
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 72905 by Tony Lin last updated on 04/Nov/19
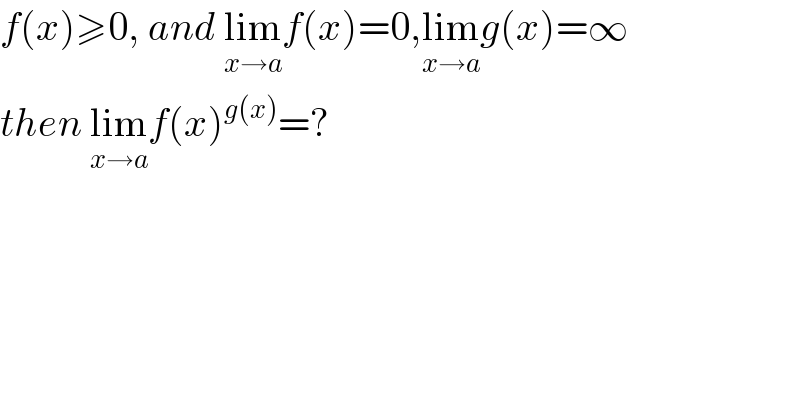
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 04/Nov/19
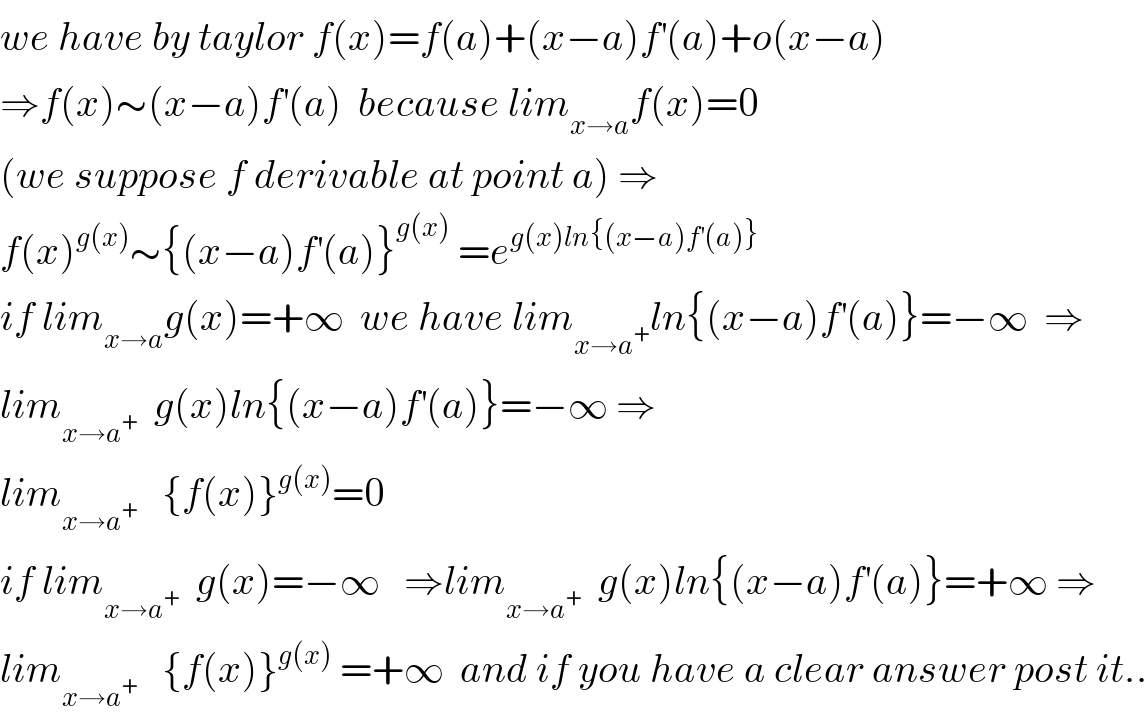
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 05/Nov/19

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 05/Nov/19
Answered by mind is power last updated on 04/Nov/19
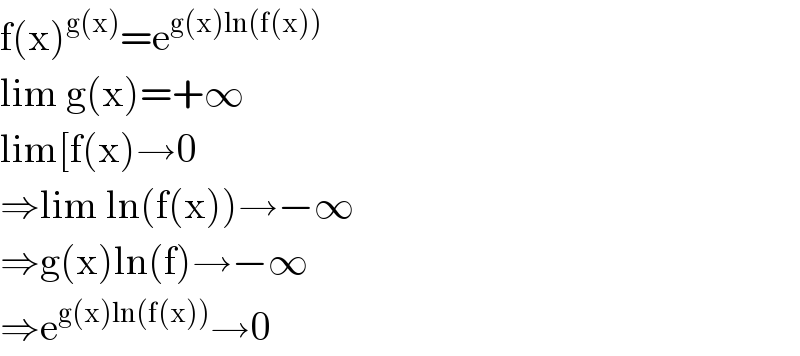
Commented by Tony Lin last updated on 05/Nov/19

Answered by Tony Lin last updated on 05/Nov/19

