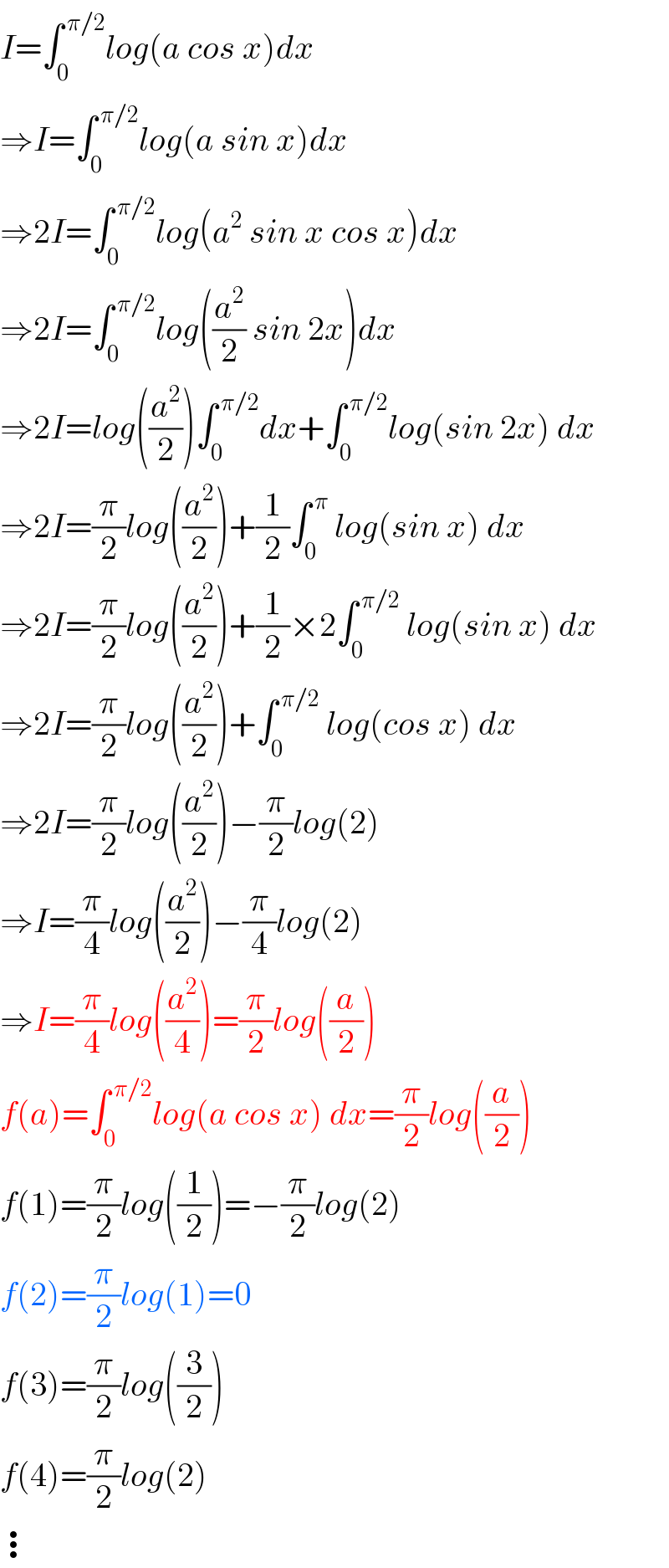Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 77464 by naka3546 last updated on 06/Jan/20
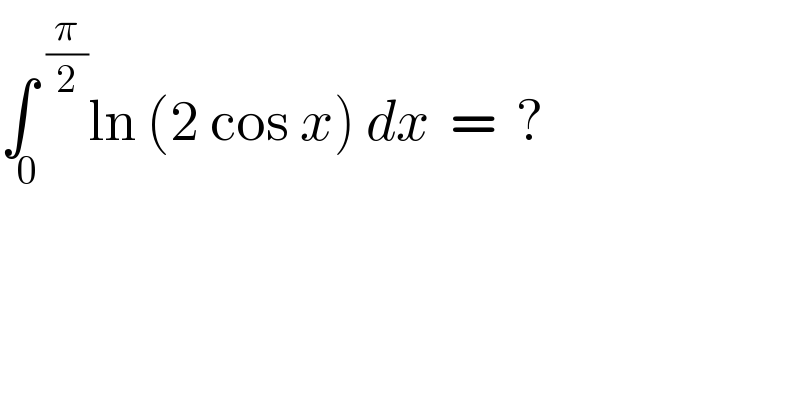
Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 06/Jan/20
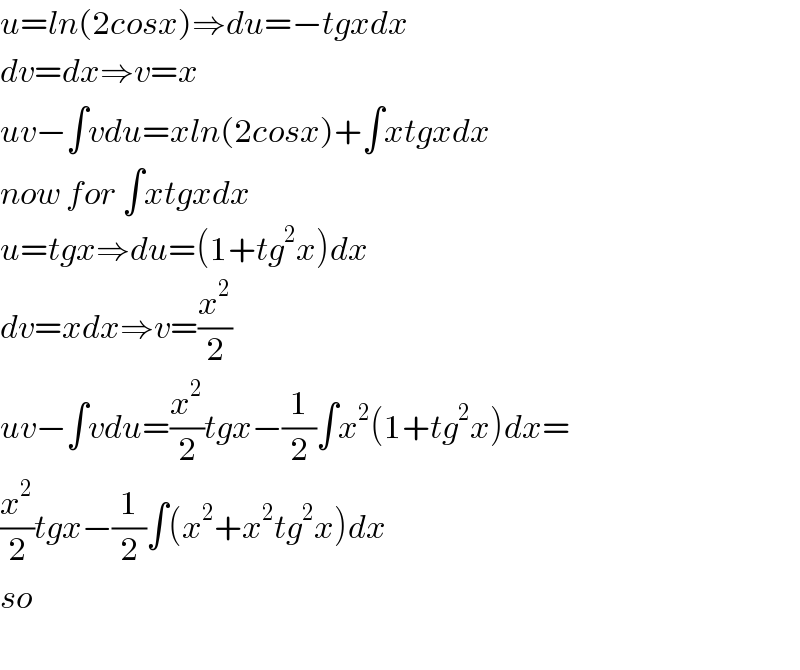
Commented by MJS last updated on 06/Jan/20

Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 06/Jan/20

Commented by MJS last updated on 06/Jan/20
![but (d/dx)[xln (2cos x) +(1/2)(x^2 tan x −x+tan x)]= =ln (2cos x) +(1/2)(tan^2 x +(x^2 /(cos^2 x)))](Q77486.png)
Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 06/Jan/20

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 06/Jan/20

Commented by kaivan.ahmadi last updated on 06/Jan/20
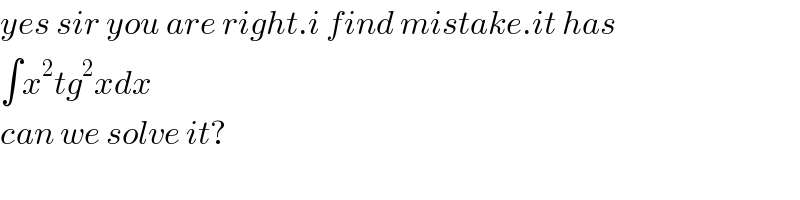
Answered by MJS last updated on 06/Jan/20
![∫ln (2cos x) dx= [t=−ix → dx=i dt] =−i∫tdt+i∫ln (e^(2t) +1) dt ∫ln (e^(2t) +1) dt= [u=−e^(2t) → dt=−(dx/(2e^(2x) ))] =(1/2)∫((ln (1−u))/u)du=−(1/2)∫−((ln (1−u))/u)du= =−(1/2)Li_2 u Li_2 x is the dilogarithm with Li_2 x =Σ_(n=1) ^∞ (x^n /n^2 )](Q77479.png)
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 07/Jan/20
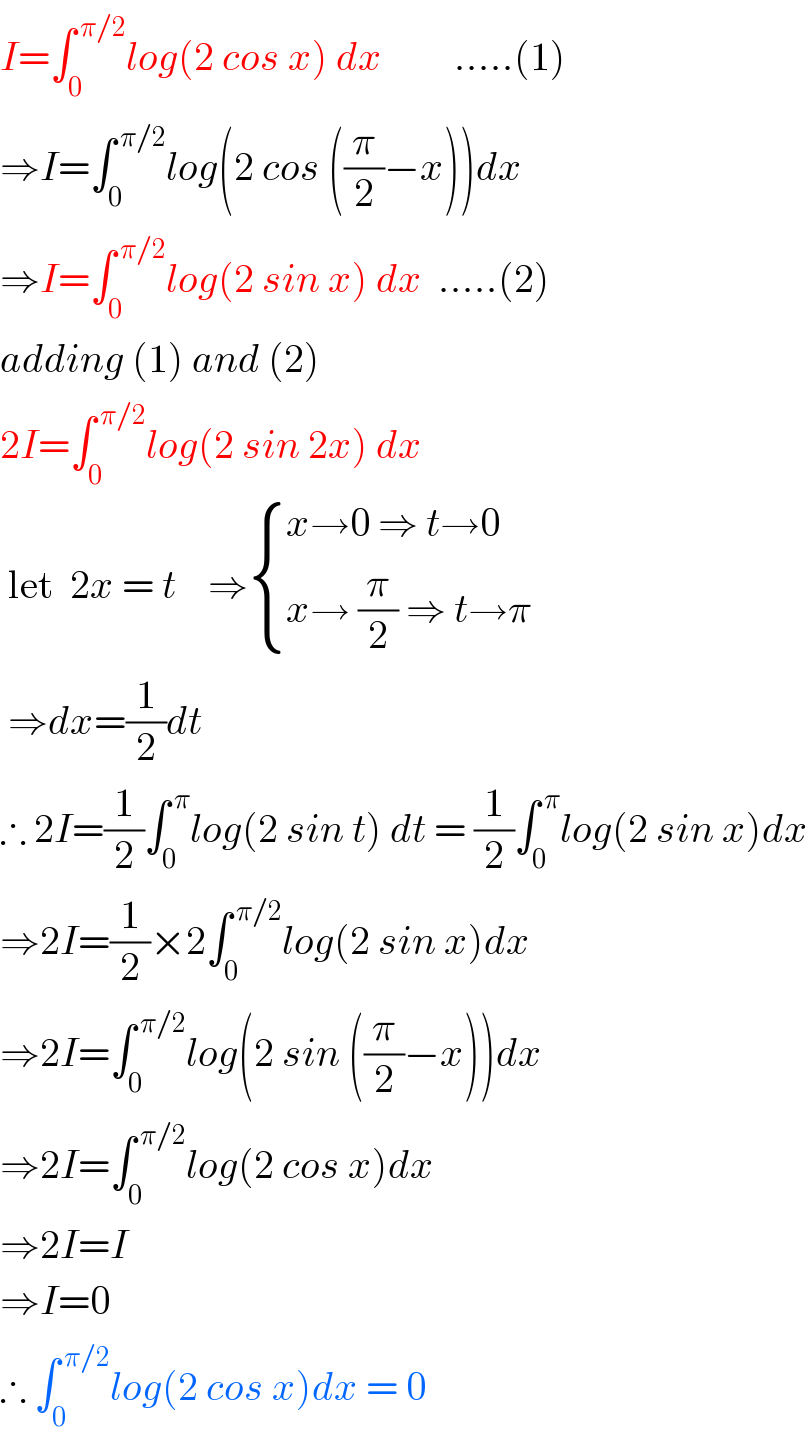
Answered by Kunal12588 last updated on 07/Jan/20