
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Differential Equation Next in Differential Equation
Question Number 70720 by oyemi kemewari last updated on 07/Oct/19
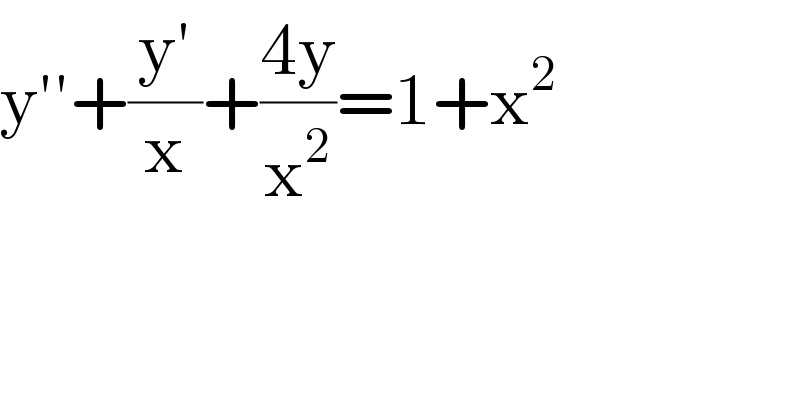
Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 07/Oct/19

Commented by Rasheed.Sindhi last updated on 07/Oct/19
Commented by oyemi kemewari last updated on 07/Oct/19
ok sir
Commented by mind is power last updated on 07/Oct/19
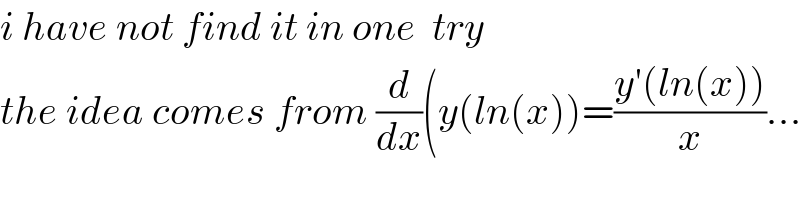
Answered by mind is power last updated on 07/Oct/19

Commented by oyemi kemewari last updated on 07/Oct/19
thank you sir
Commented by mind is power last updated on 07/Oct/19

Answered by Joel122 last updated on 08/Oct/19
![y′′ + ((1/x))y′ + ((4/x^2 ))y = 1 + x^2 x^2 y′′ + xy′ + 4y = x^2 + x^4 ... (i) • Homogeneous solution x^2 y′′ + xy′ + 4y = 0 → Euler−Cauchy eq. Let y(x) = x^m be the solution. Then, x^m [(m^2 − m) + m + 4] = 0 ⇒ m^2 + 4 = 0 ⇒ m_1 = 2i, m_2 = −2i ⇒ y_h (x) = C_1 x^(2i) + C_2 x^(−2i) = α cos (ln x^2 ) + β sin (ln x^2 ) • Particular solution Using method of undetermined parameter, we have y_p (x) = Ax^4 + Bx^3 + Cx^2 + Dx + E y_p ^′ (x) = 4Ax^3 + 3Bx^2 + 2Cx + D y_p ^(′′) (x) = 12Ax^2 + 6Bx + 2C Plugging these equations to (i) x^2 [12Ax^2 + 6Bx + 2C] + x[4Ax^3 + 3Bx^2 + 2Cx + D] + 4[Ax^4 + Bx^3 + Cx^2 + Dx + E] = x^2 + x^4 ⇒ 20Ax^4 + 13Bx^3 + 8Cx^2 + 5Dx + 4E = x^4 + x^2 By comparing the coefficients, we have A = (1/(20)), B = 0, C = (1/8), D = 0, E = 0 ⇒ y_p (x) = (x^4 /(20)) + (x^2 /8) ∴ y(x) = y_h (x) + y_p (x)](Q70745.png)
