
Question and Answers Forum
Previous in Relation and Functions Next in Relation and Functions
Question Number 81434 by abdomathmax last updated on 13/Feb/20
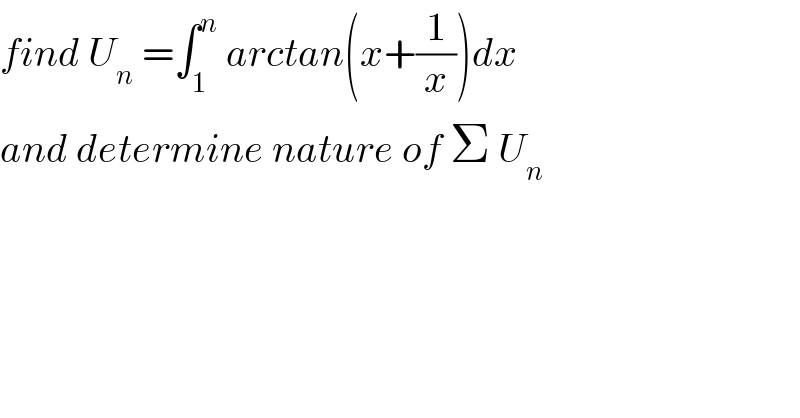
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 13/Feb/20
![by parts U_n =[xarctan(x+(1/x))]_1 ^n −∫_1 ^n x×((1−(1/x^2 ))/(1+(x+(1/x))^2 ))dx =n arctan(n+(1/n))−arctan(2)−∫_1 ^n x×((x^2 −1)/(x^2 {1+(((x^2 +1)^2 )/x^2 )}))dx =narctan(n+(1/n))−arctan(2)−∫_1 ^n ((x^3 −x)/(x^2 +(x^2 +1)^2 ))dx =narctan(n+(1/n))−arctan(2)−∫_1 ^n ((x^3 −x)/(x^2 +x^4 +2x^2 +1))dx =narctan(n+(1/n))−arctan(2)−∫_1 ^n ((x^3 −x)/(x^4 +3x^2 +1))dx x^4 +3x^2 +1=0 →u^2 +3u +1=0(u=x^2 ) ⇒ Δ=9−4=5 ⇒u_1 =((−3+(√5))/2) and u_2 =((−3−(√5))/2) ⇒F(x)=((x^3 −x)/(x^4 +3x^2 +1)) =((x^3 −x)/((x^2 −u_1 )(x^2 −u_2 ))) =((x^3 −x)/(u_1 −u_2 ))((1/(x^2 −u_1 ))−(1/(x^2 −u_2 ))) ⇒ ∫_1 ^n F(x)dx =(1/(√5))∫_1 ^n ((x^3 −x)/(x^2 −u_1 ))dx−(1/(√5)) ∫_1 ^n ((x^3 −x)/(x^2 −u_2 ))dx wehavd ∫_1 ^n ((x^3 −x)/(x^2 −u_1 ))dx =∫_1 ^n ((x(x^2 −u_1 )+xu_1 −x)/(x^2 −u_1 ))dx =(x^2 /2)]_1 ^n +∫_1 ^n (((u_1 −1)x)/(x^2 −u_1 ))dx=(x^2 /2) +((u_1 −1)/2)ln∣x^2 −u_1 ∣ =(n^2 /2)−(1/2) +((u_1 −1)/2)[ln∣x^2 −u_1 ∣]_1 ^n =((n^2 −1)/2) +((u_1 −1)/2){ln(n^2 −u_1 )−ln∣1−u_1 ∣}also we have ∫_1 ^n =((n^2 −1)/2)+((u_2 −1)/2){ln(n^2 −u_2 )−ln∣1−u_2 )} ⇒ U_n =narctan(1+(1/n))−arctan2 −(1/(√5)){((u_1 −1)/2)ln(n^2 −u_1 )−((u_2 −1)/2)ln(n^2 −u_2 ) +((u_2 −1)/2)ln∣1−u_2 ∣−((u_1 −1)/2)ln∣1−u_1 ∣}](Q81508.png)
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 13/Feb/20
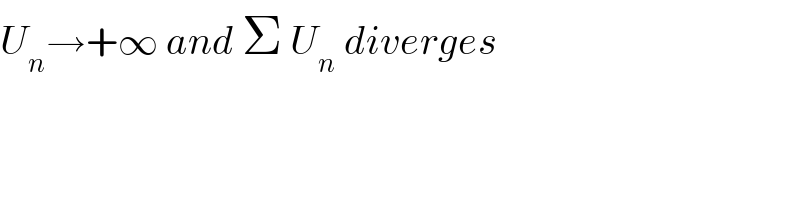
Answered by mind is power last updated on 13/Feb/20
![U_n ≥∫_1 ^n arvtan(x)dx ⇒Un≥[xarctan(x)−((ln(1+x^2 ))/2)]_1 ^n U_n ≥narctan(n)−((ln(1+n^2 ))/2)−(π/4)+((ln(2))/2) narctan(n)−((ln(1+n^2 ))/2)=n(arctan(n)−((ln(1+n^2 ))/(2n)))+((ln(2))/2)−(π/4)→∞ ⇒ΣU_n diverge](Q81476.png)
