
Question and Answers Forum
Question Number 88955 by M±th+et£s last updated on 14/Apr/20
![hello floor function ∫_a ^b ⌊x⌋ dx a,b∈z and b>a =∫_0 ^b ⌊x⌋ dx −∫_0 ^a ⌊x⌋ dx =((b^2 −b)/2)−((a^2 −a)/2) ....(1) now ∫_m ^k ⌊x⌋ dx when m,k∉z when m<a<b<k b=[k] and a=[m] ∫_m ^a ⌊x⌋dx +∫_a ^b ⌊x⌋dx +∫_b ^k ⌊x⌋dx =(a−m)⌊m⌋+((b^2 −b)/2)−((a^2 −a)/2)+(k−b)⌊k⌋ =(⌊m⌋−m)⌊m⌋+((⌊k⌋^2 −⌊k⌋)/2)−((⌊m⌋^2 −⌊m⌋)/2)+(k−⌊k⌋)⌊k⌋ ⌊m⌋^2 −m⌊m⌋ +(1/2)⌊k⌋^2 −(1/2)⌊k⌋−(1/2)⌊m⌋^2 −(1/2)⌊m⌋+k⌊k⌋−⌊k⌋^2 =k⌊k⌋−m⌊m⌋+(1/2)⌊m⌋^2 −(1/2)⌊k⌋^2 +(1/2)⌊m⌋−(1/2)⌊k⌋ ∴∫_m ^k ⌊x⌋dx=k⌊k⌋−m⌊m⌋+(1/2)(⌊m⌋−⌊k⌋)(⌊m⌋+⌊k⌋)+1 example ∫_(−1.5) ^(3.7) ⌊x⌋dx=(3.7)3−((−1.5)(−2))+(1/2)(−2−3)(−2+3+1) =11.1−3−5=3.1](Q88955.png)
Commented byM±th+et£s last updated on 14/Apr/20

Commented bymathmax by abdo last updated on 14/Apr/20
![let A =∫_n ^m [x]dx with m≥n ⇒∃q∈N /m=n+q ⇒ A =∫_n ^(n+q) [x]dx =_(x=n+t) ∫_0 ^q [n+t]dt =∫_0 ^q ndt +∫_0 ^q [t]dt =nq +Σ_(p=0) ^(q−1) ∫_p ^(p+1) p dt =nq +Σ_(p=0) ^(q−1) p =nq +(((q−1)q)/2) but q =m−n ⇒ A =n(m−n)+(((m−n−1)(m−n))/2) ⇒ A =((2n(m−n))/2) +((m−n)/2)(m−n−1) =((m−n)/2){ 2n+m−n−1} =((m−n)/2)(n+m−1) example ∫_2 ^7 [x]dx =((7−2)/2)(2+7−1) =(5/2)×8 =20 let verify ∫_2 ^7 [x]dx =∫_2 ^3 [x]dx +∫_3 ^4 [x]dx +∫_4 ^5 [x]dx +∫_5 ^6 [x]dx +∫_6 ^7 [x]dx =2+3 +4 +5 +6 =20 (the relation is correct) ∫_(−2) ^5 [x]dx =((5+2)/2)(−2+5−1) =(7/2)×2 =7 let verify ∫_(−2) ^5 [x]dx =∫_(−2) ^(−1) [x]dx +∫_(−1) ^0 [x]dx +∫_0 ^1 [x]dx +∫_1 ^2 [x]dx +∫_2 ^3 [x]dx +∫_3 ^4 x]dx +∫_4 ^5 [x]dx =−2 +(−1)+0 +1 +2+3+4 =−3+3+3+4=7 (correct!)](Q89036.png)
Commented bymr W last updated on 14/Apr/20
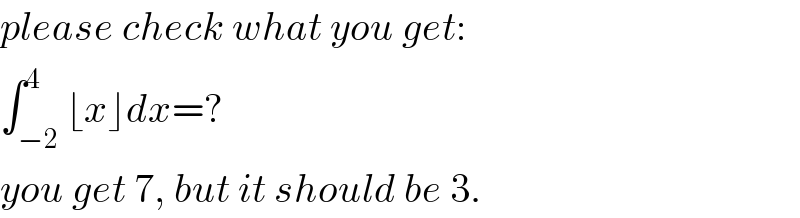
Commented byM±th+et£s last updated on 14/Apr/20
Commented byM±th+et£s last updated on 14/Apr/20
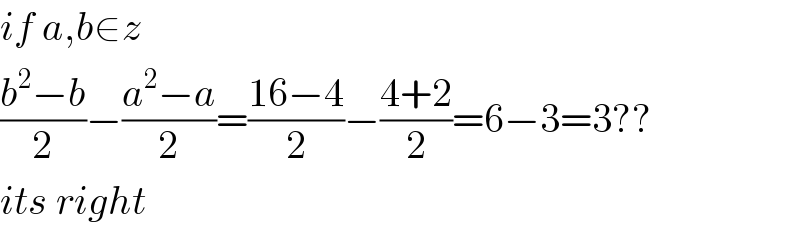
Commented bymr W last updated on 14/Apr/20
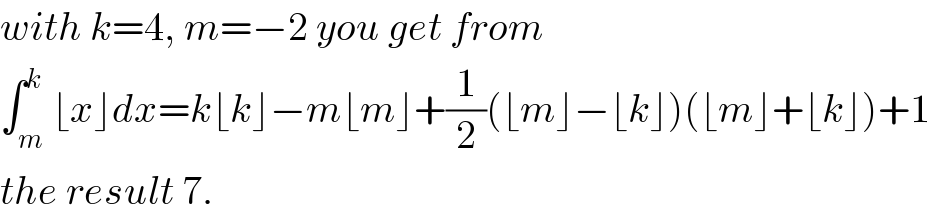
Commented byM±th+et£s last updated on 14/Apr/20

Commented bymr W last updated on 14/Apr/20
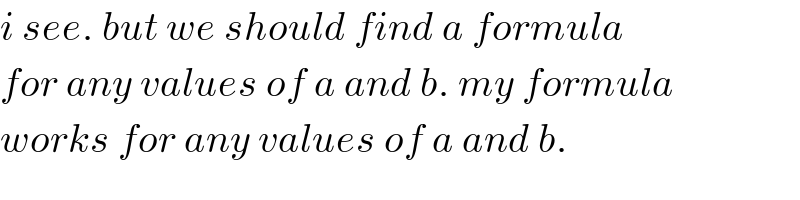
Commented byM±th+et£s last updated on 14/Apr/20
Commented bymathmax by abdo last updated on 15/Apr/20

