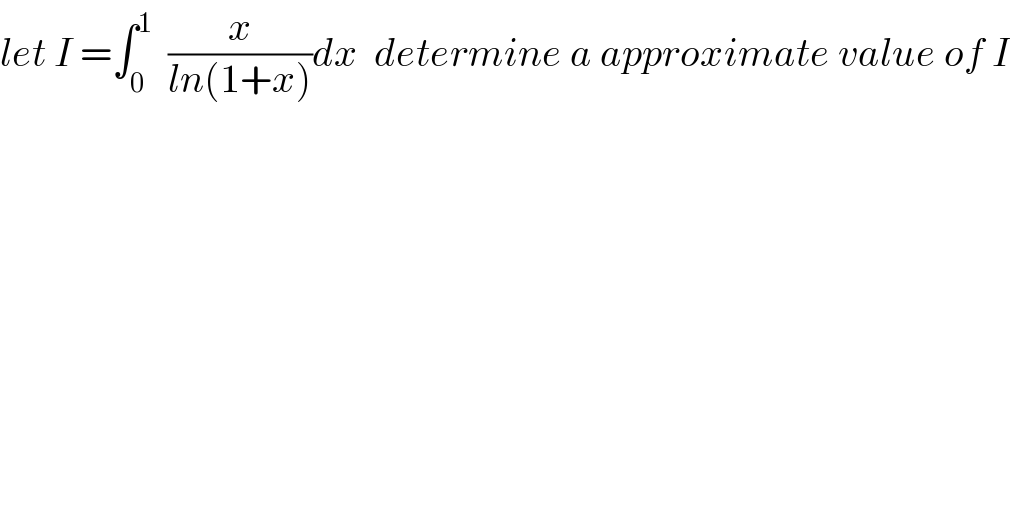
$${let}\:{I}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}{dx}\:\:{determine}\:{a}\:{approximate}\:{value}\:{of}\:{I} \\ $$
Commented by Abdo msup. last updated on 21/Sep/19

$${there}\:{a}\:{error}\:{of}\:{calculus}\:{in}\:{the}\:{answer}\:{i}\:{will}\:{hid} \\ $$$${this}\:{post}\:... \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 22/Sep/19
![we have ln^′ (1+x) =(1/(1+x)) =Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (−1)^n x^n ⇒ ln(1+x) =Σ_(n=0) ^∞ (((−1)^n x^(n+1) )/(n+1)) +c (c=0) ⇒ ln(1+x) =x−(x^2 /2) +(x^3 /3) −... ⇒x−(x^2 /2) ≤ln(1+x) ≤x ⇒ (1/x) ≤(1/(ln(1+x))) ≤(1/(x−(x^2 /2))) ⇒ 1 ≤ (x/(ln(1+x))) ≤(1/(1−(x/2))) ⇒ 1≤ ∫_0 ^1 (x/(ln(1+x)))dx ≤∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1−(x/2))) we have ∫_0 ^1 (dx/(1−(x/2))) =∫_0 ^1 ((2dx)/(2−x)) =−2 ∫_0 ^1 (dx/(x−2)) =−2[ln∣x−2∣]_0 ^1 =−2(−ln2) =2ln(2) ⇒ 1 ≤I ≤2ln(2) so v_0 =((1+2ln(2))/2) is a approximate value of I .](Q69380.png)
$${we}\:{have}\:{ln}^{'} \left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}+{x}}\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \:\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {x}^{{n}} \:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:=\sum_{{n}=\mathrm{0}} ^{\infty} \frac{\left(−\mathrm{1}\right)^{{n}} {x}^{{n}+\mathrm{1}} }{{n}+\mathrm{1}}\:+{c}\:\:\left({c}=\mathrm{0}\right)\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:={x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:+\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{3}} }{\mathrm{3}}\:−...\:\Rightarrow{x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}\:\leqslant{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)\:\leqslant{x}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}}\:\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}\:\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{x}−\frac{{x}^{\mathrm{2}} }{\mathrm{2}}}\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{1}\:\leqslant\:\frac{{x}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}\:\leqslant\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$$\mathrm{1}\leqslant\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{x}}{{ln}\left(\mathrm{1}+{x}\right)}{dx}\:\leqslant\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}\:\:{we}\:{have} \\ $$$$\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{{dx}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{{x}}{\mathrm{2}}}\:=\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\:\frac{\mathrm{2}{dx}}{\mathrm{2}−{x}}\:=−\mathrm{2}\:\int_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} \:\frac{{dx}}{{x}−\mathrm{2}}\:=−\mathrm{2}\left[{ln}\mid{x}−\mathrm{2}\mid\right]_{\mathrm{0}} ^{\mathrm{1}} =−\mathrm{2}\left(−{ln}\mathrm{2}\right) \\ $$$$=\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\Rightarrow\:\mathrm{1}\:\leqslant{I}\:\leqslant\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)\:\:{so}\:{v}_{\mathrm{0}} =\frac{\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{ln}\left(\mathrm{2}\right)}{\mathrm{2}}\:\:{is}\:{a}\:{approximate} \\ $$$${value}\:{of}\:{I}\:. \\ $$
