Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 82761 by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 24/Feb/20
![lim_(x→0) (((cosx)^(1/m) −(cosx)^(1/n) )/x^2 ) [where m and n integer]](Q82761.png)
Commented by mr W last updated on 24/Feb/20
![lim_(x→0) (((cosx)^(1/m) −(cosx)^(1/n) )/x^2 ) =lim_(x→0) (((1−2 sin^2 (x/2))^(1/m) −(1−2 sin^2 (x/2))^(1/n) )/x^2 ) =lim_(x→0) ((1−(2/m) sin^2 (x/2)+o(sin^2 (x/2))−[1−(2/n) sin^2 (x/2)+o(sin^2 (x/2))])/x^2 ) =lim_(x→0) ((2((1/n)−(1/m)) sin^2 (x/2))/x^2 ) =(1/2)((1/n)−(1/m))lim_(x→0) ((( sin (x/2))/(x/2)))^2 =(1/2)((1/n)−(1/m))](Q82762.png)
Commented by TANMAY PANACEA last updated on 24/Feb/20

Commented by jagoll last updated on 24/Feb/20
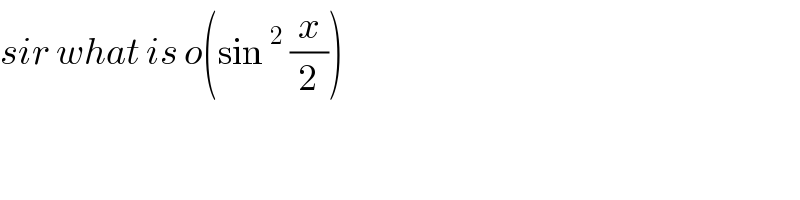
Commented by abdomathmax last updated on 24/Feb/20
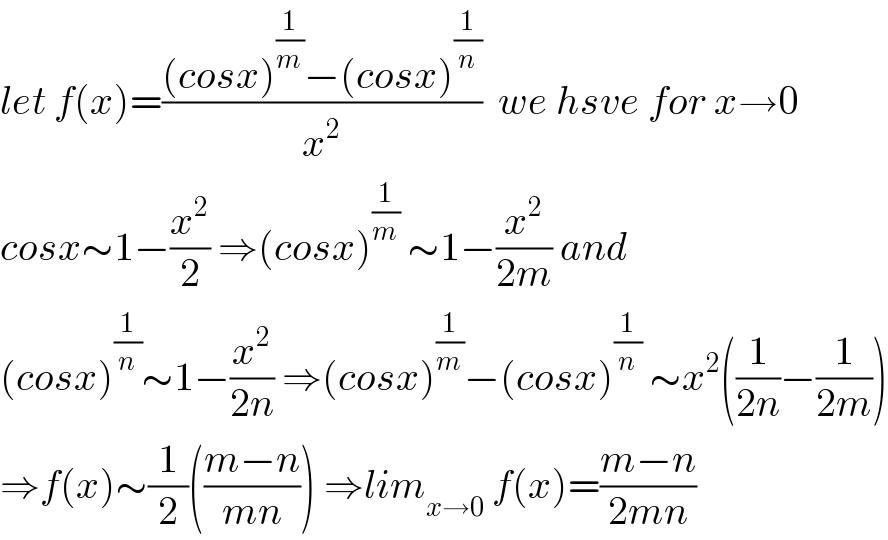
Commented by mr W last updated on 24/Feb/20

Commented by jagoll last updated on 24/Feb/20

Commented by mathmax by abdo last updated on 24/Feb/20