
Question Number 785 by rishabh last updated on 12/Mar/15
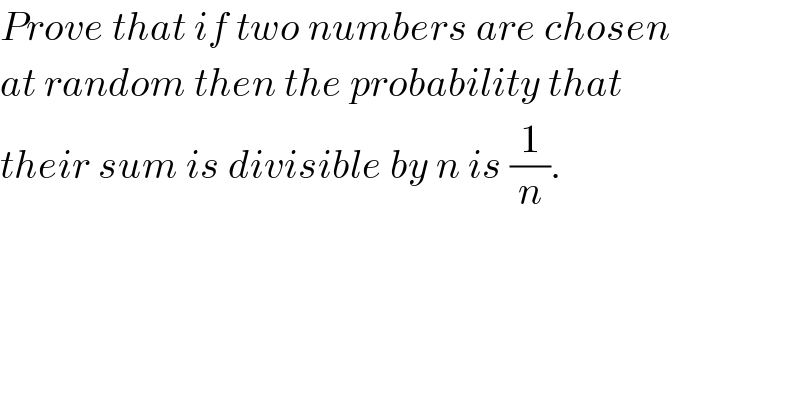
$${Prove}\:{that}\:{if}\:{two}\:{numbers}\:{are}\:{chosen} \\ $$$${at}\:{random}\:{then}\:{the}\:{probability}\:{that} \\ $$$${their}\:{sum}\:{is}\:{divisible}\:{by}\:{n}\:{is}\:\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}}. \\ $$
Answered by prakash jain last updated on 12/Mar/15

$$\mathrm{Sum}\:\mathrm{mod}\:{n}={k},\:\mathrm{where}\:\mathrm{0}\leqslant{k}\leqslant{n}−\mathrm{1}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{All}\:{n}\:\mathrm{values}\:\mathrm{for}\:{k}\:\:\mathrm{are}\:\mathrm{equally}\:\mathrm{likely}. \\ $$$$\mathrm{hence}\:\mathrm{probability}=\frac{\mathrm{1}}{{n}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{Note}:\:\mathrm{It}\:\mathrm{does}\:\mathrm{not}\:\mathrm{matter}\:\mathrm{how}\:\mathrm{many}\:\mathrm{number} \\ $$$$\mathrm{you}\:\mathrm{chose}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{random}.\:\mathrm{It}\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{same}\:\mathrm{as}\:\mathrm{choosing} \\ $$$$\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{sum}\:\mathrm{at}\:\mathrm{random}. \\ $$
