
Question Number 87382 by mathocean1 last updated on 04/Apr/20
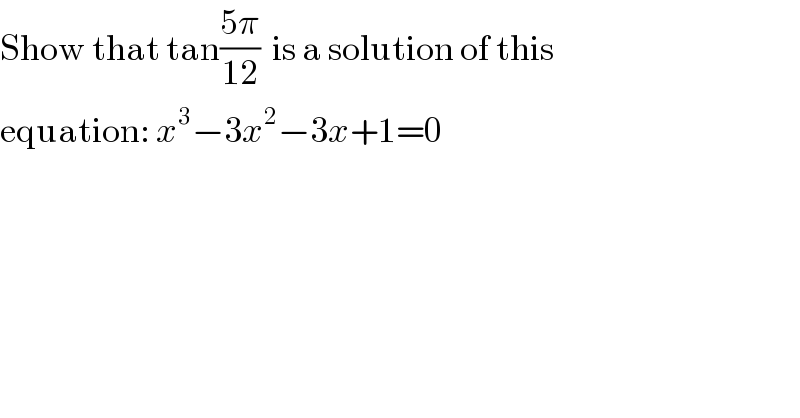
$$\mathrm{Show}\:\mathrm{that}\:\mathrm{tan}\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{12}}\:\:\mathrm{is}\:\mathrm{a}\:\mathrm{solution}\:\mathrm{of}\:\mathrm{this}\: \\ $$$$\mathrm{equation}:\:{x}^{\mathrm{3}} −\mathrm{3}{x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{3}{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$
Answered by ajfour last updated on 04/Apr/20

$${x}^{\mathrm{3}} +\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{3}{x}\left({x}+\mathrm{1}\right) \\ $$$${if}\:\:{x}\neq−\mathrm{1} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{3}{x} \\ $$$${x}^{\mathrm{2}} −\mathrm{4}{x}+\mathrm{1}=\mathrm{0} \\ $$$${x}=\mathrm{2}\pm\sqrt{\mathrm{3}} \\ $$$$\mathrm{tan}\:\frac{\mathrm{5}\pi}{\mathrm{12}}=\mathrm{tan}\:\mathrm{75}°\:=\mathrm{tan}\:\left(\mathrm{30}°+\mathrm{45}°\right) \\ $$$$=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}+\mathrm{1}}{\mathrm{1}−\frac{\mathrm{1}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{1}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}−\mathrm{1}}\:=\:\frac{\mathrm{4}+\mathrm{2}\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}}{\mathrm{2}}=\mathrm{2}+\sqrt{\mathrm{3}}\:. \\ $$
