
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 83297 by Rio Michael last updated on 29/Feb/20
![Write down a series expansion for ln [((1−2x)/((1+2x)^2 ))] in ascending powers of x up to and including the term in x^4 . if x is small that terms in x^2 and higher powers are negleted show that (((1−2x)/(1+2x)))^(1/(2x)) ≅ (1 + x)e^(−3)](Q83297.png)
Commented by mr W last updated on 29/Feb/20
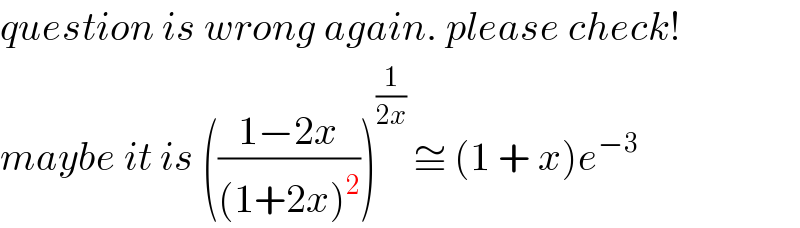
Answered by mr W last updated on 29/Feb/20
![ln [((1−2x)/((1+2x)^2 ))]=ln (1−2x)−2 ln (1+2x) =(−2x)−(((−2x)^2 )/2)+(((−2x)^3 )/3)−... −2[(2x)−(((2x)^2 )/2)+(((2x)^3 )/3)−...] =−6x+2x^2 −8x^3 +o(x^3 ) (1/(2x))ln [((1−2x)/((1+2x)^2 ))]=−3+x−4x^2 +o(x^2 ) (((1−2x)/((1+2x)^2 )))^(1/(2x)) =e^((1/(2x))ln ((1−2x)/((1+2x)^2 ))) =e^(−3+x−4x^2 +o(x^2 )) =e^(−3) e^(x−4x^2 +o(x^2 )) =e^(−3) (1+x+o(x)) ≈e^(−3) (1+x)](Q83308.png)
Commented by Rio Michael last updated on 29/Feb/20

Commented by peter frank last updated on 29/Feb/20

