
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 79094 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 22/Jan/20
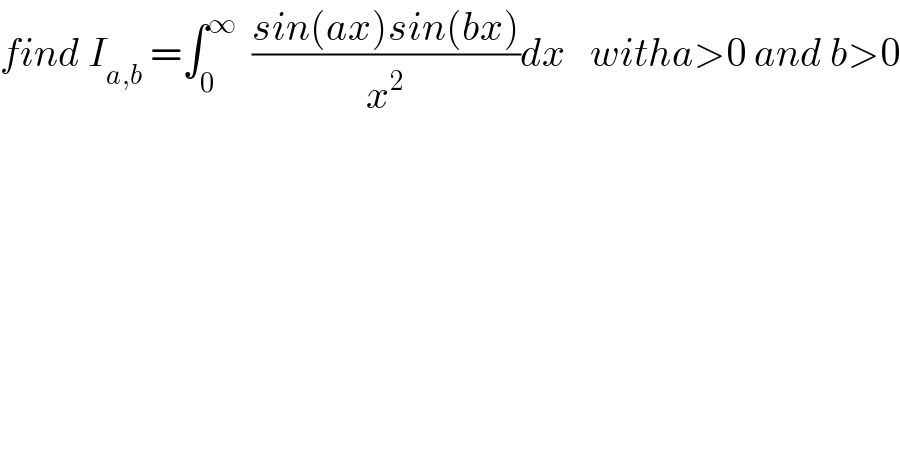
Answered by mind is power last updated on 23/Jan/20
![2sin(ax)sin(bx)=cos((a−b)x)−cos((a+b)x) f(z)=∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ) dx z∈R well defind in zero cos(zx)−1=−((z^2 x^2 )/2)+o(x^3 ) for z>1 ((∣cos(zx)−1∣)/x^2 )≤(2/x^2 ),integrabl in [1,+∞[ ∀(z,x)∈IR×R^∗ (z,x)→((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ) ∈C_∞ C_1 is what we need (∂/∂z)(((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ))=−((sin(zx))/x)∈C_1 ]0,+∞[ ∫_0 ^(+∞) −((sin(zx))/x)dx <∞ ⇒f(z)∈C_1 f′(z)=∫_0 ^(+∞) (∂/∂z)(((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ))=−∫_0 ^(+∞) ((sin(zx))/x)dx,u=zx if z>0 =−∫_0 ^(+∞) ((sin(u))/u)du=−(π/2),z<0 =(π/2) ⇒f′(z)=−sign(z)(π/2) f(z)=−((zsign(z)π)/2)+c f(0)=0⇒c=0 f(z)=((−zsign(z)π)/2) I_(a,b) =∫_0 ^(+∞) ((sin(ax)sin(bx))/x^2 )dx =∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a−b)x)−cos((a+b)x))/(2x^2 ))dx =∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a−b)x)−1−(cos((a+b)x)−1))/(2x^2 ))dx =(1/2)∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a−b)x)−1)/x^2 )−(1/2)∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a+b)x)−1)/x^2 ) =(1/2)f((a−b))−(1/2)f(a+b))=−(((a−b)sivn(a−b)π)/4)+(((a+b)sign(a+b)π)/4) =(π/4)((a+b)sign(a+b)−(a−b)sign(a−b))](Q79197.png)
Commented bymsup trace by abdo last updated on 23/Jan/20

| ||
Question and Answers Forum | ||
Question Number 79094 by mathmax by abdo last updated on 22/Jan/20 | ||
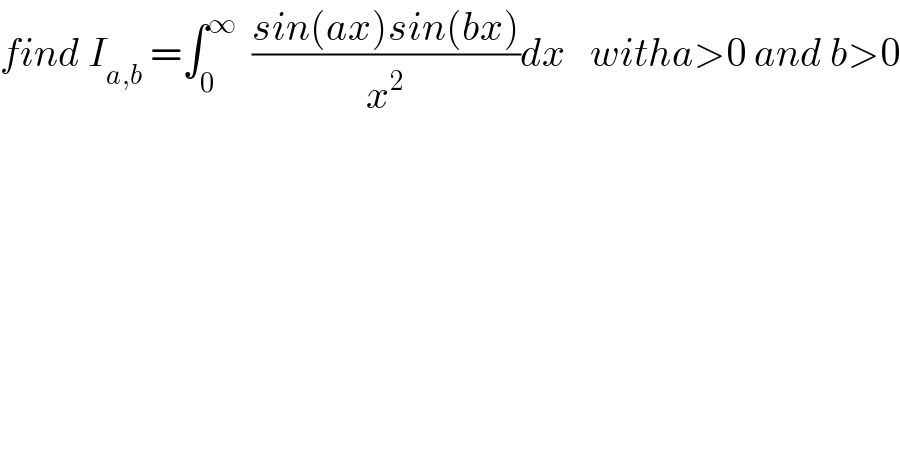 | ||
Answered by mind is power last updated on 23/Jan/20 | ||
![2sin(ax)sin(bx)=cos((a−b)x)−cos((a+b)x) f(z)=∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ) dx z∈R well defind in zero cos(zx)−1=−((z^2 x^2 )/2)+o(x^3 ) for z>1 ((∣cos(zx)−1∣)/x^2 )≤(2/x^2 ),integrabl in [1,+∞[ ∀(z,x)∈IR×R^∗ (z,x)→((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ) ∈C_∞ C_1 is what we need (∂/∂z)(((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ))=−((sin(zx))/x)∈C_1 ]0,+∞[ ∫_0 ^(+∞) −((sin(zx))/x)dx <∞ ⇒f(z)∈C_1 f′(z)=∫_0 ^(+∞) (∂/∂z)(((cos(zx)−1)/x^2 ))=−∫_0 ^(+∞) ((sin(zx))/x)dx,u=zx if z>0 =−∫_0 ^(+∞) ((sin(u))/u)du=−(π/2),z<0 =(π/2) ⇒f′(z)=−sign(z)(π/2) f(z)=−((zsign(z)π)/2)+c f(0)=0⇒c=0 f(z)=((−zsign(z)π)/2) I_(a,b) =∫_0 ^(+∞) ((sin(ax)sin(bx))/x^2 )dx =∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a−b)x)−cos((a+b)x))/(2x^2 ))dx =∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a−b)x)−1−(cos((a+b)x)−1))/(2x^2 ))dx =(1/2)∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a−b)x)−1)/x^2 )−(1/2)∫_0 ^(+∞) ((cos((a+b)x)−1)/x^2 ) =(1/2)f((a−b))−(1/2)f(a+b))=−(((a−b)sivn(a−b)π)/4)+(((a+b)sign(a+b)π)/4) =(π/4)((a+b)sign(a+b)−(a−b)sign(a−b))](Q79197.png) | ||
| ||
Commented bymsup trace by abdo last updated on 23/Jan/20 | ||
 | ||