
Question Number 7654 by Rohit last updated on 07/Sep/16

$${Q}.\mathrm{1}\:{which}\:{term}\:{of}\:{the}\:{sequence}\:\mathrm{2005}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{2000},\mathrm{1995},\mathrm{1990},\mathrm{1985},........................ \\ $$$${is}\:{the}\:{first}\:{negative}\:{term}. \\ $$$${plese}\:{give}\:{answer} \\ $$$${Q}.\mathrm{2}\:{for}\:{an}\:{A}.{P}.\:{show}\:{that}\:{t}_{{m}} +{t}_{\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}} \\ $$$$=\:\mathrm{2}{t}_{{m}+{n}} \\ $$$${give}\:{answer} \\ $$$${Q}.\mathrm{3}\:{find}\:{the}\:{maximum}\:{sum}\:{of}\:{the}\: \\ $$$${A}.{P}.\:\mathrm{40}+\mathrm{38}+\mathrm{36}+\mathrm{34}+\mathrm{32}+........ \\ $$$${give}\:{answer}\:{plese}\:{sir} \\ $$$$ \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 07/Sep/16
![Q.2 for an A.P. show that t_m +t_(2n+m) =2t_(m+n) −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− Let the first term and common differnce are a and d respectively. t_m =a+(m−1)d t_(2n+m) =a+(2n+m−1)d t_(m+n) =a+(m+n−1)d LHS: t_m +t_(2n+m) =( a+(m−1)d )+( a+(2n+m−1)d ) =2a+(m−1+2n+m−1)d =2a+(2m+2n−2)d =2[ a+(m+n−1)d ] =2 t_(m+n) =RHS Proved.](Q7658.png)
$${Q}.\mathrm{2}\:{for}\:{an}\:{A}.{P}.\:{show}\:{that}\: \\ $$$${t}_{{m}} +{t}_{\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}} =\mathrm{2}{t}_{{m}+{n}} \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${Let}\:{the}\:{first}\:{term}\:{and}\:{common}\:{differnce} \\ $$$${are}\:\:{a}\:\:{and}\:\:\:{d}\:\:\:\:{respectively}. \\ $$$${t}_{{m}} ={a}+\left({m}−\mathrm{1}\right){d} \\ $$$${t}_{\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}} ={a}+\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}−\mathrm{1}\right){d} \\ $$$${t}_{{m}+{n}} ={a}+\left({m}+{n}−\mathrm{1}\right){d} \\ $$$$ \\ $$$${LHS}:\:{t}_{{m}} +{t}_{\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\left(\:{a}+\left({m}−\mathrm{1}\right){d}\:\right)+\left(\:{a}+\left(\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}−\mathrm{1}\right){d}\:\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2}{a}+\left({m}−\mathrm{1}+\mathrm{2}{n}+{m}−\mathrm{1}\right){d} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2}{a}+\left(\mathrm{2}{m}+\mathrm{2}{n}−\mathrm{2}\right){d} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2}\left[\:{a}+\left({m}+{n}−\mathrm{1}\right){d}\:\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2}\:{t}_{{m}+{n}} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:={RHS} \\ $$$${Proved}. \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 08/Sep/16
![Q.3 Maximum sum of 40+38+36+34+32+........ −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− Maximum sum is 40+38+36+......+2 Because the next term 0 doesn′t affect the sum and after it are negative terms which decrease the sum. l=last term=40+(n−1)(−2)=2 [n is number of terms ] 40−2n+2=2 n=20 S_n =(n/2)(a+l) S_(20) =((20)/2)(40+2)=420 MAXimum Sum is 420](Q7669.png)
$${Q}.\mathrm{3}\:\:{Maximum}\:{sum}\:{of} \\ $$$$\:\mathrm{40}+\mathrm{38}+\mathrm{36}+\mathrm{34}+\mathrm{32}+........ \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${Maximum}\:{sum}\:{is} \\ $$$$\mathrm{40}+\mathrm{38}+\mathrm{36}+......+\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${Because}\:{the}\:{next}\:{term}\:\mathrm{0}\:{doesn}'{t}\:{affect}\:{the}\:{sum}\:{and}\:{after}\:{it} \\ $$$${are}\:{negative}\:{terms}\:{which}\:{decrease}\:{the}\:{sum}. \\ $$$${l}={last}\:{term}=\mathrm{40}+\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(−\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{2}\:\left[{n}\:{is}\:{number}\:{of}\:{terms}\:\right] \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{40}−\mathrm{2}{n}+\mathrm{2}=\mathrm{2} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{n}=\mathrm{20} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{S}_{{n}} =\frac{{n}}{\mathrm{2}}\left({a}+{l}\right) \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{S}_{\mathrm{20}} =\frac{\mathrm{20}}{\mathrm{2}}\left(\mathrm{40}+\mathrm{2}\right)=\mathrm{420} \\ $$$$\boldsymbol{\mathrm{MAX}}\mathrm{imum}\:\boldsymbol{\mathrm{Sum}}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{420} \\ $$
Commented by Rohit last updated on 08/Sep/16
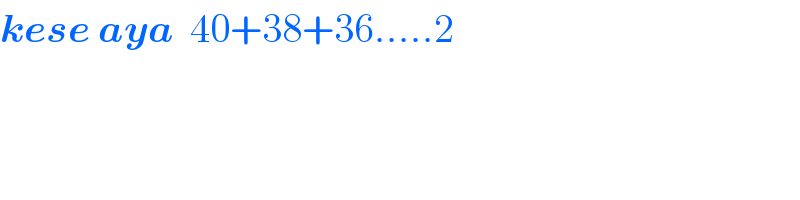
$$\boldsymbol{{kese}}\:\boldsymbol{{aya}}\:\:\mathrm{40}+\mathrm{38}+\mathrm{36}.....\mathrm{2} \\ $$
Commented by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 08/Sep/16

$${The}\:{series}\:{contains}\:{even}\:{numbers}: \\ $$$$\mathrm{40},\mathrm{38},\mathrm{36}....{So}\:{last}\:{positive}\:{term}\:{is}\:{even}\:{number}\:\mathrm{2} \\ $$$${After}\:{that}\:{is}\:\mathrm{0},{which}\:{doesn}'{t}\:{affect}\:{the}\:{sum} \\ $$$${and}\:{after}\:\mathrm{0}\:{negative}\:{even}\:{numbers}\:{come},{which} \\ $$$${will}\:{cause}\:{to}\:{decrease}\:{the}\:{sum}.{S}\:{maximum}\:{sum} \\ $$$${is}\:\mathrm{40}+\mathrm{38}+\mathrm{36}+...+\mathrm{2}. \\ $$$${Upto}\:\mathrm{2}\:{the}\:{sum}\:{is}\:{increasing}. \\ $$
Answered by Rasheed Soomro last updated on 08/Sep/16

$${Q}.\mathrm{1}\:{which}\:{term}\:{of}\:{the}\:{sequence}\:\mathrm{2005}, \\ $$$$\mathrm{2000},\mathrm{1995},\mathrm{1990},\mathrm{1985},....................... \\ $$$${is}\:{the}\:{first}\:{negative}\:{term}. \\ $$$$−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− \\ $$$${Last}\:{non}-{negative}\:\:{term}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${Let}\:\mathrm{0}\:{is}\:{nth}\:{term},{a}\:{first}\:{term},{d}\:{common}\:{difference}. \\ $$$${nth}\:{term}={a}+\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right){d} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:=\mathrm{2005}+\left({n}−\mathrm{1}\right)\left(\mathrm{2000}−\mathrm{2005}\right)=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{2005}−\mathrm{5}{n}+\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{n}=\mathrm{2010}/\mathrm{5}=\mathrm{402} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:{Last}\:{non}-{negative}\:{term}=\mathrm{402}{nd}\:{term} \\ $$$$\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\:\mathrm{403}{rd}\:{term}\:{is}\:{first}\:{negative}\:{term}. \\ $$$$ \\ $$
