
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 82701 by jagoll last updated on 23/Feb/20
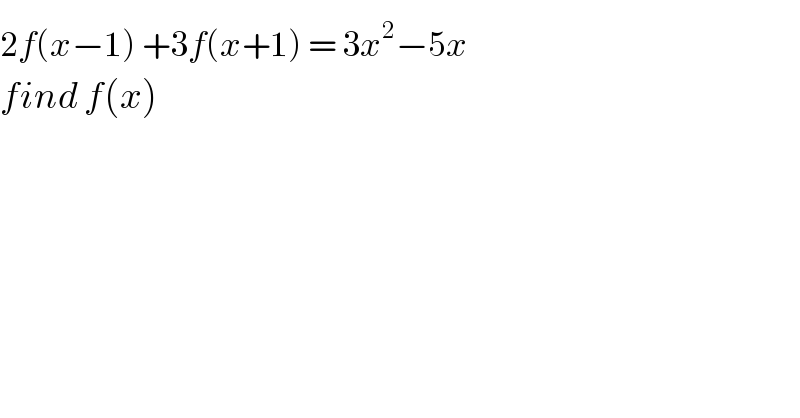
Answered by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 23/Feb/20
![f(x)=ax^2 +bx+c 2f(x−1)+3f(x+1) 2[a(x−1)^2 +b(x−1)+c]+3[a(x+1)^2 +b(x+1)+c] =[2ax^2 −4ax+2a+2bx−2b+2c+3ax^2 +6ax+3a+3bx+3b+3c] =x^2 (5a)+x(2a+5b)+(2a−2b+2c+3a+3b+3c) 5a=3→a=(3/5) 2a+5b=−5 2×(3/5)+5b=−5 5b=((−31)/5)→b=((−31)/(25)) 5a+b+5c=0 5×(3/5)+((−31)/(25))+5c=0 75−31+125c=0 →c=((−44)/(125)) f(x)=(3/5)x^2 −((31)/(25))x−((44)/(125)) pls check](Q82705.png)
Commented by jagoll last updated on 23/Feb/20

Commented by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 23/Feb/20

Commented by jagoll last updated on 23/Feb/20
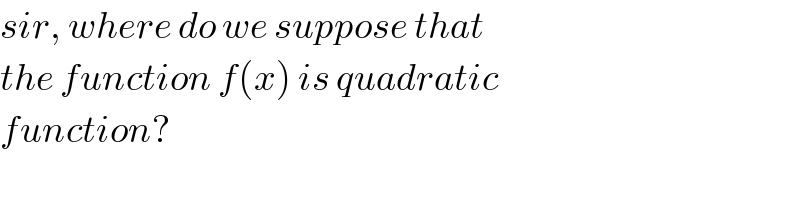
Commented by mr W last updated on 23/Feb/20

Commented by mr W last updated on 23/Feb/20

Commented by jagoll last updated on 23/Feb/20

