
Question Number 69460 by mhmd last updated on 23/Sep/19

$${find}\:{the}\:{equation}\:{of}\:{the}\:{circle}\:{whose}\:{center}\:{is}\:{the}\:{origin}\:{and}\:{touches}\:{the}\:{line}\:\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{4}{y}−\mathrm{15}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 23/Sep/19
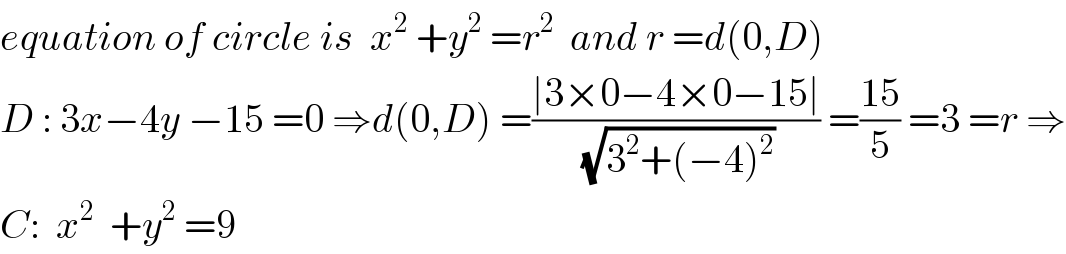
$${equation}\:{of}\:{circle}\:{is}\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:+{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:={r}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:{and}\:{r}\:={d}\left(\mathrm{0},{D}\right) \\ $$$${D}\::\:\mathrm{3}{x}−\mathrm{4}{y}\:−\mathrm{15}\:=\mathrm{0}\:\Rightarrow{d}\left(\mathrm{0},{D}\right)\:=\frac{\mid\mathrm{3}×\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{4}×\mathrm{0}−\mathrm{15}\mid}{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}^{\mathrm{2}} +\left(−\mathrm{4}\right)^{\mathrm{2}} }}\:=\frac{\mathrm{15}}{\mathrm{5}}\:=\mathrm{3}\:={r}\:\Rightarrow \\ $$$${C}:\:\:{x}^{\mathrm{2}} \:\:+{y}^{\mathrm{2}} \:=\mathrm{9} \\ $$
