
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 78021 by jagoll last updated on 13/Jan/20
![lim_(x→0) (1/x^2 )[∫^(x^2 +(π/3)) _(π/3) ((cos x)/x) dx ] =](Q78021.png)
Commented by mr W last updated on 13/Jan/20
![lim_(x→0) (1/x^2 )[∫^(x^2 +(π/3)) _(π/3) ((cos x)/x) dx ] =lim_(x→0) ((((cos (x^2 +(π/3)))/(x^2 +(π/3)))×2x)/(2x)) =lim_(x→0) ((cos (x^2 +(π/3)))/(x^2 +(π/3))) =(3/π)×(1/2)=(3/(2π))](Q78022.png)
Commented by jagoll last updated on 13/Jan/20
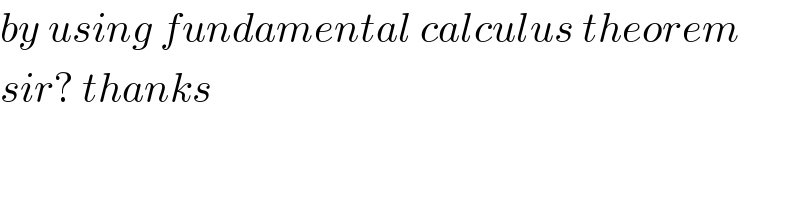
Commented by mr W last updated on 13/Jan/20

Commented by jagoll last updated on 13/Jan/20
![(d/dx)[∫_0 ^x f(u)du] = f(x) sir](Q78028.png)
Commented by mr W last updated on 13/Jan/20
![generally: (d/dx)[∫_(h(x)) ^(g(x)) f(u)du] = f(g(x))g′(x)−f(h(x))h′(x)](Q78032.png)
Commented by jagoll last updated on 13/Jan/20
Commented by msup trace by abdo last updated on 13/Jan/20
,x^2 +(π/3)[ / A(x)=(1/c) ∫_(π/3) ^(x^2 +(π/3)) cost dt =(1/c)(sin(x^2 +(π/3))−((√3)/2)) ⇒((A(x))/x^2 ) =((sin(x^2 +(π/3))−((√3)/2))/(cx^2 )) =(((1/2)sin(x^2 )+((√3)/2)cos(x^2 )−((√3)/2))/(cx^2 )) ∼(1/(2cx^2 )){x^2 +(√3)(1−(x^4 /2))−(√3)} =(1/(2c))−(x^2 /(4c)) ⇒lim_(x→0) A(x) =(1/(2×(π/3))) =(3/(2π)) .](Q78035.png)
